Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate trends and factors associated with interfacility differences in imaging modality selection in the diagnosis and management of children with suspected acute appendicitis.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective review of diagnostic imaging selection and outcomes in patients <20 years of age who underwent appendectomy at a single Children’s Hospital from June 2008 to June 2013. These results were then compared with those of referring hospitals.
Results
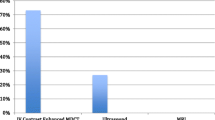
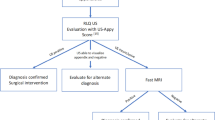
A total of 232 children underwent appendectomy during the study period. Imaging results contributed to diagnostic and management decisions in 95.3 % of cases. CT scan was utilized as first-line imaging in 50 % of cases. CTs were preferentially performed at referring institutions (78 vs. 46 %, p < 0.001). Children were five times more likely to undergo CT at referring institutions (OR = 5.5, CI 3.0–10.2). Adjusting for demographics and Alvarado score, diagnostic imaging choice was independent of patient’s clinical status.
Conclusion
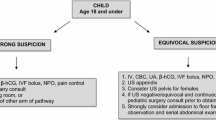
This study demonstrates that initial presentation to a referring hospital independently predicts the use of CT scan for suspected acute appendicitis. Further efforts should be undertaken to develop a clinical pathway that minimizes radiation exposure in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, with focus on access to pediatric abdominal ultrasound.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramarajan N, Krishnamoorthi R, Gharahbaghian L et al (2014) Clinical correlation needed: what do emergency physicians do after an equivocal ultrasound for pediatric acute appendicitis? J Clin Ultrasound 42:385–394
Srinivasan A, Servaes S, Pena A et al (2015) Utility of CT after sonography for suspected appendicitis in children: integration of a clinical scoring system with a staged imaging protocol. Emerg Radiol 22:31–42
Selbst SM, Friedman MJ, Singh SB (2005) Epidemiology and etiology of malpractice lawsuits involving children in US emergency departments and urgent care centers. Pediatr Emerg Care 21:165–169
Fahimi J, Herring A, Harries A et al (2012) Computed tomography use among children presenting to emergency departments with abdominal pain. Pediatrics 130:e1069–e1075
Bachur RG, Hennelly K, Callahan MJ et al (2012) Advanced radiologic imaging for pediatric appendicitis, 2005–2009: trends and outcomes. J Pediatr 160:1034–1038
Menoch MJ, Hirsh DA, Khan NS et al (2012) Trends in computed tomography utilization in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatrics 129:e690–e697
Larson DB, Johnson LW, Schnell BM et al (2011) National trends in CT use in the emergency department: 1995–2007. Radiology 258:164–173
Doria AS, Moineddin R, Kellenberger CJ et al (2006) US or CT for Diagnosis of Appendicitis in Children and Adults? A meta-analysis. Radiology 241:83–94
Miglioretti DL, Johnson E, Williams A et al (2013) The use of computed tomography in pediatrics and the associated radiation exposure and estimated cancer risk. JAMA Pediatr 167:700–707
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Computed tomography–an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med 357:2277–2284
Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP et al (2012) Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 380:499–505
Pena BM, Taylor GA, Fishman SJ et al (2002) Effect of an imaging protocol on clinical outcomes among pediatric patients with appendicitis. Pediatrics 110:1088–1093
Rezak A, Abbas HM, Ajemian MS et al (2011) Decreased use of computed tomography with a modified clinical scoring system in diagnosis of pediatric acute appendicitis. Arch Surg 146:64–67
Adibe OO, Amin SR, Hansen EN et al (2011) An evidence-based clinical protocol for diagnosis of acute appendicitis decreased the use of computed tomography in children. J Pediatr Surg 46:192–196
Thirumoorthi AS, Fefferman NR, Ginsburg HB et al (2012) Managing radiation exposure in children–reexamining the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 47:2268–2272
Raval MV, Deans KJ, Rangel SJ et al (2012) Factors associated with imaging modality choice in children with appendicitis. J Surg Res 177:131–136
Ang A (2001) Chong NK, Daneman A: pediatric appendicitis in “real-time”: the value of sonography in diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Emerg Care 17:334–340
