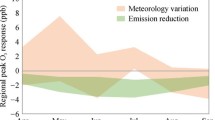
Abstract
China has been experiencing widespread air pollution due to rapid industrialization and urbanization in recent decades. The two major concerns of ambient air quality in China are particulate matter (PM) and tropospheric ozone (O3). With the implementation of air pollution prevention and control actions in the last five years, the PM pollution in China has been substantially reduced. In contrast, under the conditions of the urban air pollution complex, the elevated O3 levels in city clusters of eastern China, especially in warm seasons, have drawn increasing attention. Emissions of air pollutants and their precursors not only contribute to regional air quality, but also alter climate. Climate change in turn can change chemical processes, long-range transport, and local meteorology that influence air pollution. Compared to PM, less is known about O3 pollution and its climate effects over China. Here, we present a review of the main findings from the literature over the period 2011–18 with regard to the characteristics of O3 concentrations in China and the mechanisms that drive its interannual to decadal variations, aiming to identify robust conclusions that may guide decision-making for emissions control and to highlight critical knowledge gaps. We also review regional and global modeling studies that have investigated the impacts of tropospheric O3 on climate, as well as the projections of future tropospheric O3 owing to climate and/or emission changes.
摘 要
近几十年随着经济快速发展和工业化、城市化进程的加快, 中国的大气环境也因日益突出的空气污染问题而备受关注.自2013年大气污染防治行动计划的实施开展, 全国以细颗粒物(PM2.5)为首要污染物的空气质量总体得到了一定的改善, 但空气污染的形势依然严峻.在当前大气复合污染的背景下, 中国东部的城市群区域臭氧(O3)污染问题显现, 尤其在夏季, 对流层臭氧浓度呈升高态势, 屡屡成为继PM2.5之后的首要空气污染物.然而, 相比于颗粒物污染的研究, 我国在臭氧污染及其气候效应方面开展的研究相对较少.旨在科学认识中国臭氧污染变化规律及影响机制, 同时也为国家及地区制定合理的排放控制规划提供参考, 本文对2011-2018年期间中国地区取得的主要研究进展进行了回顾, 总结了中国对流层臭氧尤其是近地面臭氧污染的时空分布特征和变化趋势, 归纳了影响臭氧浓度年际、年代际变化的主要驱动因素及过程.此外, 概述了对流层臭氧对中国气候的影响及未来气候与排放变化对臭氧浓度的影响.最后, 本文还提出了在该领域未来需要进一步研究的科学问题和研究方向.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth, E. A., C. R. Yendrek, S. Sitch, W. J. Collins, and L. D. Emberson, 2012: The effects of tropospheric ozone on net primary productivity and implications for climate change. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 63, 637–661, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103829.
An, J. L., J. N. Zou, J. X. Wang, X. Lin, and B. Zhu, 2015: Differences in ozone photochemical characteristics between the megacity Nanjing and its suburban surroundings, Yangtze River Delta, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 19 607–19 617, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5177-0.
Berntsen, T. K., G. Myhre, F. Stordal, and I. S. A. Isaksen, 2000: Time evolution of tropospheric ozone and its radiative forcing. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 105, 8915–8930, https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JD901139.
Chang, K.-L., I. Petropavlovskikh, O. R. Cooper, M. G. Schultz, and T. Wang, 2017: Regional trend analysis of surface ozone observations from monitoring networks in eastern North America, Europe and East Asia. Elementa Science of the Anthropocene, 5, 50, https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.243.
Chang, W. Y., and H. Liao, 2009: Anthropogenic direct radiative forcing of tropospheric ozone and aerosols from 1850 to 2000 estimated with IPCC AR5 emissions inventories. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2, 201–207, https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2009.11446804.
Chang, W. Y., H. Liao, and H. J. Wang, 2009: Climate responses to direct radiative forcing of anthropogenic aerosols, tropospheric ozone, and long-lived greenhouse gases in eastern China over 1951–2000. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 748–762, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9032-4.
