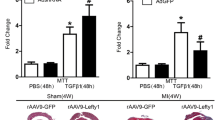
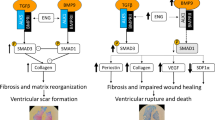
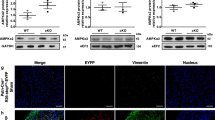
Abstract
Myocardial infarction (MI) is the leading cause of death worldwide. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) has been considered to be a promising therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. GSK-3 is a family of ubiquitously expressed serine/threonine kinases. GSK-3 isoforms appear to play overlapping, unique, and even opposing functions in the heart. Previously, our group identified that cardiac fibroblast (FB) GSK-3β acts as a negative regulator of fibrotic remodeling in the ischemic heart. However, the role of FB-GSK-3α in MI pathology is not defined. To determine the role of FB-GSK-3α in MI-induced adverse cardiac remodeling, GSK-3α was deleted specifically in the residential fibroblast or myofibroblast (MyoFB) using tamoxifen (TAM) inducible Tcf21 or Periostin (Postn) promoter-driven Cre recombinase, respectively. Echocardiographic analysis revealed that FB- or MyoFB-specific GSK-3α deletion prevented the development of dilative remodeling and cardiac dysfunction. Morphometrics and histology studies confirmed improvement in capillary density and a remarkable reduction in hypertrophy and fibrosis in the KO group. We harvested the hearts at 4 weeks post-MI and analyzed signature genes of adverse remodeling. Specifically, qPCR analysis was performed to examine the gene panels of inflammation (TNFα, IL-6, IL-1β), fibrosis (COL1A1, COL3A1, COMP, Fibronectin-1, Latent TGF-β binding protein 2), and hypertrophy (ANP, BNP, MYH7). These molecular markers were essentially normalized due to FB-specific GSK-3α deletion. Further molecular studies confirmed that FB-GSK-3α could regulate NF-kB activation and expression of angiogenesis-related proteins. Our findings suggest that FB-GSK-3α plays a critical role in the pathological cardiac remodeling of ischemic hearts, therefore, it could be therapeutically targeted.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Acharya A, Baek ST, Huang G, Eskiocak B, Goetsch S, Sung CY, Banfi S, Sauer MF, Olsen GS, Duffield JS, Olson EN, Tallquist MD (2012) The bHLH transcription factor Tcf21 is required for lineage-specific EMT of cardiac fibroblast progenitors. Development 139:2139–2149. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.079970
Ahmad F, Lal H, Zhou J, Vagnozzi RJ, Yu JE, Shang X, Woodgett JR, Gao E, Force T (2014) Cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of Gsk3alpha mitigates post-myocardial infarction remodeling, contractile dysfunction, and heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:696–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.068
Ahmad F, Singh AP, Tomar D, Rahmani M, Zhang Q, Woodgett JR, Tilley DG, Lal H, Force T (2019) Cardiomyocyte-GSK-3alpha promotes mPTP opening and heart failure in mice with chronic pressure overload. J Mol Cell Cardiol 130:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.03.020
Ahmad F, Woodgett JR (2020) Emerging roles of GSK-3alpha in pathophysiology: emphasis on cardio-metabolic disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867:118616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118616
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, Hanahan D (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2:737–744. https://doi.org/10.1038/35036374
Brauninger H, Kruger S, Bacmeister L, Nystrom A, Eyerich K, Westermann D, Lindner D (2023) Matrix metalloproteinases in coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 118:18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-023-00987-2
Brooks HL, Lindsey ML (2018) Guidelines for authors and reviewers on antibody use in physiology studies. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 314:H724–H732. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00512.2017
Chalise U, Becirovic-Agic M, Lindsey ML (2023) The cardiac wound healing response to myocardial infarction. WIREs Mech Dis 15:e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.1584
Cinetto F, Ceccato J, Caputo I, Cangiano D, Montini B, Lunardi F, Piazza M, Agostini C, Calabrese F, Semenzato G, Rattazzi M, Gurrieri C, Scarpa R, Felice C, Vianello F (2021) GSK-3 inhibition modulates metalloproteases in a model of lung inflammation and fibrosis. Front Mol Biosci 8:633054. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.633054
Cortes-Vieyra R, Silva-Garcia O, Gomez-Garcia A, Gutierrez-Castellanos S, Alvarez-Aguilar C, Baizabal-Aguirre VM (2021) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta modulates the inflammatory response activated by bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Front Immunol 12:675751. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.675751
