Abstract
Purpose
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RD) has diagnostically been divided into macula-OFF or macula-ON. The aim of this study was to describe the demographics and primary outcome of patients with RD following surgery with respect to the macular status, and to determine risk factors for macular involvement.
Methods
This prospective, observational, mono-centric cohort study was conducted at the Jules-Gonin Eye Hospital, from February 2015 until March 2017. The study included 194 eligible patients with primary RD. All patients underwent surgical treatment after baseline clinical examination. The dataset was analyzed using descriptive and analytic statistics.
Results
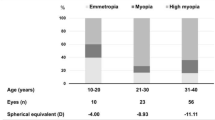
A total of 52.6% (102/194) of patients presented with macula-OFF RD. Mean age was 63.9 ± 12.0 vs. 59.7 ± 11.2 years in the OFF and ON group, respectively. There were 129 men (66.5%) and 65 (33.5%) women, and there were significantly more right eyes affected [right vs. left eyes 123 (63.4%) vs. 71 (36.6%), p = 0.000]. Significantly more myopes (<−3D) presented with a macula-ON RD (p = 0.04). There were more phakic patients in the cohort (55.7%), and phakic eyes were more likely to present with macula-ON RD (p = 0.01). Multivariate modeling showed that pseudophakic lens status and eyes with axial length less than 25 mm (p = 0.06) are independent predictive factors for macula-OFF RD (p = 0.02), whereas sex and laterality were not risk factors for macular involvement.
Conclusion
Pseudophakic lens status and axial length < 25 mm are independent predictive factors for macula-OFF RD. While pseudophakic lens status is a recognized risk factor for RD, shorter axial length has not been previously identified as a risk factor for the macula-OFF RD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitry D, Charteris DG, Fleck BW, Campbell H, Singh J (2010) The epidemiology of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: geographical variation and clinical associations. Br J Ophthalmol 94(6):678–684
Wolfensberger TJ (2004) Foveal reattachment after macula-off retinal detachment occurs faster after Vitrectomy than after buckle surgery. Ophthalmology 111:1340–1343
Laatikainen L, Tolppanen EM, Harju H (1985) Epidemiology of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in a Finnish population. Acta Ophthalmol 63(1):59–64
Mitry D, Tuft S, McLeod D, Charteris DG (2011) Laterality and gender imbalances in retinal detachment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 249(7):1109–1110
Mitry D, Charteris DG, Yorston D, Siddiqui MR, Campbell H, Murphy AL et al (2010) The epidemiology and socioeconomic associations of retinal detachment in Scotland: a two-year prospective population-based study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(10):4963–4968
Cheng CY, Yen MY, Lin HY, Hsia WW, Hsu WM (2004) Association of ocular dominance and anisometropic myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(8):2856–2860
Coyle JT (1984) Keratoconus and eye rubbing. Am J Ophthalmol 97(4):527–528
Ioannidis AS, Speedwell L, Nischal KK (2005) Unilateral keratoconus in a child with chronic and persistent eye rubbing. Am J Ophthalmol 139(2):356–357
Alshareef RA, Khuthaila MK, Januwada M, Goud A, Ferrara D, Chhablani J (2017) Choroidal vascular analysis in myopic eyes: evidence of foveal medium vessel layer thinning. Int J retina vitreous 3:28
Flores-Moreno I, Lugo F, Duker JS, Ruiz-Moreno JM (2013) The relationship between axial length and choroidal thickness in eyes with high myopia. Am J Ophthalmol 155(2):314–319
Sayman Muslubas I, Hocaoglu M, Ersoz MG, Arf S, Karacorlu M (2017) Choroidal thickness in chronic rhegmatogenous retinal detachment before and after surgery, and comparison with acute cases. Int Ophthalmol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0556-9
Iwase T, Kobayashi M, Yamamoto K, Yanagida K, Ra E, Terasaki H (2017) Change in choroidal blood flow and choroidal morphology due to segmental scleral buckling in eyes with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Sci Rep 7(1):5997
Sheu SJ, Ger LP, Ho WL (2010) Late increased risk of retinal detachment after cataract extraction. Am J Ophthalmol 149(1):113–119
Sheu SJ, Ger LP, Chen JF (2007) Male sex as a risk factor for pseudophakic retinal detachment after cataract extraction in Taiwanese adults. Ophthalmology 114(10):1898–1903
Wang J, McLeod D, Henson DB, Bishop PN (2003) Age-dependent changes in the basal retinovitreous adhesion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44(5):1793–1800
Chen SN, Lian IB, Wei YJ (2016) Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Taiwan. Br J Ophthalmol 100(9):1216–1220
Park SJ, Cho SC, Choi NK, Park KH, Woo SJ (2017) Age, sex, and time-specific trends in surgical approaches for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: a Nationwide, population-based study using the National Claim Registry. Retina. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0000000000001485
Van de Put MA, Hooymans JM, Los LI, Group D. R. R. D. S (2013) The incidence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in the Netherlands. Ophthalmology 120(3):616–622
Howie AR, Darian-Smith E, Allen PL, Vote B (2016) Whole population incidences of patients presenting with rhegmatogenous retinal detachments within Tasmania, Australia. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 44(2):144–146
Rosman M, Wong TY, Ong SG, Ang CL (2001) Retinal detachment in Chinese, Malay and Indian residents in Singapore: a comparative study on risk factors, clinical presentation and surgical outcomes. Int Ophthalmol 24(2):101–106
Lee KE, Klein BE, Klein R, Quandt Z, Wong TY (2009) Association of age, stature, and education with ocular dimensions in an older white population. Arch Ophthalmol 127(1):88–93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no financial interest in any aspect of this article.
The authors have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest.
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee (Ethical Committee of Canton Vaud, Switzerland, protocol no. 483/14) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potic, J., Bergin, C., Giacuzzo, C. et al. Primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: risk factors for macular involvement. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256, 489–494 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-017-3880-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-017-3880-x