Chen, W., L. Yan, and H. M. Zhao, 2015: Seasonal variations of atmospheric pollution and air quality in Beijing. Atmosphere, 6, 1753–1770, https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6111753.
Cooper, O. R., and Coauthors, 2014: Global distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone: An observation-based review. Elementa Science of the Anthropocene, 2, 000029, https://doi.org/10.12952/journal.elementa.000029.
Ding, A. J., T. Wang, V. Thouret, J. P. Cammas, and P. Nédélec, 2008: Tropospheric ozone climatology over Beijing: Analysis of aircraft data from the MOZAIC program. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 8, 1–13, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-8-1-2008.
Ding, A. J., and Coauthors, 2013: Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13, 5813–5830, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-5813-2013.
Doherty, R. M., and Coauthors, 2013: Impacts of climate change on surface ozone and intercontinental ozone pollution: A multi-model study. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 118, 3744–3763, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50266.
Dufour, G., and Coauthors, 2018: Lower tropospheric ozone over the North China Plain: Variability and trends revealed by IASI satellite observations for 2008–2016. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 16 439–16 459, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-16439-2018.
Feng, T., and Coauthors, 2016: Summertime ozone formation in Xi’an and surrounding areas, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 4323–4342, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-4323-2016.
Feng, Z. Z., E. Z. Hu, X. K. Wang, L. J. Jiang, and X. J. Liu, 2015: Ground-level O3 pollution and its impacts on food crops in China: A review. Environmental Pollution, 199, 42–48, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.016.
Fiore, A. M., and Coauthors, 2012: Global air quality and climate. Chemical Society Reviews, 41, 6663–6683, https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35095e.
Fiore, A. M., V. Naik, and E. M. Leibensperger, 2015: Air quality and climate connections. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 65, 645–685, https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2015.1040526.
Fu, Y., and H. Liao, 2012: Simulation of the interannual variations of biogenic emissions of volatile organic compounds in China: Impacts on tropospheric ozone and secondary organic aerosol. Atmos. Environ., 59, 170–185, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.05.053.
Fu, Y., and H. Liao, 2014: Impacts of land use and land cover changes on biogenic emissions of volatile organic compounds in China from the late 1980s to the mid-2000s: implications for tropospheric ozone and secondary organic aerosol. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 66, 24987.
Fu, Y., and A. P. K. Tai, 2015: Impact of climate and land cover changes on tropospheric ozone air quality and public health in East Asia between 1980 and 2010. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 10 093–10 106, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-10093-2015.
Gaudel, A., and Coauthors, 2018: Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone relevant to climate and global atmospheric chemistry model evaluation. Elementa Science of the Anthropocene, 6, 39, https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.291.
Geng, F., X. Tie, A. Guenther, G. Li, J. Cao, and P. Harley, 2011: Effect of isoprene emissions from major forests on ozone formation in the city of Shanghai, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 10 449–10 459.
Guenther, A. B., X. Jiang, C. L. Heald, T. Sakulyanontvittaya, T. Duhl, L. K. Emmons, and X. Wang, 2012: The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): An extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions. Geoscientific Model Development, 5, 1471–1492, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-5-1471-2012.
Hayashida, S., X. Liu, A. Ono, K. Yang, and K. Chance, 2015: Observation of ozone enhancement in the lower troposphere over East Asia from a space-borne ultraviolet spectrometer. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 9865–9881, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-9865-2015.
Hong, C. P., Q. Zhang, K. B. He, D. B. Guan, M. Li, F. Liu, and B. Zheng, 2017: Variations of China’s emission estimates: Response to uncertainties in energy statistics. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 1227–1239, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-1227-2017.
Hu, J. L., J. J. Chen, Q. Ying, and H. L. Zhang, 2016: One-year simulation of ozone and particulate matter in China using WRF/CMAQ modeling system. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 10 333–10 350, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-10333-2016.
