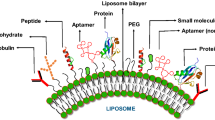
Abstract
Some amphiphilic conjugates of amino- or carboxy-mPEG2000 or mPEG5000 with a series of lipoamino acids as a lipid anchor (PEG-LAA), recently synthetized as novel surface modifiers for drug nanocarriers, were used to decorate the surface of multilamellar liposomes (MLV). For comparison, MLV were also prepared using commercial PEG lipid derivatives (DSPE-PEG and PEG 40 monostearate), commonly used to produce stealth nanocarriers. Two experimental models were used to check the ability of the PEG-LAA conjugates to organize themselves on the surface of liposomes: an in vitro uptake study, using murine macrophage cultures, that confirmed the ability of PEG-LAA conjugates to hinder or retard the cellular internalization of the vesicles. Second, the measurement of the zeta potential values of negatively charged MLV produced with the various PEG-LAAs, which confirmed their shielding effect on the MLV surface charge, linearly to their molar concentration and as a function of the structures of PEG and LAA used.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pignatello R, Musumeci T, Basile L, Carbone C, Puglisi G (2011) Biomembrane models and drug-biomembrane interaction studies: involvement in drug design and development. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 3:4–14
Wiśniewska-Becker A, Gruszecki WI (2013) Biomembrane models. In: Pignatello R (ed) Drug-biomembrane interaction studies—the application of calorimetric techniques. Woodhead/Elsevier, Cambridge, pp 47–95
Samad A, Sultana Y, Aqil M (2007) Liposomal drug delivery systems: an update review. Curr Drug Deliv 4:297–305
Schwendener RA (2007) Liposomes in biology and medicine. Adv Exp Med Biol 620:117–128
Iwamoto T (2013) Clinical application of drug delivery systems in cancer chemotherapy: review of the efficacy and side effects of approved drugs. Biol Pharm Bull 36:715–718
Owens DE 3rd, Peppas NA (2006) Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 307:93–102
Koshkaryev A, Sawant RR, Deshpande M, Torchilin V (2013) Immunoconjugates and long circulating systems: origins, current state of the art and future directions. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:24–35
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC (2001) Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: theory to practice. Pharmacol Rev 53:283–318
Yan X, Scherphof GL, Kamps JA (2005) Liposome opsonization. J Lipos Res 15:109–139
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L (2006) Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomed (Lond) 1:297–315
Otsuka H, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K (2003) PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:403–419
Jokerst JV, Lobovkina T, Zare RN, Gambhir SS (2011) Nanoparticle PEGylation for imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine (Lond) 6:715–728
Milla P, Dosio F, Cattel L (2012) PEGylation of proteins and liposomes: a powerful and flexible strategy to improve the drug delivery. Curr Drug Metab 13:105–119
Domínguez A, Suárez-Merino B, Goñi-de-Cerio F (2014) Nanoparticles and blood–brain barrier: the key to central nervous system diseases. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14:766–779
Patel A, Cholkar K, Mitra AK (2014) Recent developments in protein and peptide parenteral delivery approaches. Ther Deliv 5:337–365
Giddam AK, Zaman M, Skwarczynski M, Toth I (2012) Liposome-based delivery system for vaccine candidates: constructing an effective formulation. Nanomedicine (Lond) 7:1877–1893
Allen TM, Hansen C, Martin F, Redemann C, Yau-Young A (1991) Liposomes containing synthetic lipid derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) show prolonged circulation half-lives in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta 1066:29–36
Li J, Kao WJ (2003) Synthesis of polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives and PEGylated-peptide biopolymer conjugates. Biogeosciences 4:1055–1067
Romberg B, Hennink WE, Storm G (2008) Sheddable coatings for long-circulating nanoparticles. Pharm Res 25:55–71
Xu H, Deng Y, Chen D, Hong W, Lu Y, Dong X (2008) Esterase-catalyzed dePEGylation of pH-sensitive vesicles modified with cleavable PEG-lipid derivatives. J Control Rel 130:238–245
Pignatello R, Pantò V, Basile L, Cardile V, Craparo E, Impallomeni G, Puglisi G, Ballistreri A (2009) New amphiphilic derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) as surface modifiers of colloidal drug carriers. Proc. 36th Annual Meeting and Exposition of the Controlled Release Society; Copenhagen, July 18–22; pp. 392–393
Pignatello R, Pantò V, Basile L, Impallomeni G, Ballistreri A, Pistarà V, Craparo EF, Puglisi G (2010) New amphiphilic conjugates of mono- and bis(carboxy)-PEG2000 polymers with lipoamino acids as surface modifiers of colloidal drug carriers. Macromol Chem Phys 211:1148–1156
Toth I (1994) A novel chemical approach to drug delivery: lipidic amino acid conjugates. J Drug Target 2:217–239
Wong A, Toth I (2001) Lipid, sugar and liposaccharide based delivery systems. Curr Med Chem 8:1123–1136
