Abstract
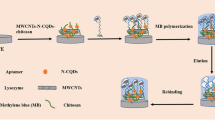
Thermo-responsive lysozyme/calcium alginate-g-poly-N-isopropylacrylamide nanohydrogels (Lys/CA-g-PNIPAAm NHs) were prepared from the self-assembly of Lys and sodium alginate-g-poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (SA-g-PNIPAAm) and the ionic cross-linking of CaCl2 in aqueous solution. The Lys/CA-g-PNIPAAm NHs were immobilized on the cleaned surface of a transducer to fabricate a Lys molecularly imprinted sensor (Lys@MIP NHs sensor), which can selectively rebind to Lys in a mixture of closely related compounds. The effects of temperature on the size and the morphology of the Lys/CA-g-PNIPAAm NHs, the removal of Lys templates, the rebinding of Lys targets, and the detection performance of the Lys@MIP NHs sensor were investigated by dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscope, and differential pulse voltammetry measurements. Compared with other Lys sensors, the fabricated Lys@MIP NHs sensor exhibited the wide linear range from 1 × 10−9 to 1 × 10−3 mg·mL−1 at 30 °C and showed short analysis times, high accuracy, satisfactory selectivity, stability, repeatability, reproducibility, and practical application for Lys detection in urine sample.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Wulff G, Sarhan A (1972) Use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for resolution of racemates. Angew Chem Int Edit 11:341–344
Chen LX, Wang XY, Lu WH, Wu XQ, Li JH (2016) Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45:2137–2211
Zahedi P, Ziaee M, Abdouss M, Farazin A, Mizaikoff B (2016) Biomacromolecule template-based molecularly imprinted polymers with an emphasis on their synthesis strategies: a review. Polym Adv Technol 27:1124–1142
Liu JQ, Ying XG, Wang HX, Li X, Zhang WY (2016) BSA imprinted polyethylene glycol grafted calcium alginate hydrogel microspheres. J Appl Polym Sci 133:43617
Zhang RL, Xu S, Zhu Y, Zhao W, Luo J, Liu XY, Tang DX (2016) Molecularly imprinted nanohybrids based on dopamine-modified poly(γ-glutamic acid) for electrochemical sensing of melamine. Biosens Bioelectron 85:381–386
Moein MM (2021) Advancements of chiral molecularly imprinted polymers in separation and sensor fields: a review of the last decade. Talanta 224:121794
Mazzotta E, Giulio TD, Malitesta C (2022) Electrochemical sensing of macromolecules based on molecularly imprinted polymers: challenges, successful strategies, and opportunities. Anal Bioanal Chem 1–36
Yang XL, Liu H, Ji YT, Xu S, Xia CM, Zhang RL, Zhang CG, Miao ZC (2022) A molecularly imprinted biosensor based on water-compatible and electroactive polymeric nanoparticles for lysozyme detection. Talanta 236:122891
Zhang RL, Xu S, Luo J, Liu XY (2015) Molecularly imprinted photo-sensitive polyglutamic acid nanoparticles for electrochemical sensing of hemoglobin. Microchim Acta 182:175–183
Dhanashree S, Priyanka M, Manisha K, Vilasrao K (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymers: novel discovery for drug delivery. Curr Drug Deliv 13:632–645
Dabrowski M, Lach P, Cieplak M, Kutner W (2018) Nanostructured molecularly imprinted polymers for protein chemosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 102:17–26
Shumyantseva VV, Bulko TV, Baychorov IH, Archakov AI (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) in electroanalysis of proteins. Biochem Mos-Suppl S 10:145–151
Qiao J, Qi L (2019) Progress of stimuli-responsive molecular imprinted materials for capture/release of proteins. Chinese Sci Bull 64:1330–1339
Zhao W, Li B, Xu S, Huang XW, Luo J, Zhu Y, Liu XY (2019) Electrochemical protein recognition based on macromolecular self-assembly of molecularly imprinted polymer: a new strategy to mimic antibody for label-free biosensing. J Mater Chem B 7:2311–2319
Song WQ, Qian LW, Yang YX, Zhao YZ, Miao ZC, Zhang QY (2021) Constructing high-recognition protein-imprinted materials using “specially designed” block macromolecular chains as functional monomers and crosslinkers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:54428–54438
Xu S, Liu YY, Zhao W, Wu Q, Chen YR, Huang XW, Sun ZJ, Zhu Y, Liu XY (2020) Hierarchical 0D–2D bio-composite film based on enzyme-loaded polymeric nanoparticles decorating graphene nanosheets as a high-performance bio-sensing platform. Biosens Bioelectron 156:112134
Ayankojo AG, Boroznjak R, Reut J, Ӧpik A, Syritski V (2022) Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical sensor for quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 353:131160
Lee MH, Thomas JL, Su ZL, Yeh WK, Monzel AS, Bolognin S, Schwamborn JC, Yang CH, Lin HY (2021) Transition metal dichalcogenides to optimize the performance of peptide-imprinted conductive polymers as electrochemical sensors. Microchim Acta 188:203