Hu, J., and Coauthors, 2018: An important mechanism of regional O3 transport for summer smog over the Yangtze River Delta in Eastern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 16 239–16 251, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-16239-2018.
Huang, J., and Coauthors, 2015: Origin of springtime ozone enhancements in the lower troposphere over Beijing: In situ measurements and model analysis. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 5161–5179, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-5161-2015.
Jacob, D. J., 2000: Heterogeneous chemistry and tropospheric ozone. Atmos. Environ., 34, 2131–2159, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00462-8.
Jacob, D. J., and D. A. Winner, 2009: Effect of climate change on air quality. Atmos. Environ., 43, 51–63, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.09.051.
Jeong, J. I., and R. J. Park, 2013: Effects of the meteorological variability on regional air quality in East Asia. Atmos. Environ., 69, 46–55, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.061.
Kurokawa, J., T. Ohara, T. Morikawa, S. Hanayama, G. Janssens-Maenhout, T. Fukui, K. Kawashima, and H. Akimoto, 2013: Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 2. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13, 11 019–11 058, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-11019-2013.
Lee, J. B., and Coauthors, 2015: Projections of summertime ozone concentration over East Asia under multiple IPCC SRES emission scenarios. Atmos. Environ., 106, 335–346, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.019.
Li, B. G., and Coauthors, 2016a: The contribution of China’s emissions to global climate forcing. Nature, 531, 357–361, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17165.
Li, D., and J. C. Bian, 2015: Observation of a summer tropopause fold by ozonesonde at Changchun, China: Comparison with reanalysis and model simulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 32, 1354–1364, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-015-5022-x.
Li, G. H., and Coauthors, 2017a: Widespread and persistent ozone pollution in eastern China during the non-winter season of 2015: Observations and source attributions. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 2759–2774, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-2759-2017.
Li, J., and Coauthors, 2011: Impacts of aerosols on summertime tropospheric photolysis frequencies and photochemistry over Central Eastern China. Atmos. Environ., 45, 1817–1829, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.01.016.
Li, J. F., and Coauthors, 2014: Fast increasing of surface ozone concentrations in Pearl River Delta characterized by a regional air quality monitoring network during 2006–2011. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26, 23–36, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60377-0.
Li, K., D. J. Jacob, H. Liao, L. Shen, Q. Zhang, and K. H. Bates, 2019: Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116, 422–427, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1812168116.
Li, M. M., Y. Song, M. X. Liu, H. Yao, X. Huang, X. S. Wang, and Y. H. Zhang, 2015: Impacts of decadal variations in natural emissions due to land-cover changes on ozone production in southern China. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 67, 27676, https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v67.27676.
Li, M. M., Y. Song, Z. C. Mao, M. X. Liu, and X. Huang, 2016b: Impacts of thermal circulations induced by urbanization on ozone formation in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ., 127, 382–392, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.10.075.
Li, M., and Coauthors, 2017b: MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 935–963, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-935-2017.
Li, S., and Coauthors, 2018a: Impact of East Asian summer monsoon on surface ozone pattern in China. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 123, 1401–1411, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027190.
Li, S., T. J. Wang, P. Zanis, D. Melas, and B. L. Zhuang, 2018b: Impact of tropospheric ozone on summer climate in China. J. Meteor. Res., 32, 279–287, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-018-7094-x.
Li, Y., A. K. H. Lau, J. C. H. Fung, J. Y. Zheng, and S. Liu, 2013: Importance of NOx control for peak ozone reduction in the Pearl River Delta region. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 118, 9428–9443, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50659.
Liao, H., and J. H. Seinfeld, 2005: Global impacts of gas-phase chemistry-aerosol interactions on direct radiative forcing by anthropogenic aerosols and ozone. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 110, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD005907.
Liao, J. B., and Coauthors, 2015: WRF/Chem modeling of the impacts of urban expansion on regional climate and air pollutants in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ., 106, 204–214, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.01.059.
