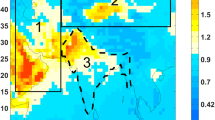
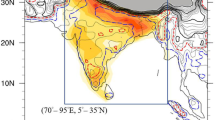
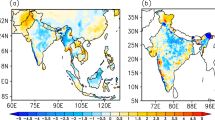
Abstract
In the present study, we examine the responses of South Asian Monsoon (SAM) rainfall at intra-seasonal scale to remote dust emissions from west Asia, Tibetan Plateau and local dust emissions from within south Asia using a state of the art coupled atmosphere-slab ocean model CESM1-SOM. A series of systematically designed idealized simulations are carried out in such a way that dust emissions from the selected source regions are either perpetually suppressed or enhanced from these source regions and the response of the intra-seasonal oscillations (ISOs) of SAM rainfall to such perturbations in dust emissions are investigated. It is noted that the intra-seasonal variability of SAM rainfall is dominated by three different ISOs with periodicities of 10–20 days, 30–60 days and 60–90 days. Modulations in the characteristics of each of these three ISOs are studied for each of the dust perturbation experiments. Statistically robust K–S test and F test performed on the results from various dust perturbation experiments suggest that the perpetual perturbations in dust emissions from remote sources as well as locally from south Asia can significantly modulate the spatial and temporal structure of the ISOs of rainfall across scales during the monsoon season. Substantial changes are also noted in the spatial scales and propagation characteristics of ISOs attributable to the dust emission changes made over local and remote source regions in our idealized simulations. Our results suggest that perturbations in dust emissions over remote locations can substantially modulate the depth and duration of active and break rainfall events in the south Asian monsoon region. Results presented here have implications for better understanding and predicting the SAM rainfall variability at the intra-seasonal scales or at shorter time scales (~ less than a season) under variable dust emissions from remote and local source regions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Razzak H, Ghan SJ (2000) A parameterization of aerosol activation: 2. Multiple aerosol types. J Geophys Res 105:6837–6844. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JD901161
Albani S, Mahowald NM, Perry AT et al (2014) Improved dust representation in the community atmosphere model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 6:541–570. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013MS000279
Annamalai H, Slingo JM (2001) Active/break cycles: diagnosis of the intra-seasonal variability of the Asian Summer Monsoon. Clim Dyn 18:85–102
Benjamin JR, Cornell CA (1970) Probability, statistics, and decision for civil engineers. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Bhawar RL, Rahul PRC (2013) Aerosol–cloud-interaction variability induced by atmospheric brown clouds during the 2009 Indian summer monsoon drought. Aerosol Air Qual Res 13:1384–1391. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2012.11.0329
Bollasina M, Nigam S (2009) Absorbing aerosols and pre-summer monsoon hydroclimate variability over the Indian subcontinent: the challenge in investigating links. Atmos Res 94:338–344
Bretherton CS, Park S (2009) A new moist turbulence parameterization in the community atmosphere model. J Clim 22:3422–3448
Cakmur RV, Miller RL, Perlwitz J et al (2006) Constraining the magnitude of the global dust cycle by minimizing the difference between a model and observations. J Geophys Res 111:D06207. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD005791
Chatterjee P, Goswami BN (2004) Structure, genesis and scale selection of the tropical Quasi-biweekly mode. Q J R Meteorol Soc 130:1171–1194
Chen TC, Chen JM (1993) The 10–20-day mode of the 1979 Indian monsoon: its relation with the time variation of monsoon rainfall. Mon Weather Rev 121:2465–2482
Chowdhury A, Sinha Ray KC, Mukhopadhyay RK (1988) Intra-seasonal cloud variations over India during summer monsoon. Mausam 39:359–366
Dakshinamurthy J, Keshavamurthy R (1976) On oscillations of period around one month in the Indian summer monsoon. Indian J Meteorol Geophys 27:201–203
Gadgil S, Joseph PV (2003) On breaks of the Indian monsoon. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Earth Planet Sci) 112:529–558
Ganguly D, Rasch PJ, Wang H, Yoon JH (2012) Climate response of the South Asian monsoon system to anthropogenic aerosols. J Geophys Res 117:D13209. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD017508
Gettelman A, Liu X, Ghan SJ et al (2010) Global simulations of ice nucleation and ice supersaturation with an improved cloud scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model. J Geophys Res 115:D18216. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013797
Ghan SJ, Zaveri RA (2007) Parameterization of optical properties for hydrated internally-mixed aerosol. J Geophys Res 112:D10201. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007927
