Abstract
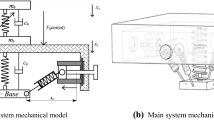
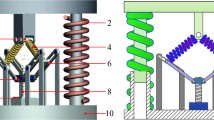
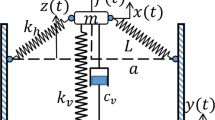
Based on the principle of dynamic vibration absorption, a quasi-zero stiffness (QZS) vibration isolation system for coupled a linear dynamic vibration absorber was designed. The dynamic model of the coupled system is established, and the frequency domain analytical solutions and the expression of force transmissibility are deduced by the averaging method. The effects of mass, stiffness and damping of the vibration absorber on the dynamic response and force transmissibility characteristics of the coupled system are analyzed numerically, and compared with an equivalent QZS vibration isolation system. The results reveal that the amplitude curve of the primary system shifts to the low-frequency range with the increase of mass ratio, the valley value appears and lower to \(2 \times 10^{ - 4}\) when the excitation frequency equals to the natural frequency of the absorber. Increase stiffness ratio can reduce the valley amplitude and the second peak amplitude of the primary system. The large the damping of the absorber, the lower the valley amplitude of the primary system can be acquired. As the mass ratio increases from 0.2 to 1, the initial isolation frequency of the coupled system decreases by 23.2%, which enlarges the bandwidth of the effective isolation frequency range. Large stiffness ratio or larger damping ratio of the absorber can improve the isolation performance in the frequency range near the second peak amplitude. Compared with the equivalent QZS isolation system, the coupled system possesses more excellent performance in the frequency domain near the valley amplitude and wider vibration isolation frequency bandwidth.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niu, F., Meng, L.S., Wu, W.J., Sun, J.G., Su, W.H., Meng, G., Rao, Z.S.: Recent advances in quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolation systems. Appl. Mech. Mater. 397–400, 295–303 (2013)
Platus, D.L.: Negative-stiffness-mechanism vibration isolation systems. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 3786, 44–54 (1999)
Winterflood, J., Barber, T.A., Blair, D.G.: Mathematical analysis of an Euler spring vibration isolator. Phys. Lett. A 300(2–3), 131–139 (2002)
Winterflood, J., Blair, D.G., Slagmolen, B.: High performance vibration isolation using springs in Euler column buckling mode. Phys. Lett. A 300(2–3), 122–130 (2002)
Virgin, L.N., Davis, R.B.: Vibration isolation using buckled struts. J. Sound Vib. 260(5), 965–973 (2003)
Plaut, R.H., Sidbury, J.E., Virgin, L.N.: Analysis of buckled and pre-bent fixed-end columns used as vibration isolators. J. Sound Vib. 283(3–5), 1216–1228 (2005)
Zhang, J.Z., Li, D., Dong, S., Chen, M.Z.: Study on Euler spring used in ultra-low frequency vertical vibration isolation system. J. Sound Vib. 26, 237–241 (2004)
Lee, C.M., Goverdovskiy, V.N., Temnikov, A.I.: Design of springs with “negative” stiffness to improve vehicle driver vibration isolation. J. Sound Vib. 302(4–5), 865–874 (2007)
Zhou, N., Liu, K.: A tunable high-static-low-dynamic stiffness vibration isolator. J. Sound Vib. 329(9), 1254–1273 (2010)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P.: Static analysis of a passive vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 301(3–5), 678–689 (2007)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Kovacic, I., Waters, T.P.: On the force transmissibility of a vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 322(4–5), 707–717 (2009)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P.: Force and displacement transmissibility of a nonlinear isolator with high-static-low-dynamic-stiffness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 55(1), 22–29 (2012)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T., Holmes, P.: Nonlinear oscillations. J. Appl. Mech. 47(3), 692 (1980)
Cheng, C., Li, S.M., Wang, Y., Jiang, X.X.: Force and displacement transmissibility of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with geometric nonlinear damping. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(4), 1–13 (2016)
Xu, D.L., Zhang, Y.Y., Zhou, J.X.: On the analytical and experimental assessment of performance of a quasi-zero-stiffness isolator. J. Vib. Control 20(15), 2314–2325 (2014)
Sun, X.T., Jing, X.J.: A nonlinear vibration isolator achieving high-static-low-dynamic stiffness and tunable anti-resonance frequency band. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 80, 166–188 (2016)
Dong, G.X., Zhang, X.N., Luo, Y.J., Zhang, Y.H.: Investigation on the design of magnetic spring-beam vibration isolator with negative stiffness characteristic. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. 52, 1321–1329 (2016)
Sun, X.T., Jing, X.J., Xu, J., Cheng, L.: Vibration isolation via a scissor-like structured platform. J. Sound Vib. 333(9), 2404–2420 (2014)
Jing, X.J., Lang, Z.Q., Billings, S.A., et al.: Frequency domain analysis for suppression of output vibration from periodic disturbance using nonlinearities. J. Sound Vib. 314(3–5), 536–557 (2008)