Liao, Z. H., M. Gao, J. R. Sun, and S. J. Fan, 2017: The impact of synoptic circulation on air quality and pollution-related human health in the Yangtze River Delta region. Science of the Total Environment, 607–608, 838–846, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.031.
Lim, S. S., and Coauthors, 2012: A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet, 380, 2224–2260.
Lin, M. Y., A. M. Fiore, L. W. Horowitz, A. O. Langford, S. J. Oltmans, D. Tarasick, and H. E. Rieder, 2015: Climate variability modulates western US ozone air quality in spring via deep stratospheric intrusions. Nature Communications, 6, 7105, https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8105.
Liu, H., X. M. Wang, J. M. Pang, and K. B. He, 2013a: Feasibility and difficulties of China’s new air quality standard compliance: PRD case of PM2.5 and ozone from 2010 to 2025. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13, 12 013–12 027, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-12013-2013.
Liu, J., D. Wu, S. J. Fan, Z. H. Liao, and T. Deng, 2017: Impacts of precursors and meteorological factors on ozone pollution in Pearl River Delta. China Environmental Science, 37, 813–820, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.03.002. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu, Q., K. S. Lam, F. Jiang, T. J. Wang, M. Xie, B. L. Zhuang, and X. Y. Jiang, 2013b: A numerical study of the impact of climate and emission changes on surface ozone over South China in autumn time in 2000–2050. Atmos. Environ., 76, 227–237, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.01.030.
Lou, S. J., H. Liao, and B. Zhu, 2014: Impacts of aerosols on surface-layer ozone concentrations in China through heterogeneous reactions and changes in photolysis rates. Atmos. Environ., 85, 123–138, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.12.004.
Lou, S. J., H. Liao, Y. Yang, and Q. Mu, 2015: Simulation of the interannual variations of tropospheric ozone over China: Roles of variations in meteorological parameters and anthropogenic emissions. Atmos. Environ., 122, 839–851, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.081.
Lu, K. D., and Coauthors, 2012: Observation and modelling of OH and HO2 concentrations in the Pearl River Delta 2006: A missing OH source in a VOC rich atmosphere. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 1541–1569, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-1541-2012.
Lu, X., and Coauthors, 2018: Severe surface ozone pollution in China: A global perspective. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 5, 487–494, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00366.
Ma, J. Z., X. B. Xu, C. S. Zhao, and P. Yan, 2012: A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China: Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29, 1006–1026, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-1188-7.
Ma, Z. Q., X. L. Zhang, J. Xu, X. J. Zhao, and W. Meng, 2011: Characteristics of ozone vertical profile observed in the boundary layer around Beijing in autumn. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 1316–1324, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60557-8.
Ma, Z. Q., J. Xu, W. J. Quan, Z. Y. Zhang, W. L. Lin, and X. B. Xu, 2016: Significant increase of surface ozone at a rural site, north of eastern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 3969–3977, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-3969-2016.
Monks, P. S., 2005: Gas-phase radical chemistry in the troposphere. Chemical Society Reviews, 34, 376–395, https://doi.org/10.1039/b307982c.
Monks, P. S., and Coauthors, 2015: Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 8889–8973, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-8889-2015.
Myhre, G., and Coauthors, 2013: Anthropogenic and natural radiative forcing. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, T. F. Stocker et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press.
Myhre, G., and Coauthors, 2017: Multi-model simulations of aerosol and ozone radiative forcing due to anthropogenic emission changes during the period 1990–2015. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 2709–2720, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-2709-2017.
Newell, R. E., and M. J. Evans, 2000: Seasonal changes in pollutant transport to the North Pacific: The relative importance of Asian and European sources. Geophys. Res. Lett., 27, 2509–2512, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011501.
Ohara, T., H. Akimoto, J. Kurokawa, N. Horii, K. Yamaji, X. Yan, and T. Hayasaka, 2007: An Asian emission inventory of anthropogenic emission sources for the period 1980–2020. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 7, 4419–4444, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-4419-2007.