Ghan SJ, Leung LR, Easter RC, Abdul-Razzak K (1997) Prediction of cloud droplet number in a general circulation model. J Geophys Res 102:21777–21794. https://doi.org/10.1029/97jd01810
Ghan SJ, Liu X, Easter RC, Zaveri R, Rasch PJ, Yoon JH, Eaton B (2012) Toward a minimal representation of aerosols in climate models: comparative decomposition of aerosol direct, semi-direct and indirect radiative forcing. J Clim 25:6461–6476. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00650.1
Ginoux P, Chin M, Tegen I, Prospero J, Holben B, Dubovik O, Lin SJ (2001) Sources and distributions of dust aerosols simulated with the GOCART model. J Geophys Res 106:20255–20273
Ginoux P, Prospero JM, Gill TE, Hsu NC, Zhao M (2012) Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev Geophys 50:RG3005. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012rg000388
Goswami BN (2005) Intraseasonal variability in the atmosphere-ocean climate system. Springer, Praxis
Goswami BN, AjayaMohan RS (2001) Intra-seasonal oscillations and interannual variability of the Indian Summer Monsoon. J Clim 14:1180–1198
Goswami BN, Shukla J et al (1984) Study of the dynamics of the intertropical convergence zone with a symmetric version of the GLAS climate model. J Atmos Sci 41:5–19
Goswami BN, Venugopal V, Sengupta D, Madhusoodanan MS, Xavier PK (2006) Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 314:1442–1445
Hartmann DL, Michelsen ML (1989) Intraseasonal periodicities in Indian Rainfall. J Atmos Sci 46:2838–2862
Hazra A, Goswami BN, Chen JP (2013) Role of interactions between aerosols radiative effect, dynamics, and cloud microphysics on transitions of monsoon intraseasonal oscillations. J Atmos Sci 70:2073–2087. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-12-0179.1
Hess M, Koepke P, Schult I (1998) Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: the software package OPAC. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:831–844
Hoyos CD, Webster PJ (2007) The role of the intraseasonal variability in the nature of Asian monsoon precipitation. J Clim 20:4402–4424
Hurrell JW et al (2013) The community earth system model: a framework for collaborative research. B Am Meteorol Soc 94:1339–1360. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-1112-00121
Iacono MJ, Delamere JS, Mlawer EJ, Shephard MW, Clough SA, Collins WD (2008) Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J Geophys Res 113:D13103. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD009944
Jin Q, Wei J, Yang ZL (2014) Positive response of Indian summer rainfall to Middle East dust. Geophy Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL059980
Jin Q, Wei J, Yang ZL, Pu B, Huang J (2015) Consistent response of Indian summer monsoon to Middle East dust in observations and simulations. Atmos Chem Phys 15:9897–9915. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-9897-2015
Jin Q, Yang ZL, Wei J (2016a) Seasonal responses of Indian summer monsoon to dust aerosols in the Middle East, India, and China. J Clim 29:6329–6349. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0622.1
Jin Q, Yang ZL, Wei J (2016b) High sensitivity of Indian summer monsoon to Middle East dust absorptive properties. Sci Rep 6:30690. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30690
Karmakar N, Krishnamurti TN (2018) Characteristics of northward propagating intra-seasonal oscillation in the Indian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4268-2
Kok JF, Ridley DA, Zhou Q, Miller RL, Zhao C, Heald CL, Ward DS, Albani S, Haustein K (2017) Smaller desert dust cooling effect estimated from analysis of dust size and abundance. Nat Geosci 10(274–278):2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2912
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni A, Sabade SS, Revadekar JV, Patwardhan SK, Kulkarni JR (2004) Intra-seasonal oscillations during Monsoon 2002 and 2003. Curr Sci 87:325–331
Krishnamurthy V, Shukla J (2000) Intraseasonal and interannual variability of rainfall over India. J Clim 13:4366–4377
Krishnamurthy V, Shukla J (2007a) Intra-seasonal and seasonally persisting patterns of Indian monsoon rainfall. J Clim 20:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3981.1
Krishnamurthy V, Shukla J (2007b) Seasonal persistence and propagation of intra-seasonal patterns over the Indian Monsoon Region. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-007-0300-7
Krishnamurti TN, Ardanuy P (1980) The 10 to 20-day westward propagating mode and “Breaks in the Monsoon”. Tellus A 32:15–26
Krishnamurti TN, Bhalme HN (1976) oscillations of a monsoon system Part I. Observational aspects. J Atmos Sci 33:1937–1954
Krishnan R, Zhang C, Sugi M (2000) Dynamics of breaks in the Indian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 57:1354–1372
Kulkarni A, Sabade SS, Kripalani RH (2006) Intra-seasonal vagaries of the Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. Research report No RR-114 IITM (Pune)
