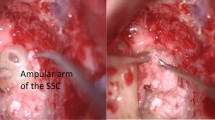
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the long-term outcomes of trans-mastoid plugging of superior semicircular canal dehiscence (SSCD), focusing on complicated cases.
Methods
In this cohort study, we included all patients who underwent trans-mastoid plugging of SSCD between 2009 and 2019. We evaluated the symptoms (autophony, sound-/pressure-induced vertigo, disequilibrium, aural fullness and pulsatile tinnitus) before and 1 year after surgery in the medical records. We systematically assessed the current symptoms 6.2 ± 3 years postoperative (range 2.2–12.3 years) using questionnaires sent by post and validated by telephone interviews. We also documented any complications and the need for further procedures. We compared pure tone and speech audiometry before and 1 year after surgery. Finally, the degree of mastoid pneumatisation and mastoid tegmen anatomy were reviewed on preoperative CT scans.
Results
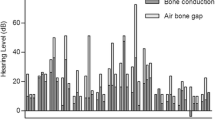
We included 24 ears in 23 patients. No complications were recorded, and none required a second procedure for SSCD. Following surgery, oscillopsia and Tullio phenomena resolved in all patients. Hyperacusis, autophony, and aural fullness were also settled in all patients except one. Balance impairment persisted to some degree in 35% of patients. No deterioration over the years was reported regarding the above symptoms. On average, bone conduction pure tone average pre- and 1 year postoperative were 13.7 ± 17 and 20.5 ± 18 dB, respectively (P = 0.002). Air bone gaps were reduced from 12.7 ± 8 to 5.9 ± 6 (P = 0.001). Two patients had a significant sclerotic mastoid, three had a prominent low-lying mastoid tegmen, and two had both. Anatomy had no effect on outcome.
Conclusion
Trans-mastoid plugging of SSCD is a reliable and effective technique which achieves long-lasting symptom control, even in cases with sclerotic mastoid or low-lying mastoid tegmen.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Minor LB (2005) Clinical manifestations of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope 115(10):1717–1727. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000178324.55729.b7
Minor LB, Solomon D, Zinreich JS, Zee DS (1998) Sound- and/or pressure-induced vertigo due to bone dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124(3):249–258. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.124.3.249
Zhou G, Gopen Q, Poe DS (2007) Clinical and diagnostic characterization of canal dehiscence syndrome: a great otologic mimicker. Otol Neurotol 28(7):920–926
Carey JP, Minor LB, Nager GT (2000) Dehiscence or thinning of bone overlying the superior semicircular canal in a temporal bone survey. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126(2):137–147. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.126.2.137
Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ (2008) Conductive hearing loss caused by third-window lesions of the inner ear. Otol Neurotol 29(3):282–289. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0b013e318161ab24
Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ, McKenna MJ (2007) Superior semicircular canal dehiscence mimicking otosclerotic hearing loss. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 65:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1159/000098790
Mau C, Kamal N, Badeti S, Reddy R, Ying YM, Jyung RW et al (2018) Superior semicircular canal dehiscence: diagnosis and management. J Clin Neurosci 48:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.11.019
Stimmer H, Hamann KF, Zeiter S, Naumann A, Rummeny EJ (2012) Semicircular canal dehiscence in HR multislice computed tomography: distribution, frequency, and clinical relevance. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(2):475–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1688-6
Palma Diaz M, Cisneros Lesser JC, Vega AA (2017) Superior Semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome—diagnosis and surgical management. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 21(2):195–198. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1599785
Zhao YC, Somers T, van Dinther J, Vanspauwen R, Husseman J, Briggs R (2012) Transmastoid repair of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 73(4):225–229. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1312713
Ward BK, Agrawal Y, Nguyen E, Della Santina CC, Limb CJ, Francis HW et al (2012) Hearing outcomes after surgical plugging of the superior semicircular canal by a middle cranial fossa approach. Otol Neurotol 33(8):1386–1391. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e318268d20d
Silverstein H, Kartush JM, Parnes LS, Poe DS, Babu SC, Levenson MJ et al (2014) Round window reinforcement for superior semicircular canal dehiscence: a retrospective multi-center case series. Am J Otolaryngol 35(3):286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2014.02.016
Hillman TA, Kertesz TR, Hadley K, Shelton C (2006) Reversible peripheral vestibulopathy: the treatment of superior canal dehiscence. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(3):431–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2005.10.033
