Abstract
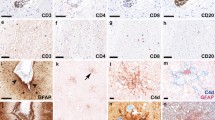
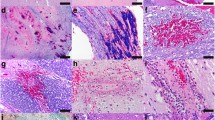
Chronic encephalitis has been recognized as a cause of epilepsy since the work of Rasmussen et al. in the late 1950s. Despite this, few immunohistochemical studies of the affected brain tissue have been attempted. We have studied specimens of brain tissue from seven patients with this condition who underwent therapeutic multilobar cortical resection or hemispherectomy. Immunohistochemical studies were carried out using antibodies to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA, PC10), T lymphocytes (UCHL-1), B lymphocytes (L26), macrophages and microglia (HAM-56), and major histocompatibility complex molecules (LN3 and β2microglobulin). Additionally, the results of preliminary immunohistochemical and ultrastructural investigation of possible immune complex deposition in blood vessel walls of affected brain tissue are presented. The pattern of GFAP immunoreactivity suggested a patchy and/or laminar disease process in most patients. GFAP immunoreactive cells were especially prominent around microvessels in some cases, suggesting an abnormality of the blood-brain barrier. Both microglial nodules and perivascular collections of inflammatory cells, seen to a variable extent in all cases, contained abundant cells immunolabelled with UCHL-1, LN3 and β2microglobulin. L26-labelled B lymphocytes were extremely sparse. Anti-PCNA frequently labelled microvascular endothelial cells, rare pericytes and occasional cells with microglial/macrophage morphology. The data suggest that chronic encephalitis found in patients with epilepsy results from patchy but widespread parenchymal brain injury, in the course of which cells of both microglial and lymphocyte series accumulate or proliferate within brain. Despite the lack of clear evidence of a causal viral pathogen from other studies, the predominant T cell lymphocytic infiltrate is consistent with a viral cause for this disorder. However, autoimmune factors (possibly triggered by viral infection) may contribute to the extensive neuropathological abnormalities. Very preliminary results using anti-IgG immunocytochemistry showed that in Rasmussen's encephalitis brain there was scattered labelling of neuronal cell bodies and some microvessels. Ultrastructural examination of brain tissue from one patient also showed unusual electron-dense material in microvascular endothelial basement membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achim CL, Wiley CA (1992) Expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens in the brains of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51:257–263
Achim CL, Morey MK, Wiley CA (1991) Expression of major histocompatibility complex and HIV antigens within the brains of AIDS patients. AIDS 5:535–541
Aguilar MJ, Rasmussen T (1960) Role of encephalitis in pathogenesis of epilepsy. Arch Neurol 2:663–676
Alexander EL, Lijewski JE, Jerdan MS, Alexander GE (1986) Evidence of an immunopathogenic basis for central nervous system disease in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 29:122301231
Andermann F (1992) Epilepsia partialis continua and other seizures arising from the precentral gyrus: high incidence in patients with Rasmussen syndrome and neuronal migration disorders. Brain Dev 14:338–339
Andrews JM, Thompson JA, Pysher TJ, Walker ML, Hammond ME (1990) Chronic encephalitis, epilepsy, and cerebrovascular immune complex deposits. Ann Neurol 28:88–90
Beilke MA, In DR, Hamilton R, et al (1991) HLA-DR expression in macaque neuroendothelial cells in vitro and during SIV encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol 33:129–143
Booss J, Dann PR, Griffith BP, Kim JH (1989) Host defense response to cytomegalovirus in the central nervous system. Predominance of the monocyte. Am J Pathol 134:71–78
Booss J, Winkler SR, Griffith BP, Kim JH (1989) Viremia and glial nodule encephalitis after experimental systemic cytomegalovirus infection. Lab Invest 61:644–649