Pignatello R, Intravaia VD, Puglisi G (2006) A calorimetric evaluation of the interaction of amphiphilic prodrugs of idebenone with a biomembrane model. J Colloid Interface Sci 299:626–635
Pignatello R, Noce C, Campisi A, Acquaviva R, Bucolo C, Puglisi G, Toth I (2007) Evaluation of cell tolerability of a series of lipoamino acids using biological membranes and a biomembrane model. Curr Drug Deliv 4:109–121
Abdelrahim AS, Simerska P, Toth I (2012) Liposaccharide-based nanoparticulate drug delivery system. Tetrahedron 25:4967–4975
Ziora ZM, Blaskovich MA, Toth I, Cooper MA (2012) Lipoamino acids as major components of absorption promoters in drug delivery. Curr Top Med Chem 12:1562–1580
Pignatello R, Basile L, Musumeci T, Cardile V, Vicari L, Martinetti D, Gulisano M, Puglisi G (2010) In vitro assessment of the sterical stabilization of colloidal carriers decorated with novel amphiphilic PEG derivatives. Proc. 2nd Conference on Innovation in Drug Delivery. Aix-en-Provence (France), October 3–6
Basile L, Passirani C, Huynh NT, Béjaud J, Benoit JP, Puglisi G, Pignatello R (2012) Serum-stable, long-circulating paclitaxel-loaded colloidal carriers decorated with a new amphiphilic PEG derivative. Int J Pharm 426:231–238
Pignatello R, Leonardi A, Pellitteri R, Carbone C, Caggia S, Graziano ACE, Cardile V (2013) Evaluation of new amphiphilic PEG derivatives for preparing stealth lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 44:136–144
Pignatello R, Pantò V, Basile L, Leonardi A, Guarino C, La Rosa C (2013) Characterization of micellar systems produced by new amphiphilic conjugates of poly(ethylene glycol). Drug Dev Ind Pharm doi: 10.3109/03639045.2013.828226
Pignatello R, Pantò V, Impallomeni G, Carnemolla GM, Carbone C, Puglisi G (2013) New amphiphilic conjugates of amino-poly(ethylene glycols) with lipoamino acids as surface modifiers of colloidal drug carriers. Macromol Chem Phys 214:46–55
Pignatello R, Puleo A, Guccione S, Raciti G, Acquaviva R, Campisi A, Ventura CA, Puglisi G (2005) Enhancement of drug affinity for cell membranes by conjugation with lipoamino acids. I. Synthesis and biological evaluation of lipophilic conjugates of tranylcypromine. Eur J Med Chem 40:1074–1079
Pignatello R, Sarpietro MG (2013) General experimental set-up of liposomal systems for DSC. In: Pignatello R (ed) Drug-biomembrane interaction studies. The application of calorimetric techniques. Woodhead Publ. Ltd. (Elsevier), Cambridge, pp 363–379
Pirollo KF, Chang EH (2008) Does a targeting ligand influence nanoparticle tumor localization or uptake? Trends Biotechnol 26:552–558
Stolnik S, Illum I, Davis SS (1995) Long circulating microparticle drug carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 16:195–214
Storm G, Belliot SO, Daemen T, Lasic DD (1995) Surface modification of nanoparticles to oppose uptake by the mononuclear phagocyte system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 17:31–48
Georgiev GA, Sarker DK, Al-Hanbali O, Georgiev GD, Lalchev Z (2007) Effects of poly(ethylene glycol) chains conformational transition on the properties of mixed DMPC/DMPE-PEG thin liquid films and monolayers. Colloids Surf B Biointerf 59:184–193
Bedu-Addo FK, Tang P, Xu Y, Huang L (1996) Effects of polyethylene glycol chain length and phospholipid acyl chain composition on the interaction of polyethyleneglycol-phospholipid conjugates with phospholipid: implications in liposomal drug delivery. Pharm Res 13:710–717
Peracchia MT (2003) Stealth nanoparticles for intravenous administration. STP Pharm Sci 13:155–161
Malvern Instruments (application note). The use of zeta-potential measurements to study sterically stabilized liposomes. Available at: http://www.azonano.com/details.asp?ArticleID=1214. Accessed September 2014
López Cascales JJ, Berendsen HJC, García de la Torre J (1996) Molecular dynamics simulation of water between two charged layers of dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine. J Phys Chem 100:8621–8627
Torchilin VP, Omelyanenko VG, Papisov MI, Bogdanov AA, Trubetskoy VS, Herron JN, Gentry CA (1994) Polyethylene glycol on the liposome surface: on the mechanism of polymer-coated liposome longevity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1195:11–20
Barros NB, Migliaccio V, Facundo VA, Ciancaglini P, Stábeli RG, Nicolete R, Silva-Jardim I (2013) Liposomal-lupane system as alternative chemotherapy against cutaneous leishmaniasis: macrophage as target cell. Exp Parasitol 135:337–343
Acknowledgments
This study was in part supported by the University of Catania (Ricerca di Ateneo) and by the Italian Minister of University (PRIN2010-11 Project no. 2010H834LS).
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest must be declared by all the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cupri, S., Musumeci, T., Graziano, A.C.E. et al. Evaluation of amphiphilic PEG derivatives as surface modifiers for the production of stealth liposomes. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 1083–1092 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3465-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3465-8