Abstract
Background
Severe macrocephaly can still be found in developing countries. This condition is usually caused by neglected hydrocephalus and can cause a lot of morbidities. Cranial vault reconstruction cranioplasty is the main treatment option for severe macrocephaly.
Holoprosencephaly is often seen with features of microcephaly. Hydrocephalus should be considered as the main cause in HPE patients with features of macrocephaly. In this report, we present a rare case of cranial vault reduction cranioplasty procedure in patient with severe macrocephaly due to holoprosencephaly and subdural hygroma.
Case description
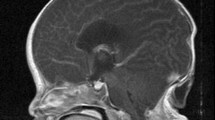
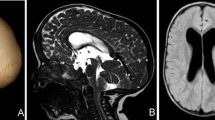
A 4-year-10-month-old Indonesian boy was admitted with head enlargement since birth. He had a history of VP shunt placement when he was 3 months old. But the condition was neglected. Preoperative head CT showed massive bilateral subdural hygroma that compressed brain parenchyma caudally. From the craniometric calculation, the occipital frontal circumference was 70.5 cm with prominent vertex expansion, the distance between nasion to inion was 11.91 cm and the vertical height was 25.59 cm. The preoperative cranial volume was 24.611 cc. The patient underwent subdural hygroma evacuation and cranial vault reduction cranioplasty. The postoperative cranial volume was 10.468 cc.
Conclusion
Subdural hygroma can be a rare cause of severe macrocephaly in holoprosencephaly patients. Cranial vault reduction cranioplasty and subdural hygroma evacuation is still the main treatment option. Our procedure successfully reduces significant cranial volume (57.46% volume reduction).



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed for this report are included in this published article.
References
Accogli A, Geraldo AF, Piccolo G et al (2022) Diagnostic approach to macrocephaly in children. Front Pediatr 9:794069. Published 2022 Jan 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.794069
Jones SG, Samanta D (2022) Macrocephaly. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560786/
Weiss K, Kruszka PS, Levey E, Muenke M (2018) Holoprosencephaly from conception to adulthood. American journal of medical genetics. Part C, Seminars Med Genet 178(2):122–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31624
Raam MS, Solomon BD, Muenke M (2011) Holoprosencephaly: a guide to diagnosis and clinical management. Indian Pediatr 48(6):457–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-011-0078-x
Dubourg C, Bendavid C, Pasquier L, Henry C, Odent S, David V (2007) Holoprosencephaly. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-2-8
Varma A, Mishra GV, Dhande R, Lakhkar BB (2022) Varied presentation of lobar holoprosencephaly as a cause of macrocephaly in a neonate. BMJ Case Rep 15(1):e248024. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2021-248024
Suryaningtyas W, Muhammad A (2020) Case report: cranial vault reduction cranioplasty for severe hydrocephalus. Folia Medica Indonesiana 56:154. https://doi.org/10.20473/fmi.v56i2.21237
Abuzayed B, Alawneh K, Qawasmeh MAL, Raffee L (2019) Modified bilateral Pi craniectomy technique for reduction cranioplasty: novel technique. J Craniofac Surg 30(8):2593–2596. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005688
Iyer RR, Carey CM, Rottgers SA, Tetreault L, Shimony N, Katzenstein J, Ruas E, Tuite GF (2018) Early postnatal cranial vault reduction and fixation surgery for severe hydrocephalic macrocephaly. J Neurosurg Pediatr 21(5):486–495. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.11.PEDS17173
Gage EA, Price AV, Swift DM, Sacco DJ, Fearon JA (2011) Limited reduction cranioplasty for the treatment of hydrocephalic macrocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 128(6):1272–1280. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182221404
Manwaring JC, Truong D, Deukmedjian AR, Carey CM, Storrs BB, Rodriguez LF, Tetreault L, Tuite GF (2013) Cranial reduction and fixation with a resorbable plate combined with cerebrospinal fluid shunting for difficult-to-manage macrocephaly related to hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 11(2):210–213. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.10.PEDS12340
Kohan E, Jackson E, Heller J, Lazareff J, Bradley JP (2010) Correction of hydrocephalic macrocephaly with total cranial vault remodeling and molding helmet therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 125(6):1763–1770. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181cc5a1b
Shen SH, Kwan AL, Wang BL, Guo JF, Tan GW, Chen SF, Liu XY, Liu F, Cai M, Wang ZX (2014) Reduction cranioplasty with the aid of simulated computer imaging for the treatment of hydrocephalic macrocephaly. J Neurosurg Pediatr 13(2):133–139. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.10.PEDS12573
Saleh E, Govshievich A, Justino J, Weil AG, Borsuk DE (2020) The Use of Virtual Surgical Planning for Reduction Cranioplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(1):e2565. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002565. PMID: 32095391; PMCID: PMC7015603
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the staff of the Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ahmad Data Dariansyah contributed to the conceptualization, data collection, writing, and editing of the study. Wihasto Suryaningtyas and Muhammad Arifin Parenrengi contributed to reviewing, editing, and finalizing the manuscript of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dariansyah, A.D., Suryaningtyas, W. & Parenrengi, M.A. Cranial vault reduction cranioplasty for severe macrocephaly due to holoprosencephaly and subdural hygroma: a case report. Childs Nerv Syst 39, 2537–2541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-06001-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-06001-3