Abstract
Background
Synkinesis is defined as involuntary movements accompanying by voluntary movements and can occur during the aftermath of peripheral facial palsy, causing functional, aesthetic and psychological problems in the patient. Botulinum toxin A (BTX-A) is frequently used as a safe and effective treatment; however, there is no standardized guideline for the use of BTX-A in synkinesis. The purpose of this article is to review and summarize studies about the BTX-A treatment of synkinesis in patients with a history of peripheral facial palsy; including given dosages, injection sites and time intervals between injections.
Materials and methods
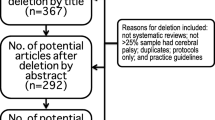
A multi-database systematic literature search was performed in October 2020 using the following databases: Pubmed, Embase, Medline, and The Cochrane Library. Two authors rated the methodological quality of the included studies independently using the ‘Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale’ for non-randomised studies’ (NOS).
Results
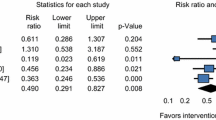
Four-thousand-five-hundred-and-nineteen articles were found of which 34 studies met the inclusion criteria, in total comprising 1314 patients. Most studies were assessed to be of ‘fair’ to ‘good’ methodological quality. The Cohen’s kappa (between author FJ and AS) was 0.78. Thirty-one studies investigated the reported dosage injected, 17 studies reported injection location and 17 studies investigated time intervals. A meta-analysis was performed for three studies comprising 106 patients, on the effects of BTX-A treatment on the Synkinesis Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) scores. The mean difference was 11.599 (range 9.422–13.766), p < 0.01. However, due to inconsistent reporting of data of the included studies, no relationship with the dosage and location could be assessed.
Conclusions
Many treatment strategies for synkinesis exist, consisting of varying BTX-A brands, dosages, time intervals and different injection locations. Moreover, the individual complaints are very specific, which complicates creating a standardized chemodenervation treatment protocol. The BTX-A treatment of long-term synkinesis is very individual and further studies should focus on a patient-tailored treatment instead of trying to standardize treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available upon reasonable request. Please email the corresponding author.
References
Esslen E (1960) Electromyographic findings on two types of misdirection of regenerating axons. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 12:738–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(60)90120-6
Yamamoto E, Nishimura H, Hirono Y (1988) Occurrence of sequelae in Bell’s palsy. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 446:93–96. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016488709121848
Fu L, Bundy C, Sadiq SA (2011) Psychological distress in people with disfigurement from facial palsy. Eye (Lond) 25(10):1322–1326. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2011.158
Borodic G, Bartley M, Slattery W et al (2005) Botulinum toxin for aberrant facial nerve regeneration: double-blind, placebo-controlled trial using subjective endpoints. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(1):36–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000169689.27829.c4
Ishii LE, Godoy A, Encarnacion CO, Byrne PJ, Boahene KDO, Ishii M (2011) What faces reveal: impaired affect display in facial paralysis. Laryngoscope 121(6):1138–1143. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.21764
Montserrat L, Benito M (1988) Facial synkinesis and aberrant regeneration of facial nerve. Adv Neurol 49:211–224
Pourmomeny AA, Asadi S (2014) Management of synkinesis and asymmetry in facial nerve palsy: a review article. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 26(77):251–256
Celik M, Forta H, Vural C (2000) The development of synkinesis after facial nerve paralysis. Eur Neurol 43(3):147–151. https://doi.org/10.1159/000008154
Husseman J, Mehta RP (2008) Management of synkinesis. Facial Plast Surg 24(2):242–249. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1075840
Kosins AM, Hurvitz KA, Evans GR, Wirth GA (2007) Facial paralysis for the plastic surgeon. Can J Plast Surg 15(2):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/229255030701500203
Devriese PP, Bronk J. Non-surgical rehabilitation of facial expression. Facial Nerve Surgery Amstelveen Kugler Med. 1977:290–294.