Ou, J. M., and Coauthors, 2016: Ambient ozone control in a photochemically active region: Short-term despiking or long-term attainment? Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 5720–5728, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00345.
Peñuelas, J., and M. Staudt, 2010: BVOCs and global change. Trends in Plant Science, 15, 133–144, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.12.005.
Pu, X., T. J. Wang, X. Huang, D. Melas, P. Zanis, D. K. Papanastasiou, and A. Poupkou, 2017: Enhanced surface ozone during the heat wave of 2013 in Yangtze River Delta region, China. Science of the Total Environment, 603–604, 807–816, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.056.
Qu, Y. W., and Coauthors, 2018: Influence of atmospheric particulate matter on ozone in Nanjing, China: Observational study and mechanistic analysis. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 35, 1381–1395, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-018-8027-4.
Schnell, J. L., and M. J. Prather, 2017: Co-occurrence of extremes in surface ozone, particulate matter, and temperature over eastern North America. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114, 2854–2589, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1614453114.
Schultz, M. G., and Coauthors, 2017: Tropospheric ozone assessment report: Database and metrics data of global surface ozone observations. Elementa Science of the Anthropocene, 5, 58, https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.244.
Seinfeld, J. H., and S. N. Pandis, 2006: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. 2nd ed. John Wiley and Sons.
Shen, L., L. J. Mickley, and A. P. K. Tai, 2015: Influence of synoptic patterns on surface ozone variability over the eastern United States from 1980 to 2012. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 10 925–10 938, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-10925-2015.
Shi, C. Z., and Coauthors, 2015: A study of aerosol optical properties during ozone pollution episodes in 2013 over Shanghai, China. Atmospheric Research, 153, 235–249, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.09.002.
Shindell, D., and Coauthors, 2013: Attribution of historical ozone forcing to anthropogenic emissions. Nature Climate Change, 3, 567–570, https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1835.
Skeie, R. B., T. K. Berntsen, G. Myhre, K. Tanaka, M. M. Kvalevåg, and C. R. Hoyle, 2011: Anthropogenic radiative forcing time series from pre-industrial times until 2010. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 11 827–11 857, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-11827-2011.
Sofen, E. D., D. Bowdalo, and M. J. Evans, 2016: How to most effectively expand the global surface ozone observing network. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 1445–1457, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-1445-2016.
Søvde, O. A., C. R. Hoyle, G. Myhre, and I. S. A. Isaksen, 2011: The HNO3 forming branch of the HO2 + NO reaction: Pre-industrial-to-present trends in atmospheric species and radiative forcings. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 8929–8943, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-8929-2011.
Stohl, A., and Coauthors, 2003: Stratosphere-troposphere exchange: A review, and what we have learned from STACCATO. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 108, 8516, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002490.
Streets, D. G., and Coauthors, 2003: An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 108, 8809, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD003093.
Streets, D. G., Q. Zhang, L. T. Wang, K. B. He, J. M. Hao, Y. Wu, Y. H. Tang, and G. R. Carmichael, 2006: Revisiting China’s CO emissions after the Transport and Chemical Evolution over the Pacific (TRACE-P) mission: Synthesis of inventories, atmospheric modeling, and observations. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos.111, D14306, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007118.
Sun, L., and Coauthors, 2016: Significant increase of summertime ozone at Mount Tai in Central Eastern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 10 637–10 650, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-10637-2016.
Tai, A. P. K., L. J. Mickley, C. L. Heald, and S. L. Wu, 2013: Effect of CO2 inhibition on biogenic isoprene emission: Implications for air quality under 2000 to 2050 changes in climate, vegetation, and land use. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, 3479–3483, https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50650.
Tang, G., Y. Wang, X. Li, D. Ji, S. Hsu, and X. Gao, 2012: Spatial-temporal variations in surface ozone in Northern China as observed during 2009–2010 and possible implications for future air quality control strategies. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 2757–2776, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-2757-2012.
