Abstract
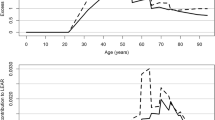
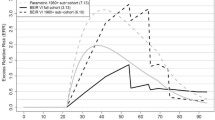
A previous analysis of the radon-related lung cancer mortality risk, in the German uranium miners cohort, using Poisson modeling techniques, noted internal (spontaneous) rates that were higher on average than the external rates by 16.5% (95% CI: 9%; 24%). The main purpose of the present paper is to investigate the nature of, and possible reasons for, this difference by comparing patterns in spontaneous lung cancer mortality rates in a cohort of male miners involved in uranium extraction at the former Wismut mining company in East Germany with national male rates from the former German Democratic Republic. The analysis is based on miner data for 3,001 lung cancer deaths, 1.76 million person-years for the period 1960–2003, and national rates covering the same calendar-year range. Simple “age–period–cohort” graphical analyses were applied to assess the main qualitative differences between the national and cohort baseline lung cancer rates. Some differences were found to occur mainly at higher attained ages above 70 years. Although many occupational risk factors may have contributed to these observed age differences, only the effects of smoking have been assessed here by applying the Peto–Lopez indirect method for calculating smoking attributability. It is inferred that the observed age differences could be due to the greater prevalence of smoking and more mature smoking epidemic in the Wismut cohort compared to the general population of the former German Democratic Republic. In view of these observed differences between external population-based rates and internal (spontaneous) cohort baseline lung cancer rates, it is strongly recommended to apply only the internal rates in future analyses of uranium miner cohorts.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
One WLM of cumulative exposure corresponds to exposure to 1 WL during one month (170 h) and is equivalent to 3.5 mJh/m3.
References
Brüske-Hohlfeld I, Rosario AS, Wolke G, Heinrich J, Kreuzer M, Kreienbrock L, Wichmann HE (2006) Lung cancer risk among former uranium miners of the WISMUT Company in Germany. Health Phys 90:208–216
Dahmann D, Bauer HD, Stoyke G (2008) Retrospective exposure assessment for respirable and inhalable dust, crystalline silica and arsenic in the former German uranium mines of SAG/SDAG Wismut. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 81:949–958
Kreuzer M, Walsh L, Schnelzer M, Tschense A, Grosche B (2008) Radon and risk of extra-pulmonary cancers—Results of the German uranium miners cohort study, 1960–2003. Br J Cancer 99:1946–1953
Kreuzer M, Schnelzer M, Tschense A, Walsh L, Grosche B (2009a) Cohort profile: the German uranium miner cohort study (WISMUT cohort), 1946–2003. Int J Epidemiol. doi:10.1093/ije/dyp216
Kreuzer M, Grosche B, Schnelzer M, Tschense A, Dufey F, Walsh L (2009b) Radon and risk of death from cancer and cardiovascular diseases in the German uranium miners cohort study: follow-up 1946–2003. Radiat Environ Biophys 49(2):177–185
Lehmann F, Hambeck L, Linkert KH, Lutze H, Meyer H, Reiber H, Renner HK, Reinisch A, Seifert T, Wolf F (1998) Belastung durch ionisierende Strahlung im Uranerzbergbau der ehemaligen DDR. Hauptverband der gewerblichen Berufsgenossenschaften, St. Augustin
Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, Thun M, Heath C Jr (1992) Mortality from tobacco in developed countries: indirect estimation from national vital statistics. Lancet 339:1268–1278
Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, Thun MJ, Heath C Jr (1994) Mortality from smoking in developed countries, 1950–2000: indirect estimates from national vital statistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford. (Second edition available online at http://www.ctsu.ox.ac.uk/~tobacco/)
Powles J (2000) The Peto/Lopez indirect method for estimating the accumulated mortality hazard caused by smoking (GBD2000 protocol). Available from: http://www.phpc.cam.ac.uk/mst/phtop/peto_lopez_method_gbd2000.doc. Accessed 1 March 2010
Preston DL, Lubin JH, Pierce DA, McConney ME (1993) Epicure user’s guide. HiroSoft, Seattle
Rittgen W, Becker N (2000) SMR Analysis of historical follow-up studies with missing death certificates. Biometrics 56:1164–1169
Runge W (editor in chief) (1999) Chronik der WISMUT, Wismut GmbH (2738 pages, in German)
Schnelzer M, Kreuzer M, Tschense A, Hammer G, Grosche B (2010) Accounting for smoking in the radon related lung cancer risk among German uranium miners: results of a nested case-control study. Health Phys 98:20–28
Statistisches Bundesamt (2005) Fachserie 14: Finanzen und Steuern, Reihe 9.1.1 Absatz von Tabakwaren, Abbildung 2.5.2: Jahrliche Pro-Kopf-Verbrauch (in Stück) an Zigaretten in Deutschland 1955 bis 2004
Thun MJ, Hannan LM, Adams-Campbell LL, Boffetta P, Buring JE, Feskanich D, Flanders WD, Jee SH, Katanode K, Kolonel LN, Lee IM, Marugame T, Palmer JR, Riboli E, Sobue T, Avila-Tang E, Wilkens LR, Samet JM (2008) Lung cancer occurrence in never-smokers: an analysis of 13 cohorts and 22 cancer registry studies. PLoS Med 5(9):1357–1371
Walsh L, Tschense A, Schnelzer M, Dufey F, Grosche B, Kreuzer M (2010a) The Influence of radon exposure on lung cancer mortality in German uranium miners, 1946–2003. Radiat Res 173:79–90
Walsh L, Dufey F, Tschense A, Schnelzer M, Grosche B, Kreuzer M (2010b) Radon and the risk of cancer mortality—Internal Poisson models for the German uranium miners cohort. Health Phys 99(3):292–300
WHO (1992) International statistical classification of diseases and health related problems: the ICD-10 (German edition 1.3.1999), Geneva
Wichmann HE, Gerken M, Wellmann J, Kreuzer M, Kreienbrock L, Keller G, Wölke G, Heinrich J (1999) Lungenkrebsrisiko durch Radon in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland (Ost)- Thuringen und Sachsen. ecomed, Landsberg. (in German)
Acknowledgments
The German Federal Commissioner for Data Protection and Freedom of Information has issued a special approval for this research, which constitutes an exemption from the necessity to obtain human subjects approvals. This work was partially funded by the EU Alpha-Risk project and by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany (Competence Network Radiation Research). The authors thank the German Federation of Institutions for Statutory Accident Insurance and Prevention (DGUV) and the Miners’ Occupational Compensation Board (Bergbau Berufsgenossenschaft) for their continuous support over many years. The field work for the follow-up was conducted by I + G Gesundheitsforschung and Mediveritas GmbH. Their commitment helped to achieve the low percentage of lost to follow-up. We also thank the members of the Wismut Working Group of the German Radiation Protection Commission for their continued advice. Special thanks are due to Prof. Werner Rühm for a valuable initial discussion and some very helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walsh, L., Dufey, F., Möhner, M. et al. Differences in baseline lung cancer mortality between the German uranium miners cohort and the population of the former German Democratic Republic (1960–2003). Radiat Environ Biophys 50, 57–66 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-010-0332-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-010-0332-y