Abstract
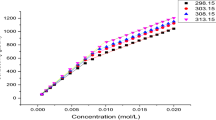
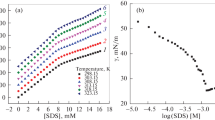
The effect of aqueous binary mixtures of isomeric butanediols on the micellization of sodium dodecyl sulfate has been investigated. Conductivity and fluorescence techniques were employed to determine the critical micellar concentration, the degree of dissociation of the counterions and the aggregation numbers of the surfactants in these binary blends. Differential conductivity plots were employed to distinguish between the cooperative and the stepwise aggregation process of the surfactant in each solvent system. The mass-action model was employed to calculate the hydrophobic and the electrostatic contributions to the Gibbs energy of micellization as well as the monomer and the counterion concentrations in the postmicellar region. The thermodynamic parameters calculated for each system indicate that the micellization process occurs more readily in the presence of cosolvent owing to the formation of mixed micelles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 July 2000 Accepted: 25 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burke, S., Andrecyk, S. & Palepu, R. Thermodynamic and aggregation properties of sodium dodecyl sulfate in aqueous binary mixtures of isomeric butanediols. Colloid Polym Sci 279, 131–138 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960000402
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960000402