Abstract
Introduction
Long-term impact of benign external hydrocephalus (BEH) on cognition is largely unknown, and indication for neurosurgical CSF diversion procedure is debated. This study reports neuropsychological and psychosocial function in operated and non-operated BEH children.
Methods
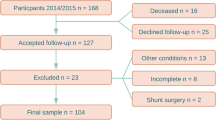
Eighty-six children (76 males) between 8 and 18 years (mean 13.9) diagnosed with BEH before 12 months were included, of whom 30.2 % were operated. Participants completed neuropsychological tests and questionnaires covering quality of life (PedsQL) and executive function (BRIEF).
Results
Both operated and non-operated BEH children performed significantly below normative means on several neuropsychological tests. The children scored themselves higher than the norm average on PedsQL; however, the parents reported life quality comparable to other children.
Operated children performed poorer compared with non-operated children on tests of psychomotor speed, attention span, executive function, motor speed and coordination, and on the BRIEF subscale Monitoring. Operated children, but not their parents, reported more problems on PedsQL subscale School than non-operated children.
Discussion
Children with BEH display long-term subtle neurocognitive difficulties. Non-operated children performed significantly better on some neuropsychological measures and reported less psychosocial problems. This difference may be caused by a selection bias: neurosurgical intervention was more likely in children with clinically more pronounced symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rekate HL (2009) A contemporary definition and classification of hydrocephalus. Semin Pediatr Neurol 16:9–15
Dandy WE (1946) Treatment of an unusual subdural hydroma (external hydrocehalus). Arch Surg 52:421–428
Zahl SM, Egge A, Helseth E et al (2011) Benign external hydrocephalus: a review, with emphasis on management. Neurosurg Rev 34:417–432
Andersson H, Elfverson J, Svendsen P (1984) External hydrocephalus in infants. Childs Brain 11:398–402
Boaz JC, Edwards-Brown MK (1999) Hydrocephalus in children: neurosurgical and neuroimaging concerns. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 9:73–91
Odita JC (1992) The widened frontal subarachnoid space. a CT comparative study between macrocephalic, microcephalic, and normocephalic infants and children. Childs Nerv Syst 8:36–39
Laubscher B, Deonna T, Uske A et al (1990) Primitive megalencephaly in children: natural history, medium term prognosis with special reference to external hydrocephalus. Eur J Pediatr 149:502–507
Muenchberger H, Assaad N, Joy P et al (2006) Idiopathic macrocephaly in the infant: long-term neurological and neuropsychological outcome. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1242–1248
Yew AY, Maher CO, Muraszko KM et al (2011) Long-term health status in benign external hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 47:1–6
Zahl SM, Wester K (2008) Routine measurement of head circumference as a tool for detecting intracranial expansion in infants: what is the gain? a nationwide survey. Pediatrics 121:e416–e420
Delis DC, Kaplan E, Kramer JH (2001) Delis-Kaplan executive function system. NCS Pearson, Inc., San Antonio
Talley JL (1992) Childrens auditory verbal learning test - professional manual, 2nd edn. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Wechsler D (2009) Wechsler intelligence scale for children-fourth edition. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wechsler D (2011) Wechsler adult intelligence scale, 4th edn. Pearson, San Antonio
Trites RL (1977) Neuropsychological test manual. grooved pegboard. Royal Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa
Wechsler D (1999) Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence. Harcourt Assessment, Inc., San Antonio
Gioia G, Isquith PK, Guy SC et al (2000) Behavior rating inventory of executive function - professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources Inc., Lutz
Gioia GA, Isquith PK (2004) Ecological assessment of executive function in traumatic brain injury. Dev Neuropsychol 25:135–158
Fallmyr O, Egeland J (2011) Psychometric properties of the Norwegian version of BRIEF. J Norwegian Psychol Assoc 48:339–343
Varni JW, Seid M, Kurtin PS (2001) PedsQL 4.0: reliability and validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 generic core scales in healthy and patient populations. Med Care 39:800–812
Reinfjell T, Diseth TH, Veenstra M (2006) Measuring health-related quality of life in young adolescents: reliability and validity in the Norwegian version of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 4.0 (PedsQL) generic core scales. Health Qual Life Outcomes 4:61
Huang IC, Thompson LA, Chi YY et al (2009) The linkage between pediatric quality of life and health conditions: establishing clinically meaningful cutoff scores for the PedsQL. Value Health 12:773–781
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power and analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale
Strauss E, Sherman EMS, Spreen O (2006) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration, norms and commentary, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Anderson VA, Anderson P, Northam E et al (2002) Relationships between cognitive and behavioral measures of executive function in children with brain disease. Child Neuropsychol 8:231–240
Follmer DJ, Stefanou CR (2014) Examining the correspondence between a direct and an indirect measure of executive functions: implications for school-based assessment. The School Psychologist 68(3)
Vriezen ER, Pigott SE (2002) The relationship between parental report on the BRIEF and performance-based measures of executive function in children with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Child Neuropsychol 8:296–303
Anderson V, Jacobs R, Anderson P (2008) Executive functions and the frontal
Authors’ contribution
The first two authors (RM and LNR) should be regarded as first authors. The last two authors should be regarded as senior authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
In accordance with the ethical guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration, an informed consent form was signed by all participants or their caregiver prior to testing. The study was approved by the Regional Committee for Medical Research Ethics.
Ethics
No ethical conflict and no financial support were present or received upon writing, editing, or sending the present work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Financial support
This study was supported by a grant from the Grieg Foundation, Bergen, Norway. Sverre Morten Zahl was supported by a Ph.D. grant from the Western Norway Regional Health Authority, project no. 911439.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikkelsen, R., Rødevand, L.N., Wiig, U.S. et al. Neurocognitive and psychosocial function in children with benign external hydrocephalus (BEH)—a long-term follow-up study. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 91–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3267-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3267-z