Villa CC, Sánchez LT, Valencia GA, Ahmed S, Gutiérrez TJ (2021) Molecularly imprinted polymers for food applications: a review. Trends Food Sci Tech 111:642–669
Li N, Yang H (2021) Construction of natural polymeric imprinted materials and their applications in water treatment: a review. J Hazard Mater 403:123643
Zou LH, Ding R, Li XL, Miao HH, Xu JJ, Pan GQ (2021) Typical fluorescent sensors exploiting molecularly imprinted hydrogels for environmentally and medicinally important analytes detection. Gels 7:67
Hernández-González AC, Téllez-Jurado L, Rodríguez-Lorenzo LM (2020) Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: a review. Carbohyd Polym 229:115514
Nazarnezhada S, Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi G, Samadian H, Khaksari M, Ghatar JM, Khastar H, Rezaei N, Mousavi SR, Shirian S, Salehi M (2020) Alginate hydrogel containing hydrogen sulfide as the functional wound dressing material: in vitro and in vivo study. Int J Biol Macromol 164:3323–3331
Salehi M, Ehterami A, Farzamfar S, Vaez A, Ebrahimi-Barough S (2021) Accelerating healing of excisional wound with alginate hydrogel containing naringenin in rat model. Drug Deliv Transl Re 11:142–153
Qi M, Zhao KY, Bao QW, Pan P, Zhao YW, Yang ZC, Wang HQ, Wei JF (2019) Adsorption and electrochemical detection of bovine serum albumin imprinted calcium alginate hydrogel membrane. Polymers 11:622
Wang S, Che Z, Guo CN, Liu YQ, Yang SH, Zhou MY, Gong YH, Li TD, Cui M, Luo XL (2021) A durable antifouling protein molecularly imprinted gel interface for human serum albumin detection and antibacterial application. Chem Eng J 421:129752
Wang HX, Ying XG, Liu JQ, Li X, Zhang WY (2017) Specific rebinding of protein imprinted polyethylene glycol grafted calcium alginate hydrogel with different crosslinking degree. J Polym Res 24:93
Li LX, Ying XG, Liu JQ, Li X, Zhang WY (2015) Molecularly imprinted polyurethane grafted calcium alginate hydrogel with specific recognition for proteins. Mater Lett 143:248–251
Liu JQ, Ying XG, Wang HX, Li X, Zhang WY (2016) BSA imprinted polyethylene glycol grafted calcium alginate hydrogel microspheres. J Appl Polym Sci 133. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.43617
Li LX, Ying XG, Liu JQ, Li X, Zhang WY (2015) Protein-imprinted polyurethane-grafted calcium alginate hydrogel microspheres. J Appl Polym Sci 132. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.42140
Ying XG, Wang HX, Liu JQ, Li X (2018) Polyacrylamide-grafted calcium alginate microspheres as protein-imprinting materials. Polym Bull 75:2139–2150
Ji SL, Li N, Shen Y, Li Q, Qiao J, Li ZB (2016) Poly(amino acid)-based thermoresponsive molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for specific recognition and release of lysozyme. Anal Chim Acta 909:60–66
Sun Y, Li SY, Yang YF, Feng XW, Wang W, Liu YT, Zhao MY, Zhang ZG (2019) Fabrication of a thermal responsive hemoglobin (Hb) biosensor via Hb-catalyzed eATRP on the surface of ZnO nanoflowers. J Electroanal Chem 848:113346
Lencina MMS, Iatridi Z, Villar MA, Tsitsilianis C (2014) Thermoresponsive hydrogels from alginate-based graft copolymers. Eur Polym J 61:33–44
Zhang RL, Jiang C, Fan XX, Yang RC, Sun YY, Zhang CG (2018) A gold electrode modified with a nanoparticulate film composed of a conducting copolymer for ultrasensitive voltammetric sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185:58–66
Li SW, Yang KG, Deng N, Min Y, Liu LK, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2016) Thermo-responsive epitope surface-imprinted nanoparticles for specific capture and release of target protein from human plasma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:5747–5751
Kerkaert B, Mestdagh F, De Meulenaer B (2010) Detection of hen’s egg white lysozyme in food: comparison between a sensitive HPLC and a commercial ELISA method. Food Chem 120:580–584
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2108085ME154, 2108085J11), the University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province (KJ2019A0140), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M691363), the Science Research Foundation of Anhui Polytechnic University (Xjky04201904, 2020YQQ015) and the National Natural Science Foundation Pre-research Project of Anhui Polytechnic University (2019yyzr09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Huo, C., Ji, Y. et al. A molecularly imprinted sensor based on thermo-responsive calcium alginate nanohydrogels for lysozyme detection. Colloid Polym Sci 301, 229–237 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05062-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05062-9