Shaia WT, Diaz RC (2013) Evolution in surgical management of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21(5):497–502. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0b013e328364b3ff
Brandolini C, Modugno GC, Pirodda A (2014) Dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal: a review of the literature on its possible pathogenic explanations. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(3):435–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2497-x
Banakis Hartl RM, Cass SP (2018) Effectiveness of transmastoid plugging for semicircular Canal Dehiscence Syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 158(3):534–540. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599817751092
Powell HR, Khalil SS, Saeed SR (2016) Outcomes of transmastoid surgery for superior semicircular Canal Dehiscence Syndrome. Otol Neurotol 37(7):e228–e233. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000001103
Nguyen T, Lagman C, Sheppard JP, Romiyo P, Duong C, Prashant GN et al (2018) Middle cranial fossa approach for the repair of superior semicircular canal dehiscence is associated with greater symptom resolution compared to transmastoid approach. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 160(6):1219–1224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3346-2
Gioacchini FM, Alicandri-Ciufelli M, Kaleci S, Scarpa A, Cassandro E, Re M (2016) Outcomes and complications in superior semicircular canal dehiscence surgery: a systematic review. Laryngoscope 126(5):1218–1224. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25662
Ziylan F, Kinaci A, Beynon AJ, Kunst HP (2017) A comparison of surgical treatments for superior semicircular canal dehiscence: a systematic review. Otol Neurotol 38(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000001277
Dai P, Zhang T, Wang K, Song J, Qian W, Wang Z (2004) Positional relationship between the facial nerve and other structures of the temporal bone. J Laryngol Otol 118(2):106–111. https://doi.org/10.1258/002221504772784540
Dai PD, Zhang HQ, Wang ZM, Sha Y, Wang KQ, Zhang TY (2007) Morphological and positional relationships between the sigmoid sinus and the jugular bulb. Surg Radiol Anat 29(8):643–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-007-0266-5
Niesten ME, McKenna MJ, Herrmann BS, Grolman W, Lee DJ (2013) Utility of cVEMPs in bilateral superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Laryngoscope 123(1):226–232. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23550
Thomeer H, Bonnard D, Castetbon V, Franco-Vidal V, Darrouzet P, Darrouzet V (2016) Long-term results of middle fossa plugging of superior semicircular canal dehiscences: clinically and instrumentally demonstrated efficiency in a retrospective series of 16 ears. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(7):1689–1696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3715-5
Gersdorff G, Blaivie C, de Foer B, Deggouj N, Wyckmans F, Somers T (2022) Evaluation of the transmastoid plugging approach for superior semicircular canal dehiscences: a retrospective series of 30 ears. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279(10):4861–4869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07316-8
Agrawal Y, Migliaccio AA, Minor LB, Carey JP (2009) Vestibular hypofunction in the initial postoperative period after surgical treatment of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Otol Neurotol 30(4):502–506. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181a32d69
Carey JP, Migliaccio AA, Minor LB (2007) Semicircular canal function before and after surgery for superior canal dehiscence. Otol Neurotol 28(3):356–364. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mao.0000253284.40995.d8
Pisano DV, Niesten ME, Merchant SN, Nakajima HH (2012) The effect of superior semicircular canal dehiscence on intracochlear sound pressures. Audiol Neurootol 17(5):338–348. https://doi.org/10.1159/000339653
Beyea JA, Agrawal SK, Parnes LS (2012) Transmastoid semicircular canal occlusion: a safe and highly effective treatment for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and superior canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope 122(8):1862–1866. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23390
Mikulec AA, Poe DS, McKenna MJ (2005) Operative management of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope 115(3):501–507. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000157844.48036.e7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CS and SW designed and performed the research, analyzed the data and drafted the paper. They are equal contributors. AD conducted the study and assisted in data analysis. JMG helped design the research and write the manuscript. RB designed the study and drafted the paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shaul, C., Weder, S., Dragovic, A. et al. Trans-mastoid plugging of superior semicircular canal dehiscence: long-term follow-up. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 281, 67–74 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08079-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08079-6