Abstract
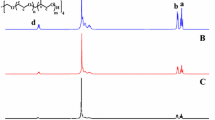
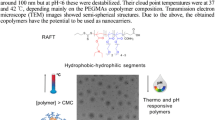
A star-shaped copolymer, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-itaconamic acid (poly(NIPAAm-co-IAM)), being pH- and thermo-dual-responsive, was synthesized by atomic transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and characterized in this work. The lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of the star copolymer increases with the molar fraction of IAM. The particle size decreases as the temperature increases but increases as the pH value increases. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) reveals that the star-shaped copolymer has a near-spherical core-shell structure that favors drug delivery. The star copolymer can be used in drug encapsulation as well as drug release. The star copolymer has different drug release rates in environments of different pH, and thus it can carry drugs in an acidic (gastric) environment and release the drugs in a neutral or less acidic (intestinal) environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloorkar NH, Kulkarmi AS, Patil RA, Ingale DJ (2012) Star polymers: an overview. Int J Pharm Sci Nanotech 5:1675–1684
Bai Y, Wei J, Yang L, He C, Lu X (2012) Temperature and pH dual-responsive behavior of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based star-block copolymer with poly(acrylic acid-block-N-isopropylacrylamide) as arms. Colloid Polym Sci 290(6):507–515
Cai J, Guo J, Ji M, Yang W, Wang C, Fu S (2007) Preparation and characterization of multiresponsive polymer composite microspheres with core–shell structure. Colloid Polym Sci 285(14):1607–1615
Carreira A, Gonçalves F, Mendonça P, Gil M, Coelho J (2010) Temperature and pH responsive polymers based on chitosan: applications and new graft copolymerization strategies based on living radical polymerization. Carbohydr Polym 80(3):618–630
Cirillo G, Iemma F, Spizzirri U, Puoci F, Curcio M, Parisi O, Picci N (2011) Synthesis of stimuli-responsive microgels for in vitro release of diclofenac diethyl ammonium. J Biomater Sci 22(4–6):823–844
Fang S, Kawaguchi H (2002) A thermosensitive amphoteric microsphere and its potential application as a biological carrier. Colloid Polym Sci 280(11):984–989
Fundueanu G, Constantin M, Stanciu C, Theodoridis G, Ascenzi P (2009) pH- and temperature-sensitive polymeric microspheres for drug delivery: the dissolution of copolymers modulates drug release. J Mater Sci Mater Med 20(12):2465–2475
Gupta B, Kumari M, Ikram S (2013) Drug release studies of N-isopropyl acrylamide/acrylic acid grafted polypropylene nonwoven fabric. J Polym Res 20(3):95
Hadjichristidis N, Pitsikalis M, Iatrou H, Driva P, Sakellariou G, Chatzichristidi M (2012) 6.03—polymers with star-related structures: synthesis, properties, and applications. In: Matyjaszewski K, Möller M (eds) Polymer science: a comprehensive reference. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 29–111. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53349-4.00161-8
Ho KM, Li WY, Wong CH, Li P (2010) Amphiphilic polymeric particles with core–shell nanostructures: emulsion-based syntheses and potential applications. Colloid Polym Sci 288(16):1503–1523
Ivan Meléndez-Ortiz H, Bucio E (2009) Stimuli-sensitive behaviour of binary graft Co-polymers (PP-g-DMAEMA)-g-NIPAAm and (PP-g-4VP)-g-NIPAAm in acidic and basic medium. Designed Monomers Polym 12(1):99–108
Lapienis G (2009) Star-shaped polymers having PEO arms. Prog Polym Sci 34(9):852–892. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.04.006
Li P, Xu R, Wang W, Li X, Xu Z, Yeung K, Chu P (2013) Thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-glycidyl methacrylate) microgels for controlled drug release. Colloid Surf B: Biointerfaces 101:251–255
Ling Y, Lu M (2009) Thermo and pH dual responsive Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels prepared in aqueous NaCl solutions and their characterization. J Polym Res 16(1):29–37
Liu Y, Cao X, Luo M, Le X, Xu W (2009) Self-assembled micellar nanoparticles of a novel star copolymer for thermo and pH dual-responsive drug release. J Colloid Interface Sci 329(2):244–252
Manakker F, Vermonden T, Nostrum C, Hennink W (2009) Cyclodextrin-based polymeric materials: synthesis, properties, and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 10(12):3157–3175
Matyjaszewski K, Miller PJ, Pyun J, Kickelbick G, Diamanti S (1999) Synthesis and characterization of star polymers with varying arm number, length, and composition from organic and hybrid inorganic/organic multifunctional initiators. Macromolecules 32(20):6526–6535
Ramkissoon-Ganorkar C, Vaudyš M, Kim SW (2000) Effect of ionic strength on the loading efficiency of model polypeptide/protein drugs in pH-/temperature-sensitive polymers. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 11(1):45–54
Rwei SP, Ku FH (2001) The dispersion of pigment slurries via incorporation with water-soluble sulfonate poly (ethylene- terephthalate). Colloid Polym Sci 279(3):274–278
Way TF, Chen YT, Chen JJ, and Teng K, US patent application No. 2013/0172490 A1
Zhang J, Ma P (2013) Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular systems for drug delivery: recent progress and future perspective. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(9):1215–1233
Zhao C, Gao X, He P, Xiao C, Zhuang X, Chen X (2011) Facile synthesis of thermo- and pH-responsive biodegradable microgels. Colloid Polym Sci 289(4):447–451
Zhao SP, Zhou F, Li LY (2012) pH- and temperature-responsive behaviors of hydrogels resulting from the photopolymerization of allylated chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide, and their drug release profiles. J Polym Res 19(9):9944
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China, Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. NSC 102-2218-E-027-015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rwei, SP., Chuang, YY., Way, TF. et al. Preparation of thermo- and pH-responsive star copolymers via ATRP and its use in drug release application. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 493–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3436-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3436-0