Abstract
Background
This study evaluated the incidence, amount, morphology and clinical significance of bone tunnel widening (TW) at a mean 5-year period after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) with a transtibial drilling technique.
Methods
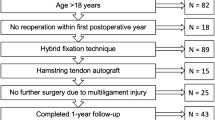
Fifty-nine patients undergoing primary ACLR using quadrupled hamstring autografts, biodegradable transfemoral pins for femoral-sided and 2-mm oversized interference screws for tibial-sided graft fixation were followed up at a mean 61 months postoperatively. Patients were examined clinically and by MRI. Tunnel cross-sectional areas (CSA) were related to drill diameters, which were significantly correlated with radiographic tunnel sizes. Tunnel morphologies were assessed and their positions determined using an anatomical coordinate system.
Results
CSA had more than doubled in all segments measured (p < 0.0001) except at the femoral notch level. Greatest CSA increases were found at the femoral graft suspension point (122 %) and at the central tibial tunnel segment (134 %). 54 (92) and 56 (95 %) patients had significant TW, i.e., CSA increase of more than 50 %, in at least one tunnel segment femorally and tibially. Four different tunnel morphologies were observed, of which the linear type was most often encountered on either side. Mean side-to-side difference in anterior-posterior laxity was 1.0 ± 1.4 mm, while Lysholm, IKDC and Tegner acitivity scores were 90 ± 12, 84 ± 15 and 4 (1–9); clinical outcomes were not found to be correlated with tunnel sizes and morphologies as were tunnel positions and tunnel sizes.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that considerable TW occurs in virtually all patients in the mid term after ACLR using a transtibial drilling technique with ‘high’ femoral tunnel positions. Yet, neither amount nor morphology or tunnel position does affect knee stability or function.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad CS, Gardner TR, Groh M, Arnouk J, Levine WN (2004) Mechanical properties of soft tissue femoral fixation devices for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med 32(3):635–640
Arnold MP, Kooloos J, van Kampen A (2001) Single-incision technique misses the anatomical femoral anterior cruciate ligament insertion: a cadaver study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9(4):194–199
Asik M, Sen C, Tuncay I, Erdil M, Avci C, Taser OF (2007) The mid- to long-term results of the anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with hamstring tendons using Transfix technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15(8):965–972
Barber FA, Dockery WD (2006) Long-term absorption of poly-l-lactic Acid interference screws. Arthroscopy 22(8):820–826
Baumfeld JA, Diduch DR, Rubino LJ et al (2008) Tunnel widening following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using hamstring autograft: a comparison between double cross-pin and suspensory graft fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16(12):1108–1113
Becker R, Voigt D, Starke C, Heymann M, Wilson GA, Nebelung W (2001) Biomechanical properties of quadruple tendon and patellar tendon femoral fixation techniques. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9(6):337–342
Brand JC Jr, Pienkowski D, Steenlage E, Hamilton D, Johnson DL, Caborn DN (2000) Interference screw fixation strength of a quadrupled hamstring tendon graft is directly related to bone mineral density and insertion torque. Am J Sports Med 28(5):705–710
Buck DC, Simonian PT, Larson RV, Borrow J, Nathanson DA (2004) Timeline of tibial tunnel expansion after single-incision hamstring anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy 20(1):34–36
Buelow JU, Siebold R, Ellermann A (2002) A prospective evaluation of tunnel enlargement in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with hamstrings: extracortical versus anatomical fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 10(2):80–85
Chhabra A, Kline AJ, Nilles KM, Harner CD (2006) Tunnel expansion after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autogenous hamstrings: a comparison of the medial portal and transtibial techniques. Arthroscopy 22(10):1107–1112
Clatworthy MG, Annear P, Bulow JU, Bartlett RJ (1999) Tunnel widening in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective evaluation of hamstring and patella tendon grafts. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 7(3):138–145
Cossey AJ, Kalairajah Y, Morcom R, Spriggins AJ (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of biodegradable transfemoral fixation used in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy 22(2):199–204
Fauno P, Kaalund S (2005) Tunnel widening after hamstring anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is influenced by the type of graft fixation used: a prospective randomized study. Arthroscopy 21(11):1337–1341
Fink C, Zapp M, Benedetto KP, Hackl W, Hoser C, Rieger M (2001) Tibial tunnel enlargement following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with patellar tendon autograft. Arthroscopy 17(2):138–143
Fules PJ, Madhav RT, Goddard RK, Newman-Sanders A, Mowbray MA (2003) Evaluation of tibial bone tunnel enlargement using MRI scan cross-sectional area measurement after autologous hamstring tendon ACL replacement. Knee 10(1):87–91
Galla M, Uffmann J, Lobenhoffer P (2004) Femoral fixation of hamstring tendon autografts using the TransFix device with additional bone grafting in an anteromedial portal technique. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124(4):281–284
Gavriilidis I, Motsis EK, Pakos EE, Georgoulis AD, Mitsionis G, Xenakis TA (2008) Transtibial versus anteromedial portal of the femoral tunnel in ACL reconstruction: a cadaveric study. Knee 15(5):364–367
Getelman MH, Friedman MJ (1999) Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 7(3):189–198
Giron F, Aglietti P, Cuomo P, Mondanelli N, Ciardullo A (2005) Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with double-looped semitendinosus and gracilis tendon graft directly fixed to cortical bone: 5-year results. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(2):81–91
Gougoulias N, Khanna A, Griffiths D, Maffulli N (2008) ACL reconstruction: can the transtibial technique achieve optimal tunnel positioning? A radiographic study. Knee 15(6):486–490