Beurskens CHG, Heymans PG (2006) Mime therapy improves facial symmetry in people with long-term facial nerve paresis: a randomised controlled trial. Aust J Physiother 52(3):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0004-9514(06)70026-5
Azizzadeh B, Irvine LE, Diels J et al (2019) Modified selective neurectomy for the treatment of post-facial paralysis synkinesis. Plast Reconstr Surg 143(5):1483–1496. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005590
Guerrissi JO (1991) Selective myectomy for postparetic facial synkinesis. Plast Reconstr Surg 87(3):459–466. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199103000-00010
Roggenkämper P, Laskawi R, Damenz W, Schröder M, Nüssgens Z (1990) Botulinum toxin treatment of synkinesia following facial paralysis. HNO 38(8):295–297
Chong PN, Ong B, Chan R (1991) Botulinum toxin in the treatment of facial dyskinesias. Ann Acad Med Sing 20(2):223–227
Dobryansky M, Korsh J, Shen AE, Aliano K (2015) Botulinum toxin type A and B primary resistance. Aesthetic Surg J 35(2):N28-30. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sju027
Dutton JJ (1996) Botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of craniocervical muscle spasms: short- and long-term, local and systemic effects. Surv Ophthalmol 41(1):51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0039-6257(97)81995-9
Dutton JJ, White JJ, Richard MJ (2006) Myobloc for the treatment of benign essential blepharospasm in patients refractory to botox. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 22(3):173–177. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.iop.0000217382.33972.c4
Critchfield J (2002) Considering the immune response to botulinum toxin. Clin J Pain 18(6 Suppl):S133–S141. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002508-200211001-00004
Guntinas-Lichius O (2003) Injection of botulinum toxin type B for the treatment of otolaryngology patients with secondary treatment failure of botulinum toxin type A. Laryngoscope 113(4):743–745. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200304000-00029
Wenzel RG (2004) Pharmacology of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Am J Heal Pharm AJHP 61(22 Suppl 6):S5-10. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/61.suppl_6.S5
de Paiva A, Meunier FA, Molgó J, Aoki KR, Dolly JO (1999) Functional repair of motor endplates after botulinum neurotoxin type A poisoning: biphasic switch of synaptic activity between nerve sprouts and their parent terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(6):3200–3205. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.6.3200
Barnes MP, Best D, Kidd L et al (2005) The use of botulinum toxin type-B in the treatment of patients who have become unresponsive to botulinum toxin type-A—initial experiences. Eur J Neurol 12(12):947–955. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2005.01095.x
Zuber M, Sebald M, Bathien N, de Recondo J, Rondot P (1993) Botulinum antibodies in dystonic patients treated with type A botulinum toxin: frequency and significance. Neurology 43(9):1715–1718. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.43.9.1715
Greene P, Fahn S, Diamond B (1994) Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Mov Disord 9(2):213–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870090216
Jankovic J, Schwartz K (1995) Response and immunoresistance to botulinum toxin injections. Neurology 45(9):1743–1746. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.45.9.1743
Lange O, Bigalke H, Dengler R, Wegner F, deGroot M, Wohlfarth K (2009) Neutralizing antibodies and secondary therapy failure after treatment with botulinum toxin type A: much ado about nothing? Clin Neuropharmacol 32(4):213–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181914d0a
Siatkowski RM, Tyutyunikov A, Biglan AW et al (1993) Serum antibody production to botulinum A toxin. Ophthalmology 100(12):1861–1866. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31384-9
Toffola ED, Furini F, Redaelli C, Prestifilippo E, Bejor M (2010) Evaluation and treatment of synkinesis with botulinum toxin following facial nerve palsy. Disabil Rehabil 32(17):1414–1418. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638280903514697
Shinn JR, Nwabueze NN, Patel P, Norton C, Ries WR, Stephan SJ (2019) Contemporary review and case report of botulinum resistance in facial synkinesis. Laryngoscope 129(10):2269–2273. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27709
Cronin GW, Steenerson RL (2003) The effectiveness of neuromuscular facial retraining combined with electromyography in facial paralysis rehabilitation. Otolaryngol Neck Surg 128(4):534–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0194-5998(03)00005-6
Kasahara T, Ikeda S, Sugimoto A et al (2017) Efficacy of tape feedback therapy on synkinesis following severe peripheral facial nerve palsy. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 42(3):139–142
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa, ON: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Published 2013. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 1 Sep 2020.
Altman DG. Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Taylor & Francis; 1990. https://books.google.nl/books?id=v-walRnRxWQC.