Jing, X.J., Lang, Z.Q., Billings, S.A., Tomlinson, G.R.: Nonlinear influence in the frequency domain: alternating series. Syst. Control Lett. 60(5), 295–309 (2011)
Liu, C.C., Jing, X.J., Daley, S., Li, F.M.: Recent advances in micro-vibration isolation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 56–57(8), 55–80 (2015)
Jing, X.J., Lang, Z.Q.: Frequency domain analysis and design of nonlinear systems based on Volterra series expansion: a parametric characteristic approach. In: Understanding Complex Systems (2015)
Jing, X.J., Lang, Z.Q.: Frequency domain analysis of a dimensionless cubic nonlinear damping system subject to harmonic input. Nonlinear Dyn. 58(3), 469–485 (2009)
Chai, K., Lou, J.J., Yang, Q.C.: Characteristic analysis of vibration isolation system based on high-static-low-dynamic stiffness. J. Vibroeng. 19(6), 4120–4137 (2017)
Le, T.D., Ahn, K.K.: A vibration isolation system in low frequency excitation region using negative stiffness structure for vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 330(26), 6311–6335 (2011)
Zheng, Y.S., Zhang, X.N., Luo, Y.J., Yan, B., Ma, C.C.: Design and experiment of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator using a negative stiffness magnetic spring. J. Sound Vib. 360, 31–52 (2016)
Zheng, Y.S., Zhang, X.N., Luo, Y.J., Zhang, Y.H., Xie, S.L.: Analytical study of a quasi-zero stiffness coupling using a torsion magnetic spring with negative stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 100, 135–151 (2018)
Dong, G.X., Zhang, X.N., Xie, S.L., Yan, B., Luo, Y.J.: Simulated and experimental studies on a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator using magnetic negative stiffness spring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 86, 188–203 (2017)
Shahadat, M.M.Z., Mizuno, T., Ishino, Y., Takasaki, M.: Cost-effective implementation of acceleration feedback to vibration system using negative stiffness. In: ASME 2012 5th Annual Dynamic Systems and Control Conference joint with the JSME 2012 11th Motion and Vibration Conference, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA (2012)
Sun, X.T., Xu, J., Jing, X.J., Cheng, L.: Beneficial performance of a quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator with time-delayed active control. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 82, 32–40 (2014)
Hua, Y.Y., Wong, W., Cheng, L.: Optimal design of a beam-based dynamic vibration absorber using fixed-points theory. J. Sound Vib. 421, 111–131 (2018)
Anh, N.D., Nguyen, N.X.: Research on the design of non-traditional dynamic vibration absorber for damped structures under ground motion. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 30(2), 593–602 (2016)
Shen, Y.J., Chen, L., Yang, X.F., Shi, D.H., Yang, J.: Improved design of dynamic vibration absorber by using the inerter and its application in vehicle suspension. J. Sound Vib. 361, 148–158 (2016)
Liu, M.C., Gu, F.H., Hua, J.H.: Integration design and optimization control of a dynamic vibration absorber for electric wheels with in-wheel motor. Energies 10(12), 2069 (2017)
Sarah, G., Mohammad, H., Ali, H., Hassan, K., Wan, G.J.: Tremor reduction at the palm of a Parkinson’s patient using dynamic vibration absorber. Bioengineering 3(3), 18 (2016)
Huang, X.C., Su, Z.W., Hua, H.X.: Application of a dynamic vibration absorber with negative stiffness for control of a marine shafting system. Ocean Eng. 155, 131–143 (2018)
Acar, M.A., Yilmaz, C.: Design of an adaptive-passive dynamic vibration absorber composed of a string-mass system equipped with negative stiffness tension adjusting mechanism. J. Sound Vib. 332(2), 231–245 (2013)
Zhou, J., Wang, X., Xu, D., Bishop, S.: Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with cam-roller-spring mechanisms. J. Sound Vib. 346, 53–69 (2015)
Liu, X.T., Huang, X.C., Hua, H.X.: On the characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness isolator using Euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector. J. Sound Vib. 332(14), 3359–3376 (2013)
Meng, Q.G., Yang, X.F., Li, W., Sheng, L.C., Lu, E.: Research and analysis of quasi-zero-stiffness isolator with geometric nonlinear damping. Shock Vib. 2017(9), 1–9 (2017)
Yang, J., Xiong, Y.P., Xing, J.T.: Vibration power flow and force transmission behaviour of a nonlinear isolator mounted on a nonlinear base. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 115–116, 238–252 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 2010118), Open Topic Funding Project of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Food Manufacturing Equipment and Technology (FM-201802), Top-notch Team Funding Project of Excellent Talents Plan of Xicheng District of Beijing, and 2020 Research and Innovation Plan for Graduate Students in Jiangsu Province (KYCX20_1927).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Ji, W., Xu, L. et al. Dynamic characteristics of quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation system for coupled dynamic vibration absorber. Arch Appl Mech 91, 3799–3818 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-01978-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-01978-2