Grossman MG, ElAttrache NS, Shields CL, Glousman RE (2005) Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: three- to nine-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 21(4):418–423
Hantes ME, Dailiana Z, Zachos VC, Varitimidis SE (2006) Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using the Bio-TransFix femoral fixation device and anteromedial portal technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14(5):497–501
Hantes ME, Mastrokalos DS, Yu J, Paessler HH (2004) The effect of early motion on tibial tunnel widening after anterior cruciate ligament replacement using hamstring tendon grafts. Arthroscopy 20(6):572–580
Heming JF, Rand J, Steiner ME (2007) Anatomical limitations of transtibial drilling in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med 35(10):1708–1715
Iorio R, Vadala A, Argento G, Di Sanzo V, Ferretti A (2007) Bone tunnel enlargement after ACL reconstruction using autologous hamstring tendons: a CT study. Int Orthop 31(1):49–55
Irrgang JJ, Ho H, Harner CD, Fu FH (1998) Use of the International Knee Documentation Committee guidelines to assess outcome following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 6(2):107–114
Kaseta MK, DeFrate LE, Charnock BL, Sullivan RT, Garrett WE Jr (2008) Reconstruction technique affects femoral tunnel placement in ACL reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(6):1467–1474
Klein JP, Lintner DM, Downs D, Vavrenka K (2003) The incidence and significance of femoral tunnel widening after quadrupled hamstring anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using femoral cross pin fixation. Arthroscopy 19(5):470–476
Kopf S, Forsythe B, Wong AK et al (2010) Nonanatomic tunnel position in traditional transtibial single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction evaluated by three-dimensional computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(6):1427–1431
Kopf S, Schenkengel JP, Wieners G, Starke C, Becker R (2010) No bone tunnel enlargement in patients with open growth plates after transphyseal ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18(11):1445–1451
Kousa P, Jarvinen TL, Vihavainen M, Kannus P, Jarvinen M (2003) The fixation strength of six hamstring tendon graft fixation devices in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Part I: femoral site. Am J Sports Med 31(2):174–181
Lajtai G, Schmiedhuber G, Unger F et al (2001) Bone tunnel remodeling at the site of biodegradable interference screws used for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: 5-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 17(6):597–602
Lysholm J, Gillquist J (1982) Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale. Am J Sports Med 10(3):150–154
Ma CB, Francis K, Towers J, Irrgang J, Fu FH, Harner CH (2004) Hamstring anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a comparison of bioabsorbable interference screw and endobutton-post fixation. Arthroscopy 20(2):122–128
Marchant MH Jr, Willimon SC, Vinson E, Pietrobon R, Garrett WE, Higgins LD (2009) Comparison of plain radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of bone tunnel widening after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18(8):1059–1064
Marti C, Imhoff AB, Bahrs C, Romero J (1997) Metallic versus bioabsorbable interference screw for fixation of bone-patellar tendon-bone autograft in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. A preliminary report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 5(4):217–221
Matsumoto A, Howell SM, Liu-Barba D (2006) Time-related changes in the cross-sectional area of the tibial tunnel after compaction of an autograft bone dowel alongside a hamstring graft. Arthroscopy 22(8):855–860
Milano G, Mulas PD, Ziranu F, Piras S, Manunta A, Fabbriciani C (2006) Comparison between different femoral fixation devices for ACL reconstruction with doubled hamstring tendon graft: a biomechanical analysis. Arthroscopy 22(6):660–668
Nebelung W, Becker R, Merkel M, Ropke M (1998) Bone tunnel enlargement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with semitendinosus tendon using endobutton fixation on the femoral side. Arthroscopy 14(8):810–815
Orrego M, Larrain C, Rosales J et al (2008) Effects of platelet concentrate and a bone plug on the healing of hamstring tendons in a bone tunnel. Arthroscopy 24(12):1373–1380
Peyrache MD, Djian P, Christel P, Witvoet J (1996) Tibial tunnel enlargement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by autogenous bone-patellar tendon-bone graft. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 4(1):2–8
Siebold R (2007) Observations on bone tunnel enlargement after double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy 23(3):291–298
Stener S, Ejerhed L, Sernert N, Laxdal G, Rostgard-Christensen L, Kartus J (2010) A long-term, prospective, randomized study comparing biodegradable and metal interference screws in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: radiographic results and clinical outcome. Am J Sports Med 38(8):1598–1605
Tegner Y, Lysholm J, Lysholm M, Gillquist J (1986) A performance test to monitor rehabilitation and evaluate anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med 14(2):156–159
Weiler A, Hoffmann RF, Siepe CJ, Kolbeck SF, Sudkamp NP (2000) The influence of screw geometry on hamstring tendon interference fit fixation. Am J Sports Med 28(3):356–359
Wilson TC, Kantaras A, Atay A, Johnson DL (2004) Tunnel enlargement after anterior cruciate ligament surgery. Am J Sports Med 32(2):543–549
Wright RW, Dunn WR, Amendola A et al (2007) Risk of tearing the intact anterior cruciate ligament in the contralateral knee and rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament graft during the first 2 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective MOON cohort study. Am J Sports Med 35(7):1131–1134
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nebelung, S., Deitmer, G., Gebing, R. et al. High incidence of tunnel widening after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with transtibial femoral tunnel placement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132, 1653–1663 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1596-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1596-2