Doble BW, Patel S, Wood GA, Kockeritz LK, Woodgett JR (2007) Functional redundancy of GSK-3alpha and GSK-3beta in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling shown by using an allelic series of embryonic stem cell lines. Dev Cell 12:957–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.04.001
Frangogiannis NG (2006) The mechanistic basis of infarct healing. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1907–1939. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.8.1907
Frangogiannis NG (2015) Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction. Compr Physiol 5:1841–1875. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c150006
Fu X, Khalil H, Kanisicak O, Boyer JG, Vagnozzi RJ, Maliken BD, Sargent MA, Prasad V, Valiente-Alandi I, Blaxall BC, Molkentin JD (2018) Specialized fibroblast differentiated states underlie scar formation in the infarcted mouse heart. J Clin Investig 128:2127–2143. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI98215
Gao E, Lei YH, Shang X, Huang ZM, Zuo L, Boucher M, Fan Q, Chuprun JK, Ma XL, Koch WJ (2010) A novel and efficient model of coronary artery ligation and myocardial infarction in the mouse. Circ Res 107:1445–1453. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223925
Ghosh S, Hayden MS (2008) New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 8:837–848. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2423
Hess A, Borchert T, Ross TL, Bengel FM, Thackeray JT (2022) Characterizing the transition from immune response to tissue repair after myocardial infarction by multiparametric imaging. Basic Res Cardiol 117:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-022-00922-x
Hesse J, Owenier C, Lautwein T, Zalfen R, Weber JF, Ding Z, Alter C, Lang A, Grandoch M, Gerdes N, Fischer JW, Klau GW, Dieterich C, Kohrer K, Schrader J (2021) Single-cell transcriptomics defines heterogeneity of epicardial cells and fibroblasts within the infarcted murine heart. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.65921
Hoffmeister L, Diekmann M, Brand K, Huber R (2020) GSK3: a kinase balancing promotion and resolution of inflammation. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040820
Humeres C, Frangogiannis NG (2019) Fibroblasts in the infarcted, remodeling, and failing heart. JACC Basic Transl Sci 4:449–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.02.006
Isogai C, Laug WE, Shimada H, Declerck PJ, Stins MF, Durden DL, Erdreich-Epstein A, DeClerck YA (2001) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating endothelial cell migration toward fibronectin. Cancer Res 61:5587–5594
Jope RS, Cheng Y, Lowell JA, Worthen RJ, Sitbon YH, Beurel E (2017) Stressed and inflamed, can GSK3 be blamed? Trends Biochem Sci 42:180–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.009
Kanisicak O, Khalil H, Ivey MJ, Karch J, Maliken BD, Correll RN, Brody MJ, Lin S-CJ, Aronow BJ, Tallquist MD, Molkentin JD (2016) Genetic lineage tracing defines myofibroblast origin and function in the injured heart. Nat Commun 7:12260. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12260
Kim HS, Skurk C, Thomas SR, Bialik A, Suhara T, Kureishi Y, Birnbaum M, Keaney JF Jr, Walsh K (2002) Regulation of angiogenesis by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Biol Chem 277:41888–41896. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M206657200
Lal H, Ahmad F, Woodgett J, Force T (2015) The GSK-3 family as therapeutic target for myocardial diseases. Circ Res 116:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303613
Lal H, Ahmad F, Zhou J, Yu JE, Vagnozzi RJ, Guo Y, Yu D, Tsai EJ, Woodgett J, Gao E, Force T (2014) Cardiac fibroblast glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates ventricular remodeling and dysfunction in ischemic heart. Circulation 130:419–430. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.008364
Lal H, Zhou J, Ahmad F, Zaka R, Vagnozzi RJ, Decaul M, Woodgett J, Gao E, Force T (2012) Glycogen synthase kinase-3alpha limits ischemic injury, cardiac rupture, post-myocardial infarction remodeling and death. Circulation 125:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.050666
Lee NV, Sato M, Annis DS, Loo JA, Wu L, Mosher DF, Iruela-Arispe ML (2006) ADAMTS1 mediates the release of antiangiogenic polypeptides from TSP1 and 2. EMBO J 25:5270–5283. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601400
Lendahl U, Muhl L, Betsholtz C (2022) Identification, discrimination and heterogeneity of fibroblasts. Nat Commun 13:3409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30633-9
Li Z, Zhu H, Liu C, Wang Y, Wang D, Liu H, Cao W, Hu Y, Lin Q, Tong C, Lu M, Sachinidis A, Li L, Peng L (2019) GSK-3beta inhibition protects the rat heart from the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation injury via suppressing FOXO3A activity. J Cell Mol Med 23:7796–7809. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14656