Monini S, De Carlo A, Biagini M et al (2011) Combined protocol for treatment of secondary effects from facial nerve palsy. Acta Otolaryngol 131(8):882–886. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2011.577447
Couch SM, Chundury RV, Holds JB (2014) Subjective and objective outcome measures in the treatment of facial nerve synkinesis with onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 30(3):246–250. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000086
Dall’Angelo A, Mandrini S, Sala V et al (2014) Platysma synkinesis in facial palsy and botulinum toxin type A. Laryngoscope 124(11):2513–2517. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24732
Filipo R, Spahiu I, Covelli E, Nicastri M, Bertoli GA (2012) Botulinum toxin in the treatment of facial synkinesis and hyperkinesis. Laryngoscope 122(2):266–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.22404
Ito H, Ito H, Nakano S, Kusaka H (2007) Low-dose subcutaneous injection of botulinum toxin type A for facial synkinesis and hyperlacrimation. Acta Neurol Scand 115(4):271–274. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00746.x
Kollewe K, Mohammadi B, Dengler R, Dressler D (2010) Hemifacial spasm and reinnervation synkinesias: long-term treatment with either Botox® or Dysport®. J Neural Transm 117(6):759–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0409-4
Laskawi R (1997) Combination of hypoglossal-facial nerve anastomosis and botulinum-toxin injections to optimize mimic rehabilitation after removal of acoustic neurinomas. Plast Reconstr Surg 99(4):1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199704000-00013
Lee JM, Choi KH, Lim BW, Kim MW, Kim J (2015) Half-mirror biofeedback exercise in combination with three botulinum toxin A injections for long-lasting treatment of facial sequelae after facial paralysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 68(1):71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2014.08.067
Mandrini S, Comelli M, Dall’angelo A et al (2016) Long-term facial improvement after repeated BoNT-A injections and mirror biofeedback exercises for chronic facial synkinesis: a case-series study. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 52(6):810–818
Maria CM, Kim J (2017) Individualized management of facial synkinesis based on facial function. Acta Otolaryngol 137(9):1010–1015. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2017.1316871
Mehta RP, Hadlock TA (2008) Botulinum toxin and quality of life in patients with facial paralysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg 10(2):84–87. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfaci.10.2.84
Mountain RE, Murray JAM, Quaba A (1992) Management of facial synkinesis with Clostridium botulinum toxin injection. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 17(3):223–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.1992.tb01831.x
Neville C, Venables V, Aslet M, Nduka C, Kannan R (2017) An objective assessment of botulinum toxin type A injection in the treatment of post-facial palsy synkinesis and hyperkinesis using the synkinesis assessment questionnaire. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 70(11):1624–1628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2017.05.048
Patel PN, Owen SR, Norton CP et al (2018) Outcomes of buccinator treatment with botulinum toxin in facial synkinesis. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 20(3):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2017.1385
Pourmomeny AA, Asadi S, Chitsaz MR (2015) Management of synkinesis with a combination of BTX-A and biofeedback: a randomized trial. Physiotherapy 101(83):e1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physio.2015.03.2157
Risoud M, Aljudaibi N, Duquennoy-Martinot V, Guerreschi P (2016) Long-term sequelae treatment of peripheral facial paralysis with botulinum toxin type A: repartition and kinetics of doses used. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 61(1):10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2015.04.002
Salles AG, Da Costa EF, Ferreira MC, Do Nascimento Remigio AF, Moraes LB, Gemperli R (2015) Epidemiologic overview of synkinesis in 353 patients with longstanding facial paralysis under treatment with botulinum toxin for 11 years. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(6):1289–1298. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001802
Shinn JR, Nwabueze NN, Du L et al (2019) Treatment patterns and outcomes in botulinum therapy for patients with facial synkinesis. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 21(3):244–251. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2018.1962
Vuppala AAD, Griepentrog GJ, Walsh RD (2020) Swallow-induced eyelid myokymia: a novel synkinesis syndrome. Neuro-Ophthalmology 44(2):108–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/01658107.2019.1587637
