Abstract
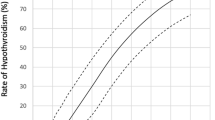
Radiation-induced human papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) is associated with chromosomal inversions that involve the genetic loci H4 and RET on chromosome 10. Recently, experimental data has shown that these loci lie in very close spatial proximity in a high proportion of adult human thyroid cells. Applying the generalized formulation of dual radiation action to this H4-to-RET geometric distance data, we predict here the radiation dose-response of H4-RET induction. The predicted H4-RET dose-response has a linear-to-quadratic transition dose of ∼7 Gy, suggesting the validity of linear risk extrapolations to very low doses for H4-RET mediated radiation-induced PTC. In conjunction with A-bomb survivor data, the predicted H4-RET dose- response yields estimates of the number of PTC target cells that are of the order of ∼106 to ∼107 cells, i.e. considerably less than the total number of follicular cells in the thyroid gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 February 2001 / Accepted: 11 July 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radivoyevitch, T., Sachs, R., Nikiforov, Y. et al. On target cell numbers in radiation-induced H4-RET mediated papillary thyroid cancer. Radiat Environ Biophys 40, 191–197 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110100108
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110100108