Tang, H. Y., G. Liu, J. G. Zhu, Y. Han, and K. Kobayashi, 2013: Seasonal variations in surface ozone as influenced by Asian summer monsoon and biomass burning in agricultural fields of the northern Yangtze River Delta. Atmospheric Research, 122, 67–76, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.10.030.
Tao, H. R., J. Xing, H. S. Zhou, X. Chang, G. J. Li, L. Chen, and J. H. Li, 2018: Impacts of land use and land cover change on regional meteorology and air quality over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ., 189, 9–21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.06.033.
Unger, N., D. T. Shindell, D. M. Koch, and D. G. Streets, 2006: Cross influences of ozone and sulfate precursor emissions changes on air quality and climate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 4377–4380, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508769103.
Verstraeten, W. W., J. L. Neu, J. E. Williams, K. W. Bowman, J. R. Worden, and K. F. Boersma, 2015: Rapid increases in tropospheric ozone production and export from China. Nature Geoscience, 8, 690–695, https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2493.
Wang, J., D. J. Allen, K. E. Pickering, Z. Q. Li, and H. He, 2016a: Impact of aerosol direct effect on East Asian air quality during the EAST-AIRE campaign. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 121, 6534–6554, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JD025108.
Wang, S. X., and Coauthors, 2014: Emission trends and mitigation options for air pollutants in East Asia. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14, 6571–6603, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-6571-2014.
Wang, T., X. L. Wei, A. J. Ding, C. N. Poon, K. S. Lam, Y. S. Li, L. Y. Chan, and M. Anson, 2009: Increasing surface ozone concentrations in the background atmosphere of Southern China, 1994–2007. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 9, 6217–6227, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-6217-2009.
Wang, T., and Coauthors, 2016b: Observations of nitryl chloride and modeling its source and effect on ozone in the planetary boundary layer of southern China. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 121, 2476–2489, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024556.
Wang, T., L. K. Xue, P. Brimblecombe, Y. F. Lam, L. Li, and L. Zhang, 2017a: Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Science of the Total Environment, 575, 1582–1596, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.081.
Wang, W. G., J. Wu, H. N. Liu, S. C. Guo, X. M. Chen, and Y. Luo, 2005: Researches on the influence of pollution emission on tropospheric ozone variation and radiation over China and its adjacent area. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 29, 734–746, https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2005.05.07. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, W. N., and Coauthors, 2017b: Assessing spatial and temporal patterns of observed ground-level ozone in China. Scientific Reports, 7, 3651, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03929-w.
Wang, X., Z. X. Shen, J. J. Cao, L. M. Zhang, L. Liu, J. J. Li, S. X. Liu, and Y. F. Sun, 2012: Characteristics of surface ozone at an urban site of Xi’an in Northwest China. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14, 116–126, https://doi.org/10.1039/C1EM10541H.
Wang, Y., and Coauthors, 2017c: Long-term O3-precursor relationships in Hong Kong: Field observation and model simulation. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 10 919–10 935, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-10919-2017.
Wang, Y. H., B. Hu, G. Q. Tang, D. S. Ji, H. X. Zhang, J. H. Bai, X. K. Wang, and Y. S. Wang, 2013a: Characteristics of ozone and its precursors in Northern China: A comparative study of three sites. Atmospheric Research, 132–133, 450–459, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.04.005.
Wang, Y. X., L. L. Shen, S. L. Wu, L. Mickley, J. W. He, and J. M. Hao, 2013b: Sensitivity of surface ozone over China to 2000–2050 global changes of climate and emissions. Atmos. Environ., 75, 374–382, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.04.045.
Wang, Z., and Coauthors, 2015: Ground-level ozone in urban Beijing over a 1-year period: Temporal variations and relationship to atmospheric oxidation. Atmospheric Research, 164–165, 110–117.