Kumar S, Arora A (2018) On the connection between remote dust aerosol and Indian summer monsoon. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2647-6
Lamarque JF et al (2010) Historical (1850–2000) gridded anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of reactive gases and aerosols: methodology and application. Atmos Chem Phys 10:7017–7039. https://doi.org/10.5194/Acp-10-7017-2010
Lau KM, Kim MK, Kim KM (2006) Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: the role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn 26:855–864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-006-0114-z
Liu X, Penner JE, Ghan SJ, Wang M (2007) Inclusion of ice microphysics in the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model version 3 (CAM3). J Clim 20:4526–4547
Liu X et al (2012) Toward a minimal representation of aerosol in climate models: description and evaluation in the Community Atmosphere Model CAM5. Geosci Model Dev 5:709–739. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-5-709-2012
Magana V, Webster PJ (1996) Atmospheric circulations during active and break periods of the Asian monsoon; Preprints of the Eighth Conference on the Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land System (GOALS). Am Meteorol Soc Atlanta GA
Mahowald NM, Muhs DR, Levis S, Rasch PJ, Yoshioka M, Zender CS, Luo C (2006) Change in atmospheric mineral aerosols in response to climate: last glacial period, preindustrial, modern, and doubled carbon dioxide climates. J Geophys Res 111:D10202. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006653
Mandke S, Sahai AK, Shinde MA, Joseph S, Chattopadhyay R (2007) Simulated changes in active/break spells during the Indian summer monsoon due to enhanced CO2 concentrations: assessment from selected coupled atmosphere–ocean global climate models. Int J Climatol 27:837–859
Manoj MG, Devara PCS, Safai PD, Goswami BN (2011) Absorbing aerosols facilitate transition of Indian monsoon breaks to active spells. Clim Dyn 37:2181–2198
Manoj MG, Devara PCS, Joseph S, Sahai AK (2012) Aerosol indirect effect during the aberrant Indian Summer Monsoon breaks of 2009. Atmos Environ 60:153–163
Morrison H, Gettelman A (2008) A new two-moment bulk stratiform cloud microphysics scheme in the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model (CAM3) Part I: description and numerical tests. J Clim 21:3642–3659
Neale RB et al. (2010) Description of the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model (CAM 5.0). NCAR/TN-486 + STR 289 Natl. Cent For Atmos Res Boulder Colo
Neale RB, Richter JH, Jochum M (2008) The impact of convection on ENSO: from a delayed oscillator to a series of events. J Clim 21:5904–5924
Oleson KW et al. (2010) Technical description of version 4.0 of the Community Land Model (CLM). NCAR Tech Note TN-4781STR 266 Natl Cent for Atmos Res Boulder Colo
Park S, Bretherton CS (2009) The University of Washington shallow convection and moist turbulence schemes and their impact on climate simulations with the Community Atmosphere Model. J Clim 22:3449–3469
Park S, Bretherton CS, Rasch PJ (2014) Integrating cloud processes in the community atmosphere model version 5. J Clim 27:6821–6856
Prospero JM, Ginoux P et al (2002) Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) Absorbing Aerosol Product. Rev Geophys 40:1002. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000RG000095
Rajeevan M et al (2006) High resolution daily gridded rainfall data for the Indian Region: analysis of break and active monsoon spells. Curr Sci 91:296–306
Rajeevan M, Gadgil S, Bhate J (2010) Active and break spells of the Indian Summer monsoon. J Earth Syst Sci 119:229–247
Ramamurthy K (1969) Monsoon of India: Some aspects of the ‘break’ in the Indian southwest monsoon during July and August. Forecasting Manual 1-57 IV 18.3 India Met Dept Poona India
Rasch PJ, Coleman DB (2006) Characteristics of transport using three formulations of atmospheric dynamics in a single GCM framework. J Clim 19:2243–2266
RaviKiran V, Rajeevan M, Rao SVB, Rao PN (2009) Analysis of variations of cloud and aerosol properties associated with active and break spells of Indian summer monsoon using MODIS data. Geophys Res Lett 36:L09706
Ross SM (2004) Introduction to probability and statistics for engineers and scientists, 3rd edn. Elsevier, New York
Scanza et al (2015) Modeling dust as component minerals in the community atmosphere model. Atmos Chem Phys 15:537–561
Sharma D, Miller RL (2017) Revisiting the observed correlation between weekly averaged Indian monsoon precipitation and Arabian Sea aerosol optical depth. Geophys Res Lett 44:10006–10016
Sharmila S, Joseph S, Chattopadhyay R, Sahai AK, Goswami BN (2014) Asymmetry in space–time characteristics of Indian summer monsoon intraseasonal oscillations during extreme years: role of seasonal mean state. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4100