Booss J, Dann PR, Winkler SR, Griffith BP, Kim JH (1990) Mechanisms of injury to the central nervous system following experimental cytomegalovirus infection. Am J Otolaryngol 11: 313–317
Curless RG, Scott GB, Post MJ, Gregorios JP (1987) Progressive cytomegalovirus encephalopathy following congenital infection in an infant with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Child's Nerv Syst 3:255–257
DeRosa MJ, Farrell MA, Burke MM, Secor DL, Vinters HV (1992) An assessment of the proliferative potential of ‘balloon cells’ in focal cortical resections performed for childhood epilepsy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18:566–574
DeRosa MJ, Secor DL, Barsom M, Fisher RS, Vinters HV (1992) Neuropathologic findings in surgically treated hemimegalencephaly: immunohistochemical, morphometric, and ultrastructural study. Acta Neuropathol 84:250–260
Dowd CF, Dillon WF, Barbaro NM, Laxer KD (1992) Intractable complex partial seizure: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging with pathology and electroencephalography. Epilepsy Res [Suppl] 5:101–110
Farrell MA, Cheng L, Cornford ME, Grody WW, Vinters HV (1991) Cytomegalovirus and Rasmussen's encephalitis. Lancet 337:1551–1552
Farrell MA, DeRosa MJ, Curran JG, Secor DL, Cornford ME, Comair YG, Peacock WJ, Shields WD, Vinters HV (1992) Neuropathologic findings in cortical resections (including hemispherectomies) performed for the treatment of intractable childhood epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol 83:246–259
Friedman H, Ch'ien L, Parham D (1977) Virus in brain of child with hemiplegia, hemiconvulsions, and epilepsy. Lancet II:666
Gordon N (1992) Chronic progresive epilepsia partialis continua of childhood: Rasmussen syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:182–185
Gown AM, Tsukada T, Ross R (1986) Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol 125:191–207
Graham DI (1992) “Hypoxia and vascular disorders”. In: Adams JH, Duchen L (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 153–268
Gray F, Serdaru M, Baron H, Daumas-Duport C, Loron P, Sauron B, Poirier J (1987) Chronic localised encephalitis (Rasmussen's) in an adult with epilepsia partialis continua. J Neurol Neursurg Psychiatry 50:747–751
Gupta PC, Roy S, Tandon PN (1974) Progressive epilepsy due to chronic persistent encephalitis. Report of four cases. J Neurol Sci 22:105–120
Gupta PC, Rapin I, Houroupian DS, Roy S, Llena JF, Tandon PN (1984) Smoldering encephalitis in children. Neuropaediatrics 15:191–197
Hayes GM, Woodroofe MN, Cuzner ML (1987) Microglia are the major cell type expressing MCH class II in human white matter. J Neurol Sci 80:25–37
Honavar M, Janota I, Polkey CE (1992) Rasmussen's encephalitis in surgery for epilepsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:3–14
Hulette CM, Downey BT, Burger PC (1992) Macrophage markers in diagnostic neuropathology. Am J Surg Pathol 16:493–499
Hunter EE (1984) Practical electron microscopy. A beginner's illustrated guide. Praeger, New York, p 121
Juul-Jensen P, Denny-Brown D (1966) Epilepsia partialis continua. A clinical, electroencephalographic, and neuropathological study of nine cases. Arch Neurol 15:563–578
Lower J, Maclennan KA, Power DG, Pound JD, Palmer JB (1989) Microglial cells in human brain have phenotypic characteristics related to possible function as dendritic antigen presenting cells. J Pathol 159:143–149
McCormick D, Hall PA (1992) The complexities of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Histopathology 21:591–594
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, McGeer EG (1988) Expression of histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR in neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol 76:550–557
McLachlan RS, Girvin JP, Blume WT, Reichman H (1993) Rasmussen's chronic encephalitis in adults. Arch Neurol 50: 269–274
Modlin JF, Dagan R, Berlin LE, Virshup DM, Yolken RH, Menegus M (1991) Focal encephalitis with enterovirus infections. Pediatrics 88:841–845
Oguni H, Andermann F, Rasmussen TB (1992) The syndrome of chronic encephalitis and epilepsy. A study based on the MNI series of 48 cases. Adv Neurol 57:419–433
