Abstract
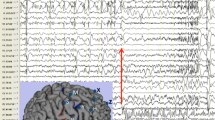
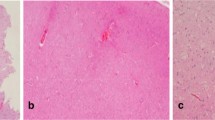
Focal Cortical Dysplasias (FCDs) are highly epileptogenic brain lesions and are a frequent cause for drug-resistant focal epilepsies in humans. FCDs present with variable histopathological patterns, including architectural, cytoarchitectural or white matter abnormalities. Pathomechanisms compromising neuroblast proliferation, migration, or differentiation are likely to play a role in the etiology of FCD variants. FCDs were subsumed, therefore, into the broad spectrum of malformations of cortical development. The most frequent subtype comprises FCD Type II, which in general occurs as isolated lesion in extratemporal location and is histopathologically characterized by dysmorphic neurons (Type IIA) and balloon cells (Type IIB). Neuroimaging hallmarks include hyperintense T2-signaling and a “transmantle sign”. Electrophysiological recordings show peculiar interictal spike patterns and complete surgical resection results in favorable seizure control. In contrast, FCD Type I can be identified in young children with severe epilepsy and psychomotor retardation. Parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes may be involved in seizure generation, although neuroimaging often reveals normal contrast intensities. Surgical resection strategies ameliorate seizure frequencies in many children, whereas complete seizure relief can be achieved only in rare cases. According to the currently used FCD classification system, the same histopathological FCD Type I variant can be diagnosed as associated lesion in the large cohort of epilepsy patients with hippocampal sclerosis, low-grade glio-neuronal tumors, vascular malformations, or glial scarring. MRI is often not helpful to detect the dysplastic cortical areas. In addition, there is no specific electrophysiological pattern for an associated dysplastic lesion. Surgical resection of the epileptogenic area results, however, in favorable seizure control. These findings argue for a revised neuropathological classification system that distinguishes isolated versus associated FCD variants to obtain a better correlation with electro-clinical findings and prediction of postsurgical seizure control.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres M, Andre VM, Nguyen S, Salamon N, Cepeda C, Levine MS, Leite JP, Neder L, Vinters HV, Mathern GW (2005) Human cortical dysplasia and epilepsy: an ontogenetic hypothesis based on volumetric MRI and NeuN neuronal density and size measurements. Cereb Cortex 15:194–210
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2005) A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology 65:1873–1887
Battaglia G, Becker AJ, Loturco J, Represa A, Baraban SC, Roper SN, Vezzani A (2009) Basic mechanisms of MCD in animal models. Epileptic Disord 11:206–214
Baybis M, Yu J, Lee A, Golden JA, Weiner H, McKhann G 2nd, Aronica E, Crino PB (2004) mTOR cascade activation distinguishes tubers from focal cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 56:478–487
Becker AJ, Urbach H, Scheffler B, Baden T, Normann S, Lahl R, Pannek HW, Tuxhorn I, Elger CE, Schramm J, Wiestler OD, Blumcke I (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia of Taylor’s balloon cell type: mutational analysis of the TSC1 gene indicates a pathogenic relationship to tuberous sclerosis. Ann Neurol 52:29–37
Blumcke I, Pieper T, Pauli E, Hildebrandt M, Kudernatsch M, Winkler P, Karlmeier A, Holthausen H (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging and neuropathological examination characterize a distinct variant of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type I in children with severe epilepsies. Epileptic Disord 12(3):1–9
Blumcke I, Vinters HV, Armstrong D, Aronica E, Thom M, Spreafico R (2009) Malformations of cortical development and epilepsies. Epileptic Disord 11:181–193
Chamberlain WA, Cohen ML, Gyure KA, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Perry A, Powell SZ, Qian J, Staugaitis SM, Prayson RA (2009) Interobserver and intraobserver reproducibility in focal cortical dysplasia (malformations of cortical development). Epilepsia 50:2593–2598
Chio A, Spreafico R, Avanzini G, Ghiglione P, Vercellino M, Mutani R (2003) Cesare Lombroso, cortical dysplasia, and epilepsy: keen findings and odd theories. Neurology 61:1412–1416
Colombo N, Salamon N, Raybaud C, Ozkara C, Barkovich AJ (2009) Imaging of malformations of cortical development. Epileptic Disord 11:194–205
Crino PB (2007) Focal brain malformations: a spectrum of disorders along the mTOR cascade. Novartis Found Symp 288:260–272 discussion 272-281
Crome L (1957) Infantile cerebral gliosis with giant nerve cells. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 20:117–124
Eriksson SH, Malmgren K, Nordborg C (2005) Microdysgenesis in epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand 111:279–290
Guerrini R, Dobyns WB, Barkovich AJ (2008) Abnormal development of the human cerebral cortex: genetics, functional consequences and treatment options. Trends Neurosci 31:154–162
