Abstract
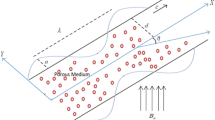
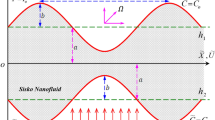
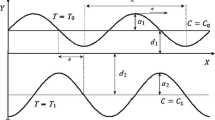
In this work, we studied the peristaltic motion of steady non-Newtonian nanofluid flow with heat transfer through a non-uniform inclined channel. The flow in this discussion obeys the power law model through a non-Darcy porous medium. Moreover, the effects of thermal radiation, heat generation, Ohmic dissipation and a uniform external magnetic field are taken in consideration. The governing equations that describe the velocity, temperature and nanoparticles concentration are simplified under the assumptions of long wave length and low-Reynolds number. These equations have been solved numerically by using Runge–Kutta–Merson method with the help of shooting and matching technique. The solutions are obtained as functions of the physical parameters entering the problem. The effects of these parameters on the obtained solutions are discussed and illustrated graphically through a set of figures. It is found that as Brownian motion parameter increases, the axial velocity decreases, whereas the nanoparticles concentration increases and it has a dual effect on the temperature distribution. Moreover, the axial velocity and temperature increase as Prandtl number increases, while the nanoparticles decrease.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, U.S.: Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles. ASME, New York (1995)
Garmroodi, M.R.D., Ahmadpour, A., Talati, F.: MHD mixed convection of nanofluids in the presence of multiple rotating cylinders in different configurations: a two-phase numerical study. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 150, 247–264 (2019)
Wang, X.Q., Mujumdar, A.S.: A review on nanofluids-part 1: theoretical and numerical investigations. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 25, 613–630 (2008)
Saidur, R., Leong, K.Y., Mohammad, H.A.: A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew. Sust. Eng. Rev. 15, 1646–1668 (2011)
Eldabe, N.T.M., Abou-zeid, M.Y., Younis, Y.M.: Magnetohydrodynamic Peristaltic flow of Jeffry nanofluid with heat transfer through a porous medium in a vertical tube. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 11, 1097–1103 (2017)
Abou-zeid, M.: Effects of thermal-diffusion and viscous dissipation on peristaltic flow of micropolar non-Newtonian nanofluid: application of homotopy perturbation method. Results Phys. 6, 481–495 (2016)
Abou-zeid, M.Y., Mohamed, M.A.A.: Homotopy perturbation method to creeping flow of non-Newtonian power-law nanofluid in a non-uniform inclined channel with peristalsis. Z. Naturforsch. A. 72, 899–907 (2017)
Prakash, J., Siva, E.P., Tripathi, D., Kothandapani, M.: Nanofluids flow driven by peristaltic pumping in occurrence of magnetohydrodynamics and thermal radiation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 100, 290–300 (2019)
Ellahi, R., Sait, S.M., Shehzad, N., Ayaz, Z.: A hybrid investigation on numerical and analytical solutions of electro-magnetohydrodynamics flow of nanofluid through porous media with entropy generation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 30, 834–854 (2020)
Akram, S., Razia, A., Afzal, F.: Effects of velocity second slip model and induced magnetic field on peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian fluid in the presence of double-diffusivity convection in nanofluids. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90, 1583–1603 (2020)
Khan, L.A., Raza, M., Mir, N.A., Ellahi, R.: Effects of different shapes of nanoparticles on peristaltic flow of MHD nanofluids filled in an asymmetric channel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 140, 879–890 (2020)
Kataria, H.R., Patel, H.R.: Heat and mass transfer in magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Casson fluid flow past over an oscillating vertical plate embedded in porous medium with ramped wall temperature. Propuls. Power Res. 7, 257–267 (2018)
Kumar, N., Bansal, A., Gupta, R.: Shear rate and mass transfer coefficient in internal loop airlift reactors involving non-Newtonian fluids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 136, 315–323 (2018)