Wei, W., Z. F. Lv, S. Y. Cheng, L. L. Wang, D. S. Ji, Y. Zhou, L. H. Han, and L. T. Wang, 2015: Characterizing ozone pollution in a petrochemical industrial area in Beijing, China: A case study using a chemical reaction model. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 377, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4620-5.
Wu, R. R., Y. Bo, J. Li, L. Y. Li, Y. Q. Li, and S. D. Xie, 2016: Method to establish the emission inventory of anthropogenic volatile organic compounds in China and its application in the period 2008–2012. Atmos. Environ., 127, 244–254, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.12.015.
Xia, Y. M., Y. Zhao, and C. P. Nielsen, 2016: Benefits of China’s efforts in gaseous pollutant control indicated by the bottom-up emissions and satellite observations 2000–2014. Atmos. Environ., 136, 43–53, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.04.013.
Xie, B., H. Zhang, Z. L. Wang, S. Y. Zhao, and Q. Fu, 2016: A modeling study of effective radiative forcing and climate response due to tropospheric ozone. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 33, 819–828, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-016-5193-0.
Xing, J., S. X. Wang, C. Jang, Y. Zhu, and J. M. Hao, 2011: Nonlinear response of ozone to precursor emission changes in China: A modeling study using response surface methodology. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 5027–5044, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-5027-2011.
Xing, J., R. Mathur, J. Pleim, C. Hogrefe, C. M. Gan, D. C. Wong, C. Wei, and J. D. Wang, 2015: Air pollution and climate response to aerosol direct radiative effects: A modeling study of decadal trends across the northern hemisphere. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 120, 12 221–12 236, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023933.
Xing, J., and Coauthors, 2017: Impacts of aerosol direct effects on tropospheric ozone through changes in atmospheric dynamics and photolysis rates. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 9869–9883, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-9869-2017.
Xu, J., and Coauthors, 2011a: Measurements of ozone and its precursors in Beijing during summertime: Impact of urban plumes on ozone pollution in downwind rural areas. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 12 241–12 252, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-12241-2011.
Xu, J., Y. H. Zhang, S. Q. Zheng, and Y. J. He, 2012: Aerosol effects on ozone concentrations in Beijing: A model sensitivity study. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24, 645–656, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60811-5.
Xu, W. Y., and Coauthors, 2011b: Characteristics of pollutants and their correlation to meteorological conditions at a suburban site in the North China Plain. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 4353–4369, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-4353-2011.
Xu, W. Y., W. L. Lin, X. B. Xu, J. Tang, J. Q. Huang, H. Wu, and X. C. Zhang, 2016: Long-term trends of surface ozone and its influencing factors at the Mt Waliguan GAW station, China — Part 1: Overall trends and characteristics. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 6191–6205, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-6191-2016.
Xu, W. Y., X. B. Xu, M. Y. Lin, W. L. Lin, D. Tarasick, J. Tang, J. Z. Ma, and X. D. Zheng, 2018: Long-term trends of surface ozone and its influencing factors at the Mt Waliguan GAW station, China — Part 2: The roles of anthropogenic emissions and climate variability. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 773–798, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-773-2018.
Xu, X. B., and W. L. Lin, 2011c: Trends of Tropospheric Ozone over China Based on Satellite Data (1979-2005). Advances in Climate Change Research, 2(1), 43–48, https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00043.
Xue, L. K., T. Wang, P. K. K. Louie, C. W. Y. Luk, D. R. Blake, and Z. Xu, 2014: Increasing external effects negate local efforts to control ozone air pollution: A case study of Hong Kong and implications for other Chinese Cities. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 10 769–10 775, https://doi.org/10.1021/es503278g.
Yan, Y. Y., J. T. Lin, and C. L. He, 2018: Ozone trends over the United States at different times of day. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 1185–1202, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-1185-2018.