Lindsey ML, Bolli R, Canty JM Jr, Du XJ, Frangogiannis NG, Frantz S, Gourdie RG, Holmes JW, Jones SP, Kloner RA, Lefer DJ, Liao R, Murphy E, Ping P, Przyklenk K, Recchia FA, Schwartz Longacre L, Ripplinger CM, Van Eyk JE, Heusch G (2018) Guidelines for experimental models of myocardial ischemia and infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 314:H812–H838. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00335.2017
Lindsey ML, Kassiri Z, Virag JAI, de Castro Bras LE, Scherrer-Crosbie M (2018) Guidelines for measuring cardiac physiology in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 314:H733–H752. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00339.2017
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017) NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Lother A, Kohl P (2023) The heterocellular heart: identities, interactions, and implications for cardiology. Basic Res Cardiol 118:30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-023-01000-6
Ma Y, Iyer RP, Jung M, Czubryt MP, Lindsey ML (2017) Cardiac fibroblast activation post-myocardial infarction: current knowledge gaps. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38:448–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.03.001
Martin TA, Harding KG, Jiang WG (1999) Regulation of angiogenesis and endothelial cell motility by matrix-bound fibroblasts. Angiogenesis 3:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009004212357
Maurer AM, Zhou B, Han ZC (2006) Roles of platelet factor 4 in hematopoiesis and angiogenesis. Growth Factors 24:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/08977190600988225
Mouton AJ, Rivera OJ, Lindsey ML (2018) Myocardial infarction remodeling that progresses to heart failure: a signaling misunderstanding. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 315:H71–H79. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00131.2018
Nakamura M, Liu T, Husain S, Zhai P, Warren JS, Hsu CP, Matsuda T, Phiel CJ, Cox JE, Tian B, Li H, Sadoshima J (2019) Glycogen synthase kinase-3alpha promotes fatty acid uptake and lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Cell Metab 29:1119-1134.e1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.01.005
Newman AC, Nakatsu MN, Chou W, Gershon PD, Hughes CC (2011) The requirement for fibroblasts in angiogenesis: fibroblast-derived matrix proteins are essential for endothelial cell lumen formation. Mol Biol Cell 22:3791–3800. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0393
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U, Emerson M, Garner P, Holgate ST, Howells DW, Karp NA, Lazic SE, Lidster K, MacCallum CJ, Macleod M, Pearl EJ, Petersen OH, Rawle F, Reynolds P, Rooney K, Sena ES, Silberberg SD, Steckler T, Wurbel H (2020) The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research. J Physiol 598:3793–3801. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP280389
Potz BA, Sabe AA, Elmadhun NY, Clements RT, Robich MP, Sodha NR, Sellke FW (2016) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibition improves myocardial angiogenesis and perfusion in a swine model of metabolic syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.003694
Saraswati S, Marrow SMW, Watch LA, Young PP (2019) Identification of a pro-angiogenic functional role for FSP1-positive fibroblast subtype in wound healing. Nat Commun 10:3027. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10965-9
Sengupta S, Gherardi E, Sellers LA, Wood JM, Sasisekharan R, Fan TP (2003) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor can induce angiogenesis independently of vascular endothelial growth factor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.0000048701.86621.d0
Shams F, Moravvej H, Hosseinzadeh S, Mostafavi E, Bayat H, Kazemi B, Bandehpour M, Rostami E, Rahimpour A, Moosavian H (2022) Overexpression of VEGF in dermal fibroblast cells accelerates the angiogenesis and wound healing function: in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci Rep 12:18529. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23304-8
Shinde AV, Frangogiannis NG (2014) Fibroblasts in myocardial infarction: a role in inflammation and repair. J Mol Cell Cardiol 70:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.11.015
Skurk C, Maatz H, Rocnik E, Bialik A, Force T, Walsh K (2005) Glycogen-Synthase Kinase3beta/beta-catenin axis promotes angiogenesis through activation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 96:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000156273.30274.f7
Tallquist MD, Molkentin JD (2017) Redefining the identity of cardiac fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cardiol 14:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2017.57
Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, Baker-Smith CM, Beaton AZ, Boehme AK, Buxton AE, Commodore-Mensah Y, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Eze-Nliam C, Fugar S, Generoso G, Heard DG, Hiremath S, Ho JE, Kalani R, Kazi DS, Ko D, Levine DA, Liu J, Ma J, Magnani JW, Michos ED, Mussolino ME, Navaneethan SD, Parikh NI, Poudel R, Rezk-Hanna M, Roth GA, Shah NS, St-Onge MP, Thacker EL, Virani SS, Voeks JH, Wang NY, Wong ND, Wong SS, Yaffe K, Martin SS, American Heart Association Council on E, Prevention Statistics C, Stroke Statistics S (2023) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2023 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 147:e93–e621. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123
Umbarkar P, Ejantkar S, Tousif S, Lal H (2021) Mechanisms of fibroblast activation and myocardial fibrosis: lessons learned from FB-specific conditional mouse models. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092412
Umbarkar P, Ruiz Ramirez SY, Toro Cora A, Tousif S, Lal H (2023) GSK-3 at the heart of cardiometabolic diseases: Isoform-specific targeting is critical to therapeutic benefit. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1869:166724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166724
Umbarkar P, Singh AP, Gupte M, Verma VK, Galindo CL, Guo Y, Zhang Q, McNamara JW, Force T, Lal H (2019) Cardiomyocyte SMAD4-dependent TGF-beta signaling is essential to maintain adult heart homeostasis. JACC Basic Transl Sci 4:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacbts.2018.10.003
Umbarkar P, Tousif S, Singh AP, Anderson JC, Zhang Q, Tallquist MD, Woodgett J, Lal H (2022) Fibroblast GSK-3alpha promotes fibrosis via RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in the injured heart. Circ Res 131:620–636. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321431
Vidal R, Wagner JUG, Braeuning C, Fischer C, Patrick R, Tombor L, Muhly-Reinholz M, John D, Kliem M, Conrad T, Guimaraes-Camboa N, Harvey R, Dimmeler S, Sauer S (2019) Transcriptional heterogeneity of fibroblasts is a hallmark of the aging heart. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.131092
Wang CQ, Huang YW, Wang SW, Huang YL, Tsai CH, Zhao YM, Huang BF, Xu GH, Fong YC, Tang CH (2017) Amphiregulin enhances VEGF-A production in human chondrosarcoma cells and promotes angiogenesis by inhibiting miR-206 via FAK/c-Src/PKCdelta pathway. Cancer Lett 385:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.010
Wang L, Wang Y, Zhang C, Li J, Meng Y, Dou M, Noguchi CT, Di L (2018) Inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase 3 reverses obesity-induced white adipose tissue inflammation by regulating apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage/CD5L-mediated macrophage migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 38:2103–2116. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311363
Wang L, Yang Y, Ma H, Xie Y, Xu J, Near D, Wang H, Garbutt T, Li Y, Liu J, Qian L (2022) Single-cell dual-omics reveals the transcriptomic and epigenomic diversity of cardiac non-myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 118:1548–1563. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvab134
Zhou J, Freeman TA, Ahmad F, Shang X, Mangano E, Gao E, Farber J, Wang Y, Ma XL, Woodgett J, Vagnozzi RJ, Lal H, Force T (2013) GSK-3alpha is a central regulator of age-related pathologies in mice. J Clin Investig 123:1821–1832. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64398
Zhou J, Lal H, Chen X, Shang X, Song J, Li Y, Kerkela R, Doble BW, MacAulay K, DeCaul M, Koch WJ, Farber J, Woodgett J, Gao E, Force T (2010) GSK-3alpha directly regulates beta-adrenergic signaling and the response of the heart to hemodynamic stress in mice. J Clin Investig 120:2280–2291. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI41407
Funding
This work was supported by research grants from the NHLBI (R01HL133290 and 1R01HL143074) to HL, American Heart Association (AHA CDA 933553) to ST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PU and HL conceived and designed the research; PU, SR, SE, and ST performed experiments; PU, SR, and SE analyzed data; PU, ST, and HL interpreted results of experiments; PU prepared figures; PU and HL drafted the manuscript; all authors contributed to editing, revision, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicting interests to disclose in relation to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Umbarkar, P., Ejantkar, S., Ruiz Ramirez, S.Y. et al. Cardiac fibroblast GSK-3α aggravates ischemic cardiac injury by promoting fibrosis, inflammation, and impairing angiogenesis. Basic Res Cardiol 118, 35 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-023-01005-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-023-01005-1