Abstract
Background
Hashimoto’s encephalopathy with serum anti-NH2-terminal of α-enolase (NAE) antibodies occasionally displays clinical symptoms such as cerebellar ataxia and parkinsonism. We studied the frequency of anti-NAE antibodies in patients with Parkinson-plus syndrome.
Methods
We examined the positive rates of anti-NAE antibodies in 47 patients with multiple system atrophy (MSA), 29 patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), eight patients with corticobasal syndrome (CBS), and 18 patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) using conventional immunoblot analysis.
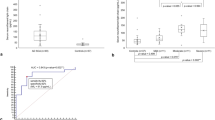
Results
Positive anti-NAE antibody rates of 31.9%, 10.3%, 50.0%, and 11.1% were reported in the MSA, PD, CBS, and PSP patients, respectively. The duration from onset to a wheelchair-bound state in seropositive MSA patients tended to be shorter than that in seronegative MSA patients.
Conclusions
Anti-NAE antibodies are detected in some patients clinically diagnosed with MSA and CBS. Although its pathophysiological significance remains uncertain, serum anti-NAE antibodies might represent a prognostic marker in the clinical course of MSA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujii A, Yoneda M, Ito T, Yamamura O, Satomi S, Higa H, Kimura A, Suzuki M, Yamashita M, Yuasa T, Suzuki H, Kuriyama M (2005) Autoantibodies against the amino terminal of alpha-enolase are a useful diagnostic marker of Hashimoto’s encephalopathy. J Neuroimmunol 162:130–136
Nakagawa H, Yoneda M, Fujii A, Kinomoto K, Kuriyama M (2007) Hashimoto’s encephalopathy presenting with progressive cerebellar ataxia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:196–197
Matsunaga A, Ikawa M, Fujii A, Nakamoto Y, Kuriyama M, Yoneda M (2013) Hashimoto’s encephalopathy as a treatable adult-onset cerebellar ataxia mimicking spinocerebellar degeneration. Eur Neurol 69:14–20
Yoneda M, Fujii A, Ito A, Yokoyama H, Nakagawa H, Kuriyama M (2007) High prevalence of serum autoantibodies against the amino terminal of alpha-enolase in Hashimoto’s encephalopathy. J Neuroimmunol 185:195–200
Inoue K, Kitamura J, Yoneda M, Imamura E, Tokinobu H (2012) Hashimoto’s encephalopathy presenting with micrographia as a typical feature of parkinsonism. Neurol Sci 33:395–397
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ, Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, Wood NW, Colosimo C, Durr A, Fowler CJ, Kaufmann H, Klockgether T, Lees A, Poewe W, Quinn N, Revesz T, Robertson D, Sandroni P, Seppi K, Vidailhet M (2008) Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 71:670–676
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Mathew R, Bak TH, Hodges JR (2012) Diagnostic criteria for corticobasal syndrome: a comparative study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:405–410
Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D, Campbell G, Dubois B, Duvoisin RC, Goetz CG, Golbe LI, Grafman J, Growdon JH, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Quinn NP, Tolosa E, Zee DS (1996) Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 47:1–9
Kishitani T, Matsunaga A, Ikawa M, Hayashi K, Yamamura O, Hamano T, Watanabe O, Tanaka K, Nakamoto Y, Yoneda M (2017) Limbic encephalitis associated with anti-NH2-terminal of alpha-enolase antibodies: a clinical subtype of Hashimoto encephalopathy. Medicine 96:e6181
Dahm L, Ott C, Steiner J, Stepniak B, Teegen B, Saschenbrecker S, Hammer C, Borowski K, Begemann M, Lemke S, Rentzsch K, Probst C, Martens H, Wienands J, Spalletta G, Weissenborn K, Stocker W, Ehrenreich H (2014) Seroprevalence of autoantibodies against brain antigens in health and disease. Ann Neurol 76:82–94
Mattozzi S, Sabater L, Escudero D, Arino H, Armangue T, Simabukuro M, Iizuka T, Hara M, Saiz A, Sotgiu S, Dalmau J, Graus F (2020) Hashimoto encephalopathy in the 21st century. Neurology 94:e217–e224
Yoneda M, Matsunaga A, Ikawa M (2020) Reader response: Hashimoto encephalopathy in the 21st century. Neurology in press
Montojo MT, Petit-Pedrol M, Graus F, Dalmau J (2015) Clinical spectrum and diagnostic value of antibodies against the potassium channel related protein complex. Neurologia 30:295–301
Lebioda L, Stec B (1991) Mapping of isozymic differences in enolase. Int J Biol Macromol 13:97–100
Subramanian A, Miller DM (2000) Structural analysis of alpha-enolase. Mapping the functional domains involved in down-regulation of the c-myc protooncogene. J Biol Chem 275:5958–5965
Kim KS, Choi YR, Park JY, Lee JH, Kim DK, Lee SJ, Paik SR, Jou I, Park SM (2012) Proteolytic cleavage of extracellular alpha-synuclein by plasmin: implications for Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem 287:24862–24872
Nakagami Y, Abe K, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N (2000) Laminin degradation by plasmin regulates long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 20:2003–2010
Matsuda K (2004) Laminin and Alzheimer’s disease. Psychogeriatrics 4:S19–S38
Rifkin DB, Mazzieri R, Munger JS, Noguera I, Sung J (1999) Proteolytic control of growth factor availability. APMIS 107:80–85
Balsara RD, Ploplis VA (2008) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: the double-edged sword in apoptosis. Thromb Haemost 100:1029–1036
Novak P, Williams A, Ravin P, Zurkiya O, Abduljalil A, Novak V (2012) Treatment of multiple system atrophy using intravenous immunoglobulin. BMC Neurol 12:131
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Grant for “the Research Committee for Ataxic Diseases” of the Research on Measures for Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (20K07923) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikuchi, A., Yoneda, M., Hasegawa, T. et al. High prevalence of serum anti-NH2-terminal of α-enolase antibodies in patients with multiple system atrophy and corticobasal syndrome. J Neurol 268, 4291–4295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10553-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10553-2