Pardridge WM, Yang J, Buciak J, Tourtellotte WW (1989) Human brain microvascular DR-antigen. J Neurosci Res 23:337–341
Piatt JH, Hwang PA, Armstrong DC, Becker LE, Hoffman HJ (1988) Chronic focal encephalitis (Rasmussen syndrome): six cases. Epilepsia 29:268–279
Pober JS, Cotran RS (1991) Immunologic interactions of T lymphocytes with vascular endothelium. Adv Immunol 50:261–302
Power C, Poland SD, Blume WT, Girvin JP, Rice GPA (1990) Cytomegalovirus and Rasmussen's encephalitis. Lancet 336: 1282–1284
Rasmussen T (1978) Further observations on the syndrome of chronic encephalitis and epilepsy. Appl Neurophysiol 41:1–12
Rasmussen T, Andermann F (1989) Update on the syndrome of “chronic encephalitis” and epilepsy. Cleveland Clin J Med 56 [Suppl 2]:S181–184
Rasmussen T, Olszewski J, Lloyd-Smith D (1958) Focal seizures due to chronic localized encephalitis. Neurology 8:435–445
Riikonen R (1978) Cytomegalovirus infection and infantile spasms. Dev Med Child Neurol 20:570–579
Robitaille Y (1991) Neuropathologic aspects of chronic encephalitis. In: Andermann F (ed) Chronic encephalitis and epilepsy — Rasmussen's syndrome. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 79–110
Rogers SW, Andrews PI, Gahring LC, Whisenand T, Cauley K, Crain B, Hughes TE, Heinemann SF, McNamara JO (1994) Autoantibodies to glutamate receptor GluR3 in Rasmussen's encephalitis. Science 265:648–651
Sasaki A, Nakanishi Y, Nakazato Y, Yamaguchi H (1991) Application of lectin and B lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies for the demonstration of human microglia in formalinfixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue. Virchows Arch [A] 419: 291–299
Sobel RA, Ames MB (1988) Major histocompatibility complex molecule expression in the human central nervous system: immunohistochemical analysis of 40 patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:19–28
Sobel RA, Mitchell ME, Fondren G (1990) Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM01) in cellular immune reactions in the human central nervous system. Am J Pathol 136:1309–1316
Springer TA (1990) Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 346:425–434
Stewart PA, Hayakawa K, Akers M-A, Vinters HV (1992) A morphometric study of the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease. Lab Invest 67:734–742
Tien RD, Ashdown BC, Lewis DV Jr, Atkins MR, Burger PC (1992) Rasmussen's encephalitis: neuroimaging findings in four patients. AJR 158:1329–1332
Vickers JC, Huntley GW, Edwards AM, Moran T, Rogers SW, Heinemann SF, Morrison JH (1993) Quantitative localization of AMPA/kainate glutamate receptor subunity immunoreactivity in neurochemically identified subpopulations of neurons in the prefrontal cortex of the macaque monkey. J Neurosci 13: 2982–2992
Vinters HV, Armstrong DL, Babb TL, Daumas-Duport C, Rotitaille Y, Bruton CJ, Farrell MA (1993) The neuropathology of human symptomatic epilepsy. In: Engel J Jr (ed) Surgical treatment of the epilepsies, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 593–608
Vinters HV, Wang B, Wiley CA (1993) Herpes viruses in chronic encephalitis associated with intractable childhood epilepsy. Hum Pathol 24:871–879
Walter GF, Renella RR (1989) Epstein-Barr virus in brain and Rasmussen's encephalitis. Lancet I:279–280
Walter GF, Renella RR, Hori A, Wirnsberger G (1989) Nachweis von Epstein-Barr-Viren bei Rasmussen's enzephalitis. Nervenarzt 60:168–170
Zupanc ML, Handler EG, Levine RL, Jahn TW, ZuRhein GM, Rozental JM, Nickles RJ, Partington CR (1990) Rasmussen encephalitis: Epilepsia partialis continua secondary to chronic encephalitis. Pediatr Neurol 6:397–401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrell, M.A., Droogan, O., Secor, D.L. et al. Chronic encephalitis associated with epilepsy: immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Acta Neuropathol 89, 313–321 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309624
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309624