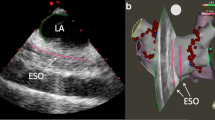
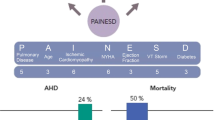
Abstract
Catheter ablation is a well-recognized treatment for a number of cardiac arrhythmias. Initially used to treat supraventricular tachycardia, this technique is now also widely used to treat ventricular arrhythmia and atrial fibrillation. This review aims to describe all the possible types of complication related to this invasive procedure. Definitions according to the current guidelines are provided, as are some details on the frequency of complications and how to diagnose and treat them appropriately. Finally, each section of the review provides guidance on how to prevent the complications associated with catheter ablation.
Zusammenfassung
Die Katheterablation ist ein anerkanntes Therapieverfahren für verschiedene Herzrhythmusstörungen. Wurde sie anfänglich zur Behandlung der supraventrikulären Tachykardie genutzt, findet sie mittlerweile auch breite Anwendung bei ventrikulären Arrhythmien und bei Vorhofflimmern. Die vorliegende Übersicht beschreibt alle möglichen Arten von Komplikationen im Zusammenhang mit diesem invasiven Verfahren. Es werden Definitionen gemäß den aktuellen Leitlinien gegeben, zudem bietet der Beitrag Einzelheiten zur Häufigkeit der Komplikationen und zum jeweiligen diagnostischen sowie therapeutischen Vorgehen. Zuletzt enthält jeder Abschnitt eine Anleitung zur Prävention der katheterablationsassoziierten Komplikationen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang SKS, Wood MA (2006) Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Saunders, Philadelphia
Josephson ME (2002) Clinical cardiac Electrophysiology: techniques and interpretations, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC et al (1998) Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Eng J Med 339:659–666
Wittkampf FHM, van Es R, Neven R (2018) JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology July 2018
Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, Kim YH, Saad EB, Aguinaga L, Akar JG, Badhwar V, Brugada J, Camm J, Chen PS, Chen SA, Chung MK, Nielsen JC, Curtis AB, Davies DW, Day JD, d’Avila A, de Groot NMSN, Di Biase L, Duytschaever M, Edgerton JR, Ellenbogen KA, Ellinor PT, Ernst S, Fenelon G, Gerstenfeld EP, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Helm RH, Hylek E, Jackman WM, Jalife J, Kalman JM, Kautzner J, Kottkamp H, Kuck KH, Kumagai K, Lee R, Lewalter T, Lindsay BD, Macle L, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, Michaud GF, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Okumura K, Packer D, Pokushalov E, Reynolds MR, Sanders P, Scanavacca M, Schilling R, Tondo C, Tsao HM, Verma A, Wilber DJ, Yamane T (2018) 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: executive summary. Europace 20(1):157–208
Cronin EM, Bogun FM, Maury P, Peichl P, Chen M, Namboodiri N, Aguinaga L, Leite LR, Al-Khatib SM, Anter E, Berruezo A, Callans DJ, Chung MK, Cuculich P, d’Avila A, Deal BJ, Della Bella P, Deneke T, Dickfeld TM, Hadid C, Haqqani HM, Neal Kay G, Latchamsetty R, Marchlinski F, Miller JM, Nogami A, Patel AR, Pathak RK, Saenz Morales LC, Santangeli P, Sapp JL Jr., Sarkozy A, Soejima K, Stevenson WG, Tedrow UB, Tzou WS, Varma N, Zeppenfeld K (2019) 2019 HRS/EHRA/APHRS/LAHRS expert consensus statement on catheter ablation of ventricular arrhythmias. J Arrhythm 35(3):323–484
Page RL, Joglar JA, Caldwell MA, Calkins H, Conti JB, Deal BJ, Estes NAM 3rd, Field ME, Goldberger ZD, Hammill SC, Indik JH, Lindsay BD, Olshansky B, Russo AM, Shen WK, Tracy CM, Al-Khatib SM (2016) 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the management of adult patients with supraventricular tachycardia: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol 67(13):e27–e115
Calkins H et al (2015) RE-CIRCUIT study-randomized evaluation of Dabigatran etexilate compared to warfarin in pulmonary vein ablation: assessment of an uninterrupted periprocedural anticoagulation strategy. Am J Cardiol 115(1):154–155
Wongcharoen W, Lin YJ, Chung FP, Chen YY, Chao TF, Chen PC, Chien KL, Chen SA (2018) Radiofrequency ablation of accessory pathways in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: long-term risk of mortality and coronary events
Hoffmann BA, Brachmann J, Andresen D et al (2011) Ablation of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia in the elderly: results from the German Ablation Registry. Heart Rhythm 8:981–987
Spector P, Reynolds MR, Calkins H et al (2009) Meta-analysis of ablation of atrial flutter and supraventricular tachycardia. Am J Cardiol 104:671–677
Wu S et al (2016) Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants compared with uninterrupted vitamin K antagonists in patients undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 117(6):926–934
Michowitz Y et al (2014) Effects of sex on the incidence of cardiac tamponade after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: results froma worldwide survey in 34 943 atrial fibrillation ablation procedures. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 7(2:274–280
Cappato R et al (2015) Uninterrupted rivaroxaban vs. uninterrupted vitamin K antagonists for catheter ablation in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 36(28):1805–1811
Tse HF et al (2003) Pulmonary vein isolation using transvenous catheter cryoablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation without risk of pulmonary vein stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 42(4):752–758
Kasper L et al (2016) Hemoptysis and lung disease as a manifestation of pulmonary vein stenosis after cryoballoon catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Pol Arch Med Wewn 126(1-2):94–96
Holmes DR Jr., Monahan KH, Packer D (2009) Pulmonary vein stenosis complicating ablation for atrial fibrillation: clinical spectrum and interventional considerations. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2(4:267–276
Fender EA, Packer DL, Holmes DR Jr. (2016) Pulmonary vein stenosis after atrial fibrillation ablation. EuroIntervention 12(Suppl X):X31–X34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Sorgente and R. Cappato declare that they have no competing interests.
For this article no studies with human participants or animals were performed by any of the authors. All studies performed were in accordance with the ethical standards indicated in each case.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorgente, A., Cappato, R. Complications of catheter ablation: incidence, diagnosis and clinical management. Herzschr Elektrophys 30, 363–370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00399-019-00652-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00399-019-00652-z
Keywords
- Complications
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular arrhythmias
- Cardiac electrophysiology