Abstract
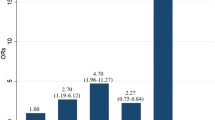
The objective of this study was to delineate whether the presence of the risk factors of microvascular disorder (MD) contribute to the prognostic outcome in patients with idiopathic sudden deafness (ISD). Retrospective clinical record review was conducted with 106 patients of ISD. Pure tone hearing thresholds were compared among the groups with or without hyperglycemia and hypercholesterolemia. Significantly better hearing recoveries were observed in cases with hyperglycemia as compared with controls. There was a tendency that the magnitude of hearing recovery in hypercholesterolemia was greater than that of controls although there was no statistical difference. The presence of the risks in MD could be an indicator of better hearing prognosis of ISD if we choose appropriate treatments. Heterogeneity of the ISD makes the establishment of the relationship between the risk factors of MD and etiology of some cases of ISD. We may have to choose the treatments for ISD considering whether the patient has any risk factor of MD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslan I, Oysu C, Veyseller B et al (2002) Does the addition of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to the conventional treatment modalities influence the outcome of sudden deafness ? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:121–126
Centers for Disease Control, Prevention (CDC) (2005) Trends in cholesterol screening and awareness of high blood cholesterol-United States, 1991–2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 54:865–870
Deramo VA, Sergott RC, Augsburger JJ et al (2003) Ischemic optic neuropathy as the first manifestation of elevated cholesterol levels in young patients. Ophthalmology 110:1041–1046
Erdem T, Ozturan O, Miman MC et al (2003) Exploration of the early auditory effects of hyperlipoproteinemia and diabetes mellitus using otoacoustic emissions. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 260:62–66
Harmel AP (2002) Treating diabetes: cardiovascular benefits of antidiabetes drugs. Am J Manag Care 8 (8 Suppl): S219–S228; quiz S229–S232
Hirano K, Ikeda K, Kawase T et al (1999) Prognosis of sudden deafness with special reference to risk factors of microvascular pathology. Auris Nasus Larynx 26:111–115
Kalaria RN (2002) Small vessel disease and Alzheimer’s dementia: pathological considerations. Cerebrovasc Dis 13(Suppl 2):48–52
Kanzaki J, Inoue Y, Ogawa K et al (2003) Effect of single-drug treatment on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 30(2):123–127
Kendall DM, Bergenstal RM (2001) Comprehensive management of patients with type2 diabetes: establishing priorities of care. Am J Manag Care 7(Suppl 10):S327–S343
Kronenberg J, Almagor M, Bendet E et al (1992) Vasoactive therapy versus placebo in the treatment of sudden hearing loss: a double-blind clinical study. Laryngoscope 102:65–68
Kubo T, Matsunaga T, Asai H, et al (1988) Efficacy of defibrinogenation and steroid therapies on sudden deafness. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 114:649–652
Nomura Y (1988) Diagnostic criteria for sudden deafness, mumps deafness and perilymphatic fistula. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) Suppl 456:7–8
Robert WV, William RW, Philip MS et al (1981) The implication of viruses in idiopathic sudden hearing loss: primary infection or reactivation of latent viruses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 89:137–141
Rust KR, Triana RJ, Michaelis IV OE et al (1992) Inner ear damage secondary to diabetes mellitus. II. Changes in aging SHR/N-cp Rats. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:397–400
Schweinfurth JM, Cacace AT (2000) Cochlear ischemia induced by circulating iron particles under magnetic control: an animal model for sudden hearing loss. Am J Otol 21:636–640
Snow V, Aronson MD, Hornbake ER et al (2004) Lipid control in the management of type2 diabetes mellitus: a clinical practice guideline from the American college of physicians. Ann Intern Med 140:644–649
Suzuki K, Kaneko M, Murai K (2000) Influence of serum lipids on auditory function. Laryngoscope 110:1736–1739
Vinters HV, Ellis WG, Zarrow C et al (2000) Neuropathologic substrates of ischemic vascular dementia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:931–945
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N (1980) The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Arch Otolaryngol 106:772–776
Glucose tolerance, mortality: comparison of WHO and American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria. The DECODE study group. European Diabetes Epidemiology Group (1999) Diabetes epidemiology: collaborative analysis of diagnostic criteria in Europe. Lancet 354:617–621
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orita, S., Fukushima, K., Orita, Y. et al. Sudden hearing impairment combined with diabetes mellitus or hyperlipidemia. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264, 359–362 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0196-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0196-6