Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the medical and the surgical treatment on the olfactory functions, clinical scoring systems and inflammation markers in patients with nasal polyposis. In addition, the secondary aim was to investigate the correlation between those investigated parameters.
Subjects and methods
A total of 30 patients, who completed the standardized medical and surgical treatment and also came to 3 months of follow-ups regularly after the surgery, were included in the study. The Sniffin’ Sticks olfactory tests, radiological and the endoscopic stagings, liver-expressed chemokine (CCL16) and endothelin (ET) levels and sino-nasal outcome test-22 (SNOT-22) were performed at the initial and at the end of the study.
Results
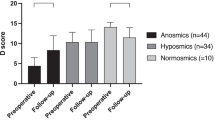
The current study had four major findings: (1) significant improvement in odor functions after treatment was determined; however, the majority of the patients had been already hyposmic. (2) In addition, significant improvement was found in ET and CCL16 levels, SNOT-22 results, and radiologic and endoscopic stagings at the end of the study. (3) However, there was no correlation between the olfactory functions and the investigated parameters. (4) There was a positive correlation between polyp recurrence and ET levels.
Conclusion
The standardized medical and surgical treatment provided a significant improvement in the olfactory functions. However, only one patient (3.3%) had become normosmic at the end of the study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewart M, Ferguson B, Fromer L (2010) Epidemiology and burden of nasal congestion. Int J Gen Med 8(3):37–45
Banglawala SM, Schlosser RJ, Wenztel J, Walsh T, Overton L, Soler ZM (2016) Trends in chronic rhinosinusitis research in the past three decades. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6(1):46–51
Workman AD, Kohanski MA, Cohen NA (2018) Biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 38(4):679–692
Youn BS, Zhang S, Broxmeyer HE, Antol K, Fraser MJ Jr, Hangoc G, Kwon BS (1998) Isolation and characterization of LMC, a novel lymphocyte and monocyte chemoattractant human CC chemokine, with myelosuppressive activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 247(2):217–222
Hedrick JA, Helms A, Vicari A, Zlotnik A (1998) Characterization of a novel CC chemokine, HCC-4, whose expression is increased by interleukin-10. Blood 91(11):4242–4247
Nakayama T, Kato Y, Hieshima K, Nagakubo D, Kunori Y, Fujisawa T, Yoshie O (2004) Liver-expressed chemokine/CC chemokine ligand 16 attracts eosinophils by interacting with histamine H4 receptor. J Immunol 173(3):2078–2083
Galli SJ, Tsai M (2010) Mast cells in allergy and infection: versatile effector and regulatory cells in innate and adaptive immunity. Eur J Immunol 40(7):1843–1851
Tsybikov NN, Egorova EV, Kuznik BI, Fefelova EV, Magen E (2016) Biomarker assessment in chronic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis: endothelin-1, TARC/CCL17, neopterin, and α-defensins. Allergy Asthma Proc 37(1):35–42
Hancı D, Altun H, Sahin E, Altımtoprak N, Cingi C (2015) Turkish translation, cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the SinoNasal Outcome Test (SNOT)-22. ENT Updates 5(2):51–57
Hummel T, Sekinger B, Wolf SR, Pauli E, Kobal G (1997) 'Sniffin' sticks': olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold. Chem Senses. 22(1):39–52
Kobal G, Klimek L, Wolfensberger M, Gudziol H, Temmel A, Owen CM, Seeber H, Pauli E, Hummel T (2000) Multicenter investigation of 1,036 subjects using a standardized method for the assessment of olfactory function combining tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 257(4):205–211
Wolfensberger M, Schnieper I, Welge-Lüssen A (2000) Sniffin'Sticks: a new olfactory test battery. Acta Otolaryngol 120(2):303–306
Hummel T, Kobal G, Gudziol H, Mackay-Sim A (2007) Normative data for the "Sniffin' Sticks" including tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds: an upgrade based on a group of more than 3,000 subjects. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264(3):237–243
Lund VJ, Mackay IS (1993) Staging in rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 31(4):183–184
Rudmik L, Soler ZM, Hopkins C, Schlosser RJ, Peters A, White AA, Orlandi RR, Fokkens WJ, Douglas R, Smith TL (2016) Defining appropriateness criteria for endoscopic sinus surgery during management of uncomplicated adult chronic rhinosinusitis: a RAND/UCLA appropriateness study. Rhinology 54(2):117–128
Deal RT, Kountakis SE (2004) Significance of nasal polyps in chronic rhinosinusitis: symptoms and surgical outcomes. Laryngoscope 114(11):1932–1935
Pearlman AN, Chandra RK, Chang D, Conley DB, Tripathi-Peters A, Grammer LC, Schleimer RT, Kern RC (2009) Relationships between severity of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis, asthma, and atopy. Am J Rhinol Allergy 23(2):145–148
Vento SI, Ertama LO, Hytönen ML, Wolff CH, Malmberg CH (2000) Nasal polyposis: clinical course during 20 years. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 85(3):209–214
Kim DW, Kim JY, Jeon SY (2011) The status of the olfactory cleft may predict postoperative olfactory function in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 25(2):e90–e94
Gupta D, Gulati A, Singh I, Tekur U (2014) Endoscopic, radiological, and symptom correlation of olfactory dysfunction in pre- and postsurgical patients of chronic rhinosinusitis. Chem Senses 39(8):705–710
Jiang RS, Lu FJ, Liang KL, Shiao JY, Su MC, Hsin CH, Chen WK (2008) Olfactory function in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis before and after functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Am J Rhinol 22(4):445–448
Dadgarnia M, Rahmani A, Baradaranfar M, Atighechi S, Zand V, Meybodian M, Mandegari M, Vaziribozorg S (2019) The relationship between endoscopic and radiologic findings and olfactory status of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps before and after the endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(2):397–400
Pade J, Hummel T (2008) Olfactory function following nasal surgery. Laryngoscope 118(7):1260–1264
Kern RC, Conley DB, Haines GK 3rd, Robinson AM (2004) Pathology of the olfactory mucosa: implications for the treatment of olfactory dysfunction. Laryngoscope 114(2):279–285
Litvack JR, Mace J, Smith TL (2009) Does olfactory function improve after endoscopic sinus surgery? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(3):312–319
Hsu CY, Wang YP, Shen PH, Weitzel EK, Lai JT, Wormald PJ (2013) Objective olfactory outcomes after revision endoscopic sinus surgery. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27(4):e96–100
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital Scientific Research Projects Directorate by Project Number 1214/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital E-16-1127/28.12.2016).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paksoy, Z.B., Cayonu, M., Yucel, C. et al. The treatment efficacy of nasal polyposis on olfactory functions, clinical scoring systems and inflammation markers. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 3367–3372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05619-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05619-x