Hayat, T., Yasmin, H., Alsaedi, A.: Convective heat transfer analysis for peristaltic flow of power-law fluid in a channel. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 37, 463–477 (2015)
Eldabe, N.T.M., El-Sayed, M.F., Ghaly, A.Y., Sayed, H.M.: Mixed convective heat and mass transfer in a non-Newtonian fluid at a peristaltic surface with temperature-dependent viscosity. Arch. Appl. Mech. 78, 599–624 (2008)
Sayed, H.M., Aly, E.H., Vajravelu, K.: Influence of slip and convective boundary conditions on peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian nanofluids in an inclined asymmetric channel. Alex. Eng. J. 55, 2209–2220 (2016)
Ellahi, R., Zeeshan, R., Hussain, F., Abbas, T.: Thermally charged MHD Bi-phase flow coatings with non-Newtonian nanofluid and Hafnium particles along slippery walls. Coatings 9, 300 (2019)
Reddappa, B., Parandhama, A., Sreenadh, S.: Peristaltic transport of conducting Williamson fluid in a porous channel. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 10, 277–288 (2020)
Hayat, T., Farooq, S., Ahmad, B., Alsaedi, A.: Effectiveness of entropy generation and energy transfer on peristaltic flow of Jeffrey material with Darcy resistance. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 244–252 (2017)
Hayat, T., Ali, N.: On mechanism of peristaltic flows for power-law fluids. Physica A 371, 188–194 (2006)
Rao, A.R., Mishra, M.: Peristaltic transport of a power-law fluid in a porous tube. J. Non Newton. Fluid Mech. 121, 163–174 (2004)
Shaaban, A.A., Abou-zeid, M.Y.: Effects of heat and mass transfer on MHD peristaltic flow of a non-Newtonian fluid through a porous medium between Two Coaxial Cylinders. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 819683 (2013)
Chaube, M.K., Tripathi, D., Bég, O.A., Sharma, S., Pandey, V.S.: Peristaltic creeping flow of power law physiological fluids through a non uniform channel with slip effect. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2015, ID 152802 (2015)
https://tse1.mm.bing.net/th?id=OIP.W7kOvQzcyWhsVw3uoUU20AHaFK&pid=Api&P=0&w=258&h=181
Mohamed, M.A., Abou-zeid, M.Y.: MHD peristaltic flow of micropolar Casson nanofluid through a porous medium between two co-axial tubes. J. Porous Media 22(9), 1079–1093 (2019)
Hussain, T., Hussain, S., Hayat, T.: Impact of double stratification and magnetic field in mixed convective radiative flow of Maxwell nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 870–878 (2016)
Eldabe, N.T., Moatimid, G.M., Mohamed, M.A.A., Mohamed, Y.M.: Effects of Hallcurrents with heat and mass transfer on the peristaltic transport of a Casson fluid through a porous medium in a vertical circular cylinder. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI180222185E
Ramesh, K., Devakar, M.: Effect of heat transfer on the peristaltic transport of a MHDsecond grade fluid through a porous medium in an inclined asymmetric channel. Chin. J. Phys. 55, 825–844 (2017)
Shehzad, S.A., Abbasi, F.M., Hayat, T., Alsaadi, F.: MHD mixed convective peristaltic motion of nanofluid with joule heating and thermophoresis effects. PLOS ONE 9, e111417 (2014)
Willemsen, M.J., Wienken, C.J., Braun, D., Baaske, P., Duhr, S.: Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 9, 342–372 (2011)
Talbot, L., Cheng, R.K., Schefer, R.W., Willis, D.R.: Thermophoresis of particles in a heated boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 101, 737–758 (1980)
Ali, M., Alam, M.S., Alam, M.M., Alim, M.A.: Radiation and thermal diffusion effect on a steady MHD free convection heat and mass transfer flow past an inclined stretching sheet with Hall current and heat generation. IOSR-JM 9, 33–45 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the reviewers for their valuable comments, which improved and enriched our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Dabe, N.T.M., Abou-Zeid, M.Y., Mohamed, M.A.A. et al. MHD peristaltic flow of non-Newtonian power-law nanofluid through a non-Darcy porous medium inside a non-uniform inclined channel. Arch Appl Mech 91, 1067–1077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01810-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01810-3