Yang, Y., H. Liao, and J. Li, 2014a: Impacts of the East Asian summer monsoon on interannual variations of summertime surface-layer ozone concentrations over China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14, 6867–6879, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-6867-2014.
Yang, Y., H. Liao, and S. J. Lou, 2014b: Simulated impacts of sulfate and nitrate aerosol formation on surface-layer ozone concentrations in China. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 7, 441–446, https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1674-2834.14.0033.
Zhang, H., B. Xie, and Z. Wang, 2018: Effective radiative forcing and climate response to short-lived climate pollutants under different scenarios. Earth’s Future, 6, 857–866, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EF000832.
Zhang, Q., and Coauthors, 2009: Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 9, 5131–5153, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-5131-2009.
Zhang, Q., K. B. He, and H. Huo, 2012a: Cleaning China’s air. Nature, 484, 161–162, https://doi.org/10.1038/484161a.
Zhang, Q., and Coauthors, 2014: Variations of ground-level O3 and its precursors in Beijing in summertime between 2005 and 2011. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14, 6089–6101, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-6089-2014.
Zhang, X. Y., Y. Q. Wang, T. Niu, X. C. Zhang, S. L. Gong, Y. M. Zhang, and J. Y. Sun, 2012b: Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 779–799, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-779-2012.
Zhang, Y., H. T. Mao, A. J. Ding, D. R. Zhou, and C. B. Fu, 2013: Impact of synoptic weather patterns on spatio-temporal variation in surface O3 levels in Hong Kong during 1999–2011. Atmos. Environ., 73, 41–50, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.02.047.
Zhang, Y. Q., O. R. Cooper, A. Gaudel, A. M. Thompson, P. Nédélec, S.-Y. Ogino, and J. J. West, 2016: Tropospheric ozone change from 1980 to 2010 dominated by equatorward redistribution of emissions. Nature Geoscience, 9, 875–879, https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2827.
Zhao, B., and Coauthors, 2013: NOx emissions in China: Historical trends and future perspectives. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13, 9869–9897, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-9869-2013.
Zhao, W., S. J. Fan, H. Guo, B. Gao, J. R. Sun, and L. G. Chen, 2016: Assessing the impact of local meteorological variables on surface ozone in Hong Kong during 2000–2015 using quantile and multiple line regression models. Atmos. Environ., 144, 182–193, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.08.077.
Zhao, Z. J., and Y. X. Wang, 2017: Influence of the West Pacific subtropical high on surface ozone daily variability in summertime over eastern China. Atmos. Environ., 170, 197–204, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.09.024.
Zheng, B., and Coauthors, 2018: Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 14 095–14 111, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-14095-2018.
Zheng, J. Y., L. J. Zhong, T. Wang, P. K. K. Louie, and Z. C. Li, 2010: Ground-level ozone in the Pearl River Delta region: Analysis of data from a recently established regional air quality monitoring network. Atmos. Environ., 44, 814–823, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.11.032.
Zhou, D. R., and Coauthors, 2013: Impacts of the East Asian monsoon on lower tropospheric ozone over coastal South China. Environmental Research Letters, 8, 044011, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/4/044011.
Zhu, J., and H. Liao, 2016: Future ozone air quality and radiative forcing over China owing to future changes in emissions under the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs). J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 121, 1978–2001, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023926.
Zou, Y., and Coauthors, 2015: Characteristics of 1 year of observational data of VOCs, NOx and O3 at a suburban site in Guangzhou, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 6625–6636.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 91744311 and 91544219), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0600203) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41405138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Article Highlights
• Available data reveal an increasing trend of tropospheric O3 in China with more frequent pollution episodes in the last five years.
• An integrated literature review on the mechanisms of interannual to decadal variations in tropospheric O3 over China is provided.
• Future directions of O3 air quality research in China are suggested.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Y., Liao, H. & Yang, Y. Interannual and Decadal Changes in Tropospheric Ozone in China and the Associated Chemistry-Climate Interactions: A Review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 36, 975–993 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8216-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8216-9