Abstract
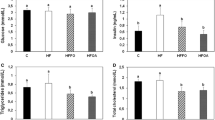
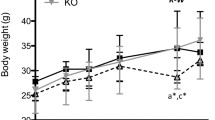
Cardiovascular benefits of dietary n-3 fatty acids have been shown. However, benefits of n-3 fatty acids as part of a high fat, low n-6:n-3 fatty acid ratio diet has not been fully characterized. Aim of this study is to investigate cardiovascular and metabolic benefits of ‘designer oils’ containing a low ratio of n-6:n-3 fatty acids in C57BL/6 mice. Three groups of C57BL/6 mice were fed an atherogenic diet supplemented with either a fish oil- or flaxseed oil-based ‘designer oil’ with an approximate n-6:n-3 fatty acid ratio of 2:1 (treated groups, n = 6 each) or with a safflower oil-based formulation with a high ratio (25:1) of n-6:n-3 fatty acids (control group, n = 6) for 6 weeks. Food intake, body weight, and blood lipid levels were monitored regularly. Fatty acid profile of the heart tissues was assessed. Histological assessment of liver samples was conducted. At the end of the study body weight and food intake was significantly higher in the flax group compared to control. The levels of 20:5n-3 and 22:6n-3 was significantly increased in the heart phospholipids in both flax and fish groups compared to control; tissue 20:4n-6 was significantly reduced in the fish group compared to control. Significant liver pathology was observed in the control group only. Lowering dietary ratio of n-6:n-3 fatty acids may significantly reduce cardiovascular and metabolic risks in mice regardless of the source of n-3 fatty acids.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ander BP, Weber AR, Rampersad PP, Gilchrist JS, Pierce GN, Lukas A (2004) Dietary flaxseed protects against ventricular fibrillation induced by ischemia-reperfusion in normal and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J Nutr 134:3250–3256
Barcelli UO, Beach DC, Pollak VE (1988) The influence of n-6 and n-3 fatty acids on kidney phospholipids composition and on eicosanoid production in aging rats. Lipids 23:309–312
Brenner RR (1974) The oxidative desaturation of unsaturated fatty acids in animals. Mol Cell Biochem 3:41–52
Chrysohoou C, Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Skoumas J, Krinos X, Chloptsios Y, Nikolaou V, Stefanadis C (2007) Long-term fish consumption is associated with protection against arrhythmia in healthy persons in a Mediterranean region—the ATTICA study. Am J Clin Nutr 85:1385–1391
Folch J, Les M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animals. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Geleijnse JM, Giltay EJ, Grobbee DE, Donders AR, Kok FJ (2002) Blood pressure response to fish oil supplementation: meta-regression analysis of randomized trial. J Hypertens 20:1493–1499
Gerster H (1998) Can adults adequately convert alpha-linolenic acid (18:3n–3) to eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5n–3) and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n–3)? Int J Vitam Nutr Res 68:159–173
Gomes MFPL, de Oliveira Massoco C, Xavier JG, Bonamin LV (2007) Comfrey (Symphytum Officinale. L.) and experimental hepatic carcinogenesis: a short-term carcinogenesis model study. eCAM advance access 2007
Harper CR, Edwards MJ, DeFilipis AP, Jacobson TA (2006) Flaxseed oil increases the plasma concentrations of cardioprotective (n-3) fatty acids in humans. J Nutr 136:83–87
Harris WS, Bulchandani D (2006) Why do omega-3 fatty acids lower serum triglycerides? Curr Opin Lipidol 17:387–393
James MJ, Gibson RA, Cleland LG (2000) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory mediator production. Am J Clin Nutr 71:343S–348S
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Natta MV, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41:1313–1321
Lee P, Prasad K (2003) Effects of flaxseed oil on serum lipids and atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolmic rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 8:227–235
Ma DWL, Ngo V, Huot PSP, Kang JX (2006) n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids endogenously synthesized in fat-1 mice are enriched in the mammary gland. Lipids 41:35–39
Maki KC, Van Elswyk ME, McCarthy D, Seeley MA, Veith PE, Hess SP, Ingram KA, Halvorson JJ, Calaguas EM, Davidson MH (2003) Lipid responses in mildly hypertriglyceridemic men and women to consumption of docosahexaenoic acid-enriched eggs. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 73:357–368
McLennan PL, Bridle TM, Abeywardena MY, Charnock JS (1993) Comparative efficacy of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in modulating ventricular fibrillation threshold in marmoset monkeys. Am J Clin Nutr 58:666–669
Riediger N, Othman R, Fitz E, Pierce GN, Suh M, Moghadasian MH (2008) Low dietary n-6:n-3 fatty acid ratio, with fish- or flaxseed oil, improves plasma lipids and alters tissue fatty acid composition in mice. Eur J Nutr 47:153–160
Simopoulos AP (2002) The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother 56:365–379
Suh M, Wierzbicki AA, Clandinin MT (1994) Dietary fat alters membrane composition in rod outer segments in normal and diabetic rats: impact on content of very-long-chain (C ≥ 24) polyenoic fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1214:54–62
Torbenson M, Chen YY, Brunt E, Cummings OW, Gottfried M, Jakate S, Liu YC, Yeh MM, Ferrell L (2006) Glycogenic hepatopathy: An underrecognized hepatic complication of diabetes mellitus. Am J Surg Pathol 30:508–513
Xu Z, Riediger N, Innis S, Moghadasian MH (2007) Fish oil significantly alters fatty acid profiles in various lipid fractions but not atherogenesis in apo E-KO mice. Eur J Nutr 46:103–110
Yamada N, Shimizu J, Wada M, Takita T, Innami S (1998) Changes in platelet aggregation and lipid metabolism in rats given dietary lipids containing different n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 44:279–289
Yamashita T, Oda E, Sano T, Yamashita T, Ijiru Y, Giddings JC, Yamamoto J (2005) Varying the ratio of dietary n-6:n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids alters the tendency to thrombosis and progress of atherosclerosis in apoE-/-LDLR-/- double knockout mouse. Thromb Res 116:393–401
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, Heart and Stroke Foundation and ARDI. NR is a recipient of an NSERC Graduate Scholarship. NA is a recipient of the Manitoba Graduate Studentship. We would also like to thank Krystal Merrells, Amy Kroeker, Melissa Ree, Rgia Othman and Aimee Cadieux for their technical and editorial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riediger, N.D., Azordegan, N., Harris-Janz, S. et al. ‘Designer oils’ low in n-6:n-3 fatty acid ratio beneficially modifies cardiovascular risks in mice. Eur J Nutr 48, 307–314 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-009-0015-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-009-0015-0