Wei LA, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ (2016) Treating buccinator with botulinum toxin in patients with facial synkinesis: a previously overlooked target. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 32(2):138–141. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000449
Akulov MA, Orlova OR, Orlova AS et al (2017) Incobotulinumtoxin A treatment of facial nerve palsy after neurosurgery. J Neurol Sci 381:130–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2017.08.3244
Wiener A, Touloei K, Glick BP (2011) A novel long-term therapy of facial synkinesis with botulinum neurotoxins type a and fillers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 4(3):45–49
Wollina U, Goldman A (2017) Botulinumtoxin-A und dermale Gewebefiller in der fazialen Rehabilitation. Wien Med Wochenschr 167(3–4):92–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-016-0512-8
Xiao L, Pan Y, Zhang X et al (2016) Facial asymmetry in patients with hemifacial spasm before and after botulinum toxin A treatment. Neurol Sci 37(11):1807–1813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2670-2
Armstrong MWJ, Mountain RE, Murray JAM (1996) Treatment of facial synkinesis and facial asymmetry with botulinum toxin type A following facial nerve palsy. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 21(1):15–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.1996.tb01018.x
Coban A, Matur Z, Hanagasi H, Parman Y (2014) Efficiency of repeated botulinum toxin type-A injections in post-stroke distal limb spasticity. J Neurol Sci 31:21–27
Boroojerdi B (1998) Botulinum toxin treatment of synkinesia and hyperlacrimation after facial palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65(1):111–114. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.65.1.111
Bran GM, Lohuis PJFM (2014) Selective neurolysis in post-paralytic Facial Nerve Syndrome (PFS). Aesthetic Plast Surg 38(4):742–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0346-y
Cecini M, Pavese C, Toffola ED. Chronic facial synkinesis : a case-series study. 2016.
Choi KH, Rho SH, Lee JM, Jeon JH, Park SY, Kim J (2013) Botulinum toxin injection of both sides of the face to treat post-paralytic facial synkinesis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 66(8):1058–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2013.04.012
House JW, Brackmann DE (1985) Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol neck Surg 93(2):146–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459988509300202
Se C, Croxson G (1995) Assessing physiotherapy rehabilitation outcomes following facial nerve paralysis. Aust J Otolaryngol 2:20–24
Ross BG, Fradet G, Nedzelski JM (1996) Development of a sensitive clinical facial grading system. Otolaryngol neck Surg 114(3):380–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0194-5998(96)70206-1
Banks CA, Jowett N, Azizzadeh B et al (2017) Worldwide testing of the eFACE facial nerve clinician-graded scale. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(2):491e–498e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002954
Coulson SE, Croxson GR, Adams RD, O’Dwyer NJ (2005) Reliability of the “Sydney”, “Sunnybrook”, and “House Brackmann” facial grading systems to assess voluntary movement and synkinesis after facial nerve paralysis. Otolaryngol neck Surg 132(4):543–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2005.01.027
Moran CJ, Neely JG (1996) Patterns of facial nerve synkinesis. Laryngoscope 106(12 Pt 1):1491–1496. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199612000-00009
Oge AE, Yayla V, Demir GA, Eraksoy M (2005) Excitability of facial nucleus and related brain-stem reflexes in hemifacial spasm, post-facial palsy synkinesis and facial myokymia. Clin Neurophysiol 116(7):1542–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2005.02.021
Rijntjes M, Tegenthoff M, Liepert J et al (1997) Cortical reorganization in patients with facial palsy. Ann Neurol 41(5):621–630. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410410511
Wang Y, Wang W-W, Hua X-Y, Liu H-Q, Ding W (2018) Patterns of cortical reorganization in facial synkinesis: a task functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neural Regen Res 13(9):1637–1642. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.235304
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Initial idea: FdJ, SP. Conception and design of the study: FdJ, AS, ZE, KI, NvH, CB, SM and SP. Literature search: FdJ, AS. Drafting and revision manuscript: FdJ, AS, ZE, KI, NvH, CB, SM and SP. Final approval: FdJ, AS, ZE, KI, NvH, CB, SM and SP. Botulinum Toxin A Treatment in Facial Palsy synkinesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Jongh, F.W., Schaeffers, A.W.M.A., Kooreman, Z.E. et al. Botulinum toxin A treatment in facial palsy synkinesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 1581–1592 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07796-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07796-8