Abstract
Introduction
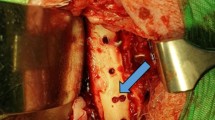
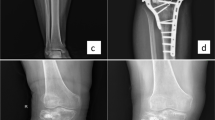
Infection after internal fixation surgery is an orthopedic serious complication which affect the fracture healing. The primary objective of this study was to verify the effects of a Peptide Mel4-coated titanium plate applied in the treatment of infection after internal fixation of open fracture.
Materials and methods
Eighty-eight rabbits were intravenously inoculated with Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa suspensions. Bacterial cultures were obtained from titanium plates at 1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th and 9th days. Blood samples were collected at 1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th and 9th days after the infection.
Results
Mel4-coated titanium plates have significant inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P < 0.05), and there are significant differences in serum IL-1 and TNF-α levels (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
We suggest that the use of Mel4-coated titanium plates may be a promising way to control postoperative infection of open fracture in vivo.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zalavras CG, Patzakis MJ, Holtom P (2004) Local antibiotic therapy in the treatment of open fractures and osteomyelitis. ClinOrthopRelat Res 427:86–93
Tribble DR, Lewandowski LR, Potter BK, Petfield JL, Stinner DJ, Ganesan A, Krauss M, Murray CK and Trauma Infectious Disease Outcomes Study G (2018) Osteomyelitis risk factors related to combat trauma open tibia fractures: a case-control analysis. J Orthop Trauma 32(9):e344
Ikem ICF, Oginni LM, Bamgboye EA, Ako-Nai AK, Onipade AO (2004) The bacteriology of open fractures in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Niger J Med 13(4):359–365
Gupta P, Vishwakarma AK, Gupta DK, Agarwal S, Singh N (2017) Comparative evaluation of results after internal fixation of fracture clavicle by titanium elastic nailing system/plate. J Bone Join Dis 32(2):10–16
Doshi P, Gopalan H, Sprague S, Pradhan C, Kulkarni S, Bhandari M (2017) Incidence of infection following internal fixation of open and closed tibia fractures in India (INFINITI): a multi-centre observational cohort study. BMC MusculoskeletDisord 18(1):156
Papakostidis C, Kanakaris NK, Pretel J, Faour O, Giannoudis PV (2011) Prevalence of complications of open tibial shaft fractures stratified as per the Gustilo-Anderson classification. Injury 42(12):1408–1415
Lyndon JA, Boyd BJ, Birbilis N (2014) Metallic implant drug/device combinations for controlled drug release in orthopaedic applications. J Control Release 179:63–75
Marr AK, Gooderham WJ, Hancock REW (2006) Antibacterial peptides for therapeutic use: obstacles and realistic outlook. CurrOpinPharmacol 6(5):468–472
Dutta D, Zhao T, Cheah KB, Holmlund L and Willcox MDP (2017) Activity of a melimine derived peptide Mel4 against Stenotrophomonas, Delftia, Elizabethkingia, Burkholderia and biocompatibility as a contact lens coating. Cont Lens Anterior Eye S1367048416301163
Yasir M, Dutta D, Willcox MDP (2019a) Comparative mode of action of the antimicrobial peptide melimine and its derivative Mel4 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 9(1):7063
Hochuli-Vieira E, Gabrielli MAC, Pereira-Filho VA, Gabrielli MFR, Padilha JG (2005) Rigid internal fixation with titanium versus bioresorbableminiplates in the repair of mandibular fractures in rabbits. Int J Oral MaxillofacSurg 34(2):167–173
Portol SM, Austin F, Nos-Barber S, Paterson C, Refojo MF (1995) Effect of poloxamer 407 on the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to corneal epithelial cells. Cornea 14(1):56–61
Zhang H, Wang J, Liu Z, Yang S, Ding S, Gu X (2019) Application of GGCX combined with inflammatory factors IL-1 and TNF-α in the evaluation of knee osteoarthritis. J Biomater Tissue Eng 9(1):134–138
Nigam A, Gupta D, Sharma A (2014) Treatment of infectious disease: beyond antibiotics. Microbiol Res 169(9–10):643–651
Nseir S, Di Pompeo C, Soubrier S, Delour P, Lenci H, Roussel-Delvallez M, Onimus T, Saulnier F, Mathieu D, Durocher A (2005) First-generation fluoroquinolone use and subsequent emergence of multiple drug-resistant bacteria in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 33(2):283–289
Yi L, Dang J, Zhang L, Wu Y, Liu B, Lü X (2016) Purification, characterization and bactericidal mechanism of a broad spectrum bacteriocin with antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant strains produced by Lactobacillus coryniformis XN8. Food Control 67:53–62
Pompilio A, Scocchi M, Pomponio S, Guida F, Primio AD, Fiscarelli E, Gennaro R, Bonaventura GD (2011) Antibacterial and anti-biofilm effects of cathelicidin peptides against pathogens isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. Peptides 32(9):1807–1814
Srour M, Inaba K, Okoye O, Chan C, Skiada D, Schnüriger B, Trump M, Lam L, Demetriades D (2015) Prospective evaluation of treatment of open fractures: effect of time to irrigation and debridement. JAMA Surg 150(4):332–336
Singh J, Rambani R, Hashim Z, Raman R, Sharma HK (2012) The relationship between time to surgical debridement and incidence of infection in grade III open fractures. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 7(1):33–37
Brook I, Frazier EH (1998) Aerobic and anaerobic microbiology of infection after trauma. Am J Emerg Med 16(6):585–591
Kojouharoff G, Hans W, Obermeier F, Mannel DN, Andus T, Scholmerich J, Gross V, Falk W (1997) Neutralization of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) but not of IL-1 reduces inflammation in chronic dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis in mice. ClinExpImmunol 107(2):353–358
Yasir M, Dutta D, Willcox MDP (2019b) Mode of action of the antimicrobial peptide Mel4 is independent of Staphylococcus aureus cell membrane permeability. PLoS ONE 14(7):e0215703
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundations of China (81702179) and Funding from Young Talent Development Plan of Changzhou Health Commission (CZQM2020059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhou, X., Liu, T. et al. The effects of Peptide Mel4-coated titanium plates on infection rabbits after internal fixation of open fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 142, 729–734 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03694-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03694-y