Abstract
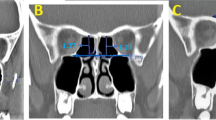
Ethmomaxillary sinus is a variation of the posterior ethmoid cells. It is formed by the extension of the posterior ethmoid cells into the maxillary sinus and drains into superior nasal meatus. It is incidentally seen on paranasal sinus computerized tomography (CT) scans. Its prevalence has been reported as 0.7 and 2% in two studies. In this study, paranasal CT scans of 466 patients were investigated for the presence of ethmomaxillary sinus. The patients had paranasal CT with the preliminary diagnoses of septal deviation, chronic inflammatory paranasal sinus disease and nasal turbinate disorders. The ethmomaxillary sinus was present in nine of those patients (1.93%). It was septated in one of them. The CTs were further investigated for other anatomical variations and co-existent mucosal disease of the paranasal sinuses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolger WE (2001) Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses. In: Kennedy DW, Bolger WE, Zinreich SJ (eds) Diseases of the sinuses. Hamilton B.C Decker, Ontario, pp 1–13
Clemente MP (2005) Surgical anatomy of the paranasal sinus. In: Levine HL, Clemente MP (eds) Sinus surgery: endoscopic and microscopic approaches. Thieme, New York, pp 1–56
Khanobthamchai K, Shankar L, Hawke M, Bingham B (1991) Ethmomaxillary sinus and hypoplasia of maxillary sinus. J Otolaryngol 20(6):425–427
Polavaram R, Devaiah AK, Sakai O, Shapshay SM (2004) Anatomic variants and pearls-functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 37(2):221–242
Sirikci A, Bayazit YA, Bayram M, Kanlikama M (2004) Ethmomaxillary sinus: a particular anatomic variation of the paranasal sinuses. Eur Radiol 14(2):281–285
Sivasli E, Sirikci A, Bayazit YA, Gumusburun E, Erbagci H, Bayram M, Kanlikama M (2003) Anatomic variations of the paranasal sinus area in pediatric patients with chronic sinusitis. Surg Radiol Anat 24(6):400–405
Stammberger H (1991) Functional endoscopic sinus surgery, 1st edn. Mosby Year-Book, St Louis
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozcan, K.M., Selcuk, A., Oruk, V. et al. Ethmomaxillary sinus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265, 185–188 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0444-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0444-4