Abstract
Background
Two new tonometers have been introduced that are based on the impedance principle. Both the TGDc-01 (transpalpebral measurement) and the iCare (corneal measurement) do not require corneal anaesthesia. The present work presents an evaluation of both devices.
Methods
Comparative measurements using one of the new tonometers and applanation tonometry were performed by one investigator according to the international standard for ocular tonometer (ISO 8612). Measurements were performed on 445 eyes without corneal pathology from 243 patients. Six measurements were performed for iCare and 3 for TGDc, immediately followed by 3 applanation tonometry measurements.
Results
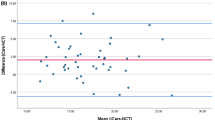
The correlation coefficient with respect to applanation tonometry was 0.81 for TGDc and 0.95 for iCare. TGDc-01 measurements showed an average deviation of 3.1 ± 2.6 mmHg to those of Perkins applanation tonometry. The maximum difference was 28.7 mmHg below and 9.8 mmHg above the results of applanation tonometry. iCare showed an average deviation of 2.5 ± 1.1 mmHg to Goldmann tonometry. The maximum difference was 14.5 mmHg below and 9.8 mmHg above.
Conclusions
The results of both new tonometers showed a good correlation with the reference applanation tonometric methods, but the strict requirements of ISO 8612 are not fulfilled by either tonometer at present. Additionally, transpalpebral measurements with the TGDc-01 showed unacceptably high variability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bron AM, Creuzot-Garcher C, Goudeau-Boutillon S, d’Athis P (1999) Falsely elevated intraocular pressure due to increased central corneal thickness. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 237:220–224
Doughty MJ, Zaman ML (2000) Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol 44:367–408
Ehlers N, Hansen FK (1974) Central corneal thickness in low-tension glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 52:740–746
Elster C, Schwenteck T, Tilgner J et al (1998) Evaluating clinical comparisons for human eye tonometers. A critical assessment of common practice. New trends Ophthalmol 12:91–96
Fernandes P, Diaz-Rey JA, Queiros A, Gonzalez-Meijome JM, Jorge J (2005) Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:436–440
Internationaler Standard für Augentonometer ISO 8612 (2001) Beuth-Verlag GmbH, Berlin
van der Jagt LH, Jansonius NM (2005) Three portable tonometers, the TGDc-01, the iCare and the Tonopen XL, compared with each other and with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:429–435, Sep
Kniestedt C, Nee M, Stamper RL (2003) Dynamic contour tonometry (DCT) and its dependence on corneal hydration in human cadaver eyes. Poster presented at: The Annual Meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology; May 4, Fort Lauderdale, FL
Kontiola A (1996–97) A new electromechanical method for measuring intraocular pressure. Doc Ophthalmol 93:265–276
Kontiola A (2000) A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 78:142–145
Kontiola A, Puska P (2004) Measuring intraocular pressure with the Pulsair 3000 and Rebound tonometers in elderly patients without an anesthetic. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:3–7
Lam AK, Lam CH, Chan R (2005) The validity of a digital eyelid tonometer (TGDc-01) and ist comparison with Goldmann applanation tonometry - a pilot study. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:205–210
Meyer MW, Gockeln R, Hoy L, Meyer A, Erb C (2004) Comparison of intraocular pressure measurements with the digitial tonometer TGDc-01’PRA’ and the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Ophthalmic Res 36:250–254
Müller A, Godenschwenger L, Lang GE, Kampmeier J (2004) Prospektiver Vergleich des neuen Indentationstonometers TGDc-01, dem Non-contact Tonometer PT 100 und dem konventionellen Goldmann Applanationstonometer. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 221:762–768
Sandner D, Bohm A, Kostov S, Pillunat L (2005) Measurement of the intraocular pressure with the transpalpebral tonometer TGDc-01 in comparison with applanation tonometry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243:563–569
Troost A, Specht K, Krummenauer F, Yun SH, Schwenn O (2005) Deviations between transpalpebral tonometry using TGDc-01 and Goldmann applanation tonometry depending on IOP level. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243:853–858
Troost A, Yun SH, Specht K, Krummenauer F, Schwenn O (2005) Transpalpebral tonometry: reliability and comparison with Goldmann applanation tonometry and palpation in healthy volunteers. Br J Ophthalmol 89:280–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No sponsoring organizations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruokonen, P.C., Schwenteck, T. & Draeger, J. Evaluation of the impedance tonometers TGDc-01 and iCare according to the international ocular tonometer standards ISO 8612. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245, 1259–1265 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-006-0483-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-006-0483-3