Abstract.
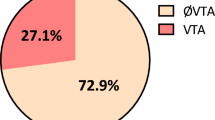
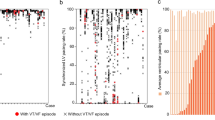
Background: The prognostic role of asymptomatic nonsustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT) and programmed ventricular stimulation (PVS) in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDC) remains controversial. Methods: The prognostic significance of ventricular arrhythmias, ejection fraction, NYHA class, atrial fibrillation and age for overall and sudden death mortality was prospectively studied in 157 patients with IDC (group 1) free of documented sustained ventricular arrhythmia and syncope. In 99 patients with asymptomatic NSVT (group 2), PVS with 2 – 3 extrastimuli was performed. Non-inducible patients were discharged without specific antiarrhythmic therapy, whereas those with inducible monomorphic ventricular tachycardia were implanted with an ICD. Results: In group 1, 48% of patients had NSVT. Overall and sudden death mortality were significantly higher in patients with NSVT (34.2 vs. 9.8%, p = 0.0001 and 15.8 vs. 3.7%, p = 0.0037; follow-up 22 ± 14 months). Multivariate analysis revealed that NSVT independently predicts both overall and sudden death mortality (p = 0.0021 and .0221, respectively; adjusted for EF, NYHA class and age). In group 2, inducibility of sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmia was 7%, but sustained monomorphic VT occurred in 3% only. Two of 7 inducible patients experienced arrhythmic events during a follow-up of 25 ± 21 months (positive predictive value 29%). Overall and sudden death mortality were 29% and 0% in the inducible group vs. 17 and 4% in the non-inducible group. Both overall and sudden death mortality were signi.cantly lower in non-inducible patients from group 2 as compared to patients from group 1 with NSVT (p = 0.0043 and 0.0048), most likely due to a more common use of betablockers and a higher EF in the former group (p < 0.001, respectively). Conclusions: In patients with IDC, NSVT independently predicts both overall and sudden death mortality. Due to a low inducibility rate and a poor positive predictive value, PVS seems inappropriate for further arrhythmia risk assessment. However, in spite of documented NSVT, the incidence of SCD in patients on optimized medical treatment including betablockers seems to be very low, questioning the need for specific arrhythmia risk stratification.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 August 2002, Returned for revision: 24 September 2002, Revision received: 8 October 2002, Accepted: 7 November 2002, Published online: 12 May 2003
Correspondence to: R. Becker, MD
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, R., Haass, M., Ick, D. et al. Role of nonsustained ventricular tachycardia and programmed ventricular stimulation for risk stratification in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 98, 259–266 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-003-0398-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-003-0398-7