Sikka DR, Gadgil S (1980) On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over Indian longitudes during the Southwest Monsoon. Mon Weather Rev 108:1840–1853
Singh C (2013) Characteristics of monsoon breaks and intraseasonal oscillations over central India during the last half century. Atmos Res 128:120–128
Singh C, Dasgupta P (2017) Unraveling the spatio-temporal structure of the atmospheric and oceanic intra-seasonal oscillations during the contrasting monsoon seasons. Atmos Res 192:48–57
Singh C, Ganguly D, Dash SK (2016) Aerosols and contrasting monsoon conditions over the Himalayan region. Remote Sens Atmos Clouds Precip VI Proc SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.222352
Singh C, Ganguly D, Dash SK (2017a) Dust load and rainfall characteristics and their relationship over the South Asian monsoon region under various warming scenarios. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027451
Singh C, Thomas L, Kumar KK (2017b) Impact of aerosols and cloud parameters on Indian summer monsoon rain at intraseasonal scale: a diagnostic study. Theoret Appl Climatol 127:381–392
Singh C, Ganguly D, Dash SK (2018a) On the dust load and rainfall relationship in South Asia: an analysis from CMIP5. Clim Dyn 50:403–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3617-x
Singh C, Ganguly D, Dash SK (2018b) Investigation of the relationship between natural aerosols and Indian summer monsoon rainfall using a climate model, Climate Change Impacts (Chapter-11) Water Sci Technol Library, vol 82. Springer, Singapore. ISBN 978-981-10-5713-7
Singh C, Ganguly D, Sharma P, Mishra S (2019) Climate response of the south Asian monsoon system to West Asia, Tibetan Plateau and local dust emissions. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-4925-8
Stolz DC, Rutledge SA, Xu W, Pierce JR (2017) Interactions between the MJO, aerosols, and convection over the Central Indian Ocean. J Atmos Sci 74:353–374. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-16-0054.1
Tegen I (2003) Modeling the mineral dust aerosol cycle in the climate system. Quat Sci Rev 22:1821–1834
Tian B, Waliser DE, Kahn Li Q, Yung YL et al (2008) Does the Madden–Julian oscillation influence aerosol variability? J Geophys Res 113:D12215. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009372
Tian B, Waliser DE, Kahn RA, Wong S (2011) Modulation of Atlantic aerosols by the Madden–Julian oscillation. J Geophys Res 116:D15108. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015201
Vernekar AD, Thapliyal V, Kripalani RH, Singh SV, Kirtman B (1993) Global structure of the Madden–Julian oscillations during two contrasting summer monsoon seasons over India. Meteorol Atmos Phys 52:37–47
Vinoj V et al (2014) Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by West Asian dust. Nat Geosci 7:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2107
Webster PJ, Magana VO, Palmer TN, Shukla J, Tomas RA, Yanai M, Yasunari T (1998) Monsoons: process, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J Geophys Res 103:14451–14510
Yasunari T (1979) Cloudiness fluctuation associated with the northern hemisphere summer monsoon. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 57:227–242
Yasunari T (1980) Quasi-stationary appearance of 30–40 day period in the cloudiness fluctuations during summer monsoon over India. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 58:225–229
Yasunari T (1981) Structure of an Indian Summer Monsoon system with around 40-day period. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 59:336–354
Zender CS, Bian H, Newman D (2003a) Mineral dust entrainment and deposition (DEAD) model: description and 1990s dust climatology. J Geophys Res 108:4416. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002775
Zender CS, Newman D, Torres O (2003b) Spatial heterogeneity in aeolian erodibility: uniform, topographic, geomorphic, and hydrologic hypotheses. J Geophys Res 108:4543. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD003039
Zhang GJ, McFarlane NA (1995) Sensitivity of climate simulations to the parameterization of cumulus convection in the Canadian climate centre general circulation mode. Atmos Ocean 33:407–446. https://doi.org/10.1080/07055900.1995.9649539
Acknowledgements
First author is thankful to Group Head MASD, Dean (A) and Director IIRS for providing support to carry out the present research. IIT Delhi and IIRS HPC facilities utilized for the model simulations and analysis respectively are thankfully acknowledged. We thank the Editor and anonymous reviewers whose comments on an earlier version of this manuscript have helped us to bring out this manuscript in the present form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, C., Ganguly, D. & Sharma, P. Impact of West Asia, Tibetan Plateau and local dust emissions on intra-seasonal oscillations of the South Asian monsoon rainfall. Clim Dyn 53, 6569–6593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04944-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04944-5