Jaremko JL, Crockett A, Rucker D et al (2011) Incidence and significance of inconclusive results in ultrasound for appendicitis in children and teenagers. Can Assoc Radiol J 62:197–202
Strouse PJ (2010) Pediatric appendicitis: an argument for US. Radiology 255:8–13
Wiersma F, Toorenvliet BR, Bloem JL et al (2009) US examination of the appendix in children with suspected appendicitis: the additional value of secondary signs. Eur Radiol 19:455–461
Escriba A, Gamell AM, Fernandez Y et al (2011) Prospective validation of two systems of classification for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Pediatr Emerg Care 27:165–169
Macklin CP, Radcliffe GS, Merei JM et al (1997) A prospective evaluation of the modified Alvarado score for acute appendicitis in children. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 79:203–205
Kulik DM, Uleryk EM, Maguire JL (2013) Does this child have appendicitis? A systematic review of clinical prediction rules for children with acute abdominal pain. J Clin Epidemiol 66:95–104
Acheson J (2010) Blindness in neurological disease: a short overview of new therapies from translational research. Curr Opin Neurol 23:1–3
Kaiser S, Jorulf H, Soderman E et al (2004) Impact of radiologic imaging on the surgical decision-making process in suspected appendicitis in children. Acad Radiol 11:971–979
Newman K, Ponsky T, Kittle K et al (2003) Appendicitis 2000: variability in practice, outcomes, and resource utilization at thirty pediatric hospitals. J Pediatr Surg 38:372–379 (discussion 372–379)
Applegate KE, Sivit CJ, Salvator AE et al (2001) Effect of cross-sectional imaging on negative appendectomy and perforation rates in children. Radiology 220:103–107
Hall EJ, Brenner DJ (2008) Cancer risks from diagnostic radiology. Br J Radiol 81:362–378
Knott EM, Thomas P, Sharp NE et al (2013) Reduced use of computed tomography in patients treated with interval appendectomy after implementing a protocol from a prospective, randomized trial. Pediatr Surg Int 29:1293–1296
Saito JM, Yan Y, Evashwick TW et al (2013) Use and accuracy of diagnostic imaging by hospital type in pediatric appendicitis. Pediatrics 131:e37–e44
Krishnamoorthi R, Ramarajan N, Wang NE et al (2011) Effectiveness of a staged US and CT protocol for the diagnosis of pediatric appendicitis: reducing radiation exposure in the age of ALARA. Radiology 259:231–239
York D, Smith A, Phillips JD et al (2005) The influence of advanced radiographic imaging on the treatment of pediatric appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 40:1908–1911
Poonai N, Gregory J, Thompson G et al (2014) Is pelvic ultrasound associated with an increased time to appendectomy in pediatric appendicitis? J Emerg Med 47:51–58
Papandria D, Goldstein SD, Rhee D et al (2013) Risk of perforation increases with delay in recognition and surgery for acute appendicitis. J Surg Res 184:723–729
Alvarado A (1986) A practical score for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ann Emerg Med 15:557–564
Samuel M (2002) Pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr Surg 37:877–881
Schneider C, Kharbanda A, Bachur R (2007) Evaluating appendicitis scoring systems using a prospective pediatric cohort. Ann Emerg Med 49:778–784, 784.e1
Saucier A, Huang EY, Emeremni CA et al (2014) Prospective evaluation of a clinical pathway for suspected appendicitis. Pediatrics 133:e88–e95
Bhatt M, Joseph L, Ducharme FM et al (2009) Prospective validation of the pediatric appendicitis score in a Canadian pediatric emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 16:591–596
Aspelund G, Fingeret A, Gross E et al (2014) Ultrasonography/MRI versus CT for diagnosing appendicitis. Pediatrics 133:586–593
Moore MM, Gustas CN, Choudhary AK et al (2012) MRI for clinically suspected pediatric appendicitis: an implemented program. Pediatr Radiol 42:1056–1063
Tkacz JN, Anderson SA, Soto J (2009) MR imaging in gastrointestinal emergencies. Radiographics 29:1767–1780
Johnson AK, Filippi CG, Andrews T et al (2012) Ultrafast 3-T MRI in the evaluation of children with acute lower abdominal pain for the detection of appendicitis. Am J Roentgenol 198:1424–1430
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michailidou, M., Sacco Casamassima, M.G., Karim, O. et al. Diagnostic imaging for acute appendicitis: interfacility differences in practice patterns. Pediatr Surg Int 31, 355–361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3669-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3669-0