Hart YM, Andermann F, Robitaille Y, Laxer KD, Rasmussen T, Davis R (1998) Double pathology in Rasmussen’s syndrome: a window on the etiology? Neurology 50:731–735
Hildebrandt M, Pieper T, Winkler P, Kolodziejczyk D, Holthausen H, Blumcke I (2005) Neuropathological spectrum of cortical dysplasia in children with severe focal epilepsies. Acta Neuropathol 110:1–11
Kremer S, De Saint Martin A, Minotti L, Grand S, Benabid AL, Pasquier B, Kahane P (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia possibly related to a probable prenatal ischemic injury. J Neuroradiol 29:200–203
Krsek P, Pieper T, Karlmeier A, Hildebrandt M, Kolodziejczyk D, Winkler P, Pauli E, Blumcke I, Holthausen H (2009) Different presurgical characteristics and seizure outcomes in children with focal cortical dysplasia type I or II. Epilepsia 50:125–137
Lerner JT, Salamon N, Hauptman JS, Velasco TR, Hemb M, Wu JY, Sankar R, Donald Shields W, Engel J Jr, Fried I, Cepeda C, Andre VM, Levine MS, Miyata H, Yong WH, Vinters HV, Mathern GW (2009) Assessment and surgical outcomes for mild type I and severe type II cortical dysplasia: a critical review and the UCLA experience. Epilepsia 50:1310–1335
Ljungberg MC, Bhattacharjee MB, Lu Y, Armstrong DL, Yoshor D, Swann JW, Sheldon M, D’Arcangelo G (2006) Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin in cytomegalic neurons of human cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 60:420–429
Marin-Padilla M, Parisi JE, Armstrong DL, Sargent SK, Kaplan JA (2002) Shaken infant syndrome: developmental neuropathology, progressive cortical dysplasia, and epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 103:321–332
Marusic P, Tomasek M, Krsek P, Krijtova H, Zarubova J, Zamecnik J, Mohapl M, Benes V, Tichy M, Komarek V (2007) Clinical characteristics in patients with hippocampal sclerosis with or without cortical dysplasia. Epileptic Disord 9(Suppl 1):S75–S82
Meencke HJ, Janz D (1984) Neuropathological findings in primary generalized epilepsy: a study of eight cases. Epilepsia 25:8–21
Mischel PS, Nguyen LP, Vinters HV (1995) Cerebral cortical dysplasia associated with pediatric epilepsy. Review of neuropathologic features and proposal for a grading system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54:137–153
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G, Babb T, Guerrini R, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Jackson G, Luders HO, Prayson R, Spreafico R, Vinters HV (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S2–S8
Rojiani AM, Emery JA, Anderson KJ, Massey JK (1996) Distribution of heterotopic neurons in normal hemispheric white matter: a morphometric analysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:178–183
Roncoroni L (1896) La fine morfologia del cervello degli epilettici e dei delinquenti. Arch Psich Scienze penali Antropol Criminale 17:92–116
Sarnat HB (1992) Cerebral dysgenesis. Embryology and clinical expression. Oxford University Press, New York
Tassi L, Colombo N, Garbelli R, Francione S, Lo Russo G, Mai R, Cardinale F, Cossu M, Ferrario A, Galli C, Bramerio M, Citterio A, Spreafico R (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological subtypes, EEG, neuroimaging and surgical outcome. Brain 125:1719–1732
Tassi L, Garbelli R, Colombo N, Bramerio M, Mai R, Francione S, Lo Russo G, Deleo F, Milesi G, Spreafico R (2010) Type I Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD I): surgical outcome related to histopathology. Epileptic Dis 12(3) (in press)
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JA (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Thom M, Eriksson S, Martinian L, Caboclo LO, McEvoy AW, Duncan JS, Sisodiya SM (2009) Temporal lobe sclerosis associated with hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: neuropathological features. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:928–938
Thom M, Sisodiya S, Harkness W, Scaravilli F (2001) Microdysgenesis in temporal lobe epilepsy. A quantitative and immunohistochemical study of white matter neurones. Brain 124:2299–2309
Torres-Reveron J, Friedlander MJ (2007) Properties of persistent postnatal cortical subplate neurons. J Neurosci 27:9962–9974
Wolf HK, Buslei R, Schmidt Kastner R, Schmidt Kastner PK, Pietsch T, Wiestler OD, Blumcke I (1996) NeuN: a useful neuronal marker for diagnostic histopathology. J Histochem Cytochem 44:1167–1171
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by the European Community (LSH-CT-2006-037315 EPICURE). We kindly thank Drs. Tassi, Colombo and D’Incerti (Milan, Italy) as well as Dr. Holthausen (Vogtareuth, Germany) for providing electrophysiological recordings and MRI pictures and Dr. Rita Garbelli (Milan, Italy) and Dr. Roland Coras (Erlangen, Germany) for providing some of the histological images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spreafico, R., Blümcke, I. Focal Cortical Dysplasias: clinical implication of neuropathological classification systems. Acta Neuropathol 120, 359–367 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0714-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0714-x