Abstract
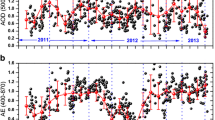
Aerosol observational data for 2012 obtained from Dunhuang Station of CARE-China (Campaign on Atmospheric Aerosol Research Network of China) were analyzed to achieve in-depth knowledge of aerosol optical properties over Dunhuang region. The results showed that the annual average aerosol optical depth (AOD) at 500 nm was 0.32±0.06, and the Ångström exponent (α) was 0.73 ± 0.27. Aerosol optical properties revealed significant seasonal characteristics. Frequent sandstorms in MAM (March–April–May) resulted in the seasonal maximum AOD, 0.41 ± 0.04, and a relatively smaller α value, 0.44±0.04. The tourism seasons, JJA (June–July–August) and SON (September–October–November) coincide with serious emissions of small anthropogenic aerosols. While in DJF (December–January–February), the composition of the atmosphere was a mixture of dust particles and polluted aerosols released by domestic heating; the average AOD and α were 0.29 ± 0.02 and 0.66 ± 0.17, respectively. Different air masses exhibited different degrees of influence on the aerosol concentration over Dunhuang in different seasons. During MAM, ranges of AOD (0.11–1.18) and α (0.06–0.82) were the largest under the dust influence of northwest-short-distance air mass in the four trajectories. Urban aerosols transported by northwest-short-distance air mass accounted for a very large proportion in JJA and the mixed aerosols observed in SON were mainly conveyed by air masses from the west. In DJF, the similar ranges of AOD and α under the three air mass demonstrated the analogous diffusion effects on regional pollutants over Dunhuang.
摘要
2012年中国气溶胶综合特性观测网 (CARE-China)敦煌站气溶胶光学特性观测分析结果表明:该地区500nm波段AOD年均值为0.32 ± 0.06, 波长指数(α)年均值为0.73 ± 0.27. 敦煌地区气溶胶光学特性呈现显著季节变化特征. 春季多沙尘天气, AOD达到最大季节均值0.41 ± 0.04, 相应α值较小, 为0.44 ± 0.04; 夏秋两季是旅游旺季, 大量游客涌入及机动车的使用排放大量人为气溶胶粒子; 冬季出现沙尘粒子和家用燃煤取暖排放的细粒子的复合型污染, AOD和α分别为0.29 ± 0.02和0.66 ± 0.17. 不同季节不同气团对该地区气溶胶浓度影响不同. 春季, 西北短程气团裹挟大量沙尘粒子影响敦煌地区, AOD和α变化范围最大, 分别为0.11–1.18和0.06–0.82; 夏季西北短程气团携带大量城市气溶胶污染敦煌地区, 而秋季主要来自西方气团对混合气溶胶的输送影响; 冬季三种气团作用下, AOD和α变化范围相似, 表明冬季不同来向气团对局地污染物具有相同的扩散作用.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alados-Arboledas, L., and Coauthors, 2008: Aerosol columnar properties retrieved from CIMEL radiometers during VELETA 2002. Atmos. Environ., 42, 2654–2667.
Ångström, A., 1964: The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus, 16, 64–75.
Bösenberg, J., and Coauthors, 2008: Plan for the Implementation of the GAW Aerosol Lidar Observation Network GALION. WMOTD No. 1443, 27–29 March 2007, Hamburg, Germany.
Bokoye, A. I., A. Royer, N. T. O’Neill, G. Fedosejevs, P. M. Teillet, and L. J. B. McArthur, 2001: Characterization of atmospheric aerosols across Canada from a ground-based Sunphotometer network: AEROCAN. Atmos.-Ocean, 39, 429–456.
Che, H. Z., Z. F. Yang, X. Y. Zhang, C. Z. Zhu, Q. L. Mac, H. G. Zhou, and P. Wang, 2009: Study on the aerosol optical properties and their relationship with aerosol chemical compositions over three regional background stations in China. Atmos. Environ., 43, 1093–1099.
Che, H. Z., and Coauthors, 2015a: Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the china aerosol remote sensing network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15, 7619–7652.
Che, H. Z., and Coauthors, 2015b: Analyses of aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over urban and industrial regions in Northeast China. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 127, 345–354.
Dubovik, O., A. Smirnov, B. N. Holben, M. D. King, Y. J. Kaufman, and T. F. Eck, 2000: Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 105(D8), 9791–9806.
Dubovik, O., and Coauthors, 2002: Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci., 59, 590–608.
Dunhuang Statistical Bureau, 2000–2012: Dunhuang Statistical Yearbook.
Fanick, E. R., S. Kroll, and S. Simescu, 2015: Sampling System Investigation for the Determination of Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds (SVOC) Emissions from Engine Exhaust. SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-1062.
Gao, Z. M., J. R. Bi, and J. P. Huang, 2013: Analysis on aerosol optical property over Northern China from AERONET and SKYNET observations. Plateau Meteorology, 32, 1293–1307. (in Chinese)
Goloub, P., and Coauthors, 2008: PHOTONS/AERONET sunphotometer network overview: Description, activities, results. Proc. SPIE 6936, Fourteenth International Symp. on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics/Atmospheric Physics, doi: 10.1117/12.783171.
He, Q. S., C. C. Li, F. H. Geng, H. Q. Yang, P. R. Li, T. T. Li, D.W. Li, and Z. Pei, 2012: Aerosol optical properties retrieved from Sun photometer measurements over Shanghai, China. J. Geophys. Res., 117(D16), D16204, doi: 10.1029/2011JD017220.
Holben, B. N., and Coauthors, 1998: AERONET-A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ., 66, 1–16.
Ichoku, C., and Coauthors, 2002: Analysis of the performance characteristics of the five-channel Microtops II sun photometer for measuring aerosol optical thickness and precipitable water vapor. J. Geophys. Res., 107(D13), AAC 5-1–AAC 5- 17.
IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Stocker et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535 pp.
Kaskaoutis, D. G., H. D. Kambezidis, N. Hatzianastassiou, P. G. Kosmopoulos, and K. V. S. Badarinath, 2007: Aerosol climatology: On the discrimination of aerosol types over four AERONET sites. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 6357–6411.
Kim, S. W., S. C. Yoon, J. Kim, and S. Y. Kim, 2007: Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over East Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR, and AERONET sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ., 41, 1634–1651.
Kojima, R., N. Fukui, and H. Watanabe, 2016: Titanium oxide liquid dispersion, titanium oxide liquid coating, and photo catalyst coating film. European Patent Application EP2974793, issued 2014.
Liu, X. Y., and P. Yue, 2007: Inversion of the optical depth of aerosol over the Dunhuang region in spring. Arid Zone Research, 24, 790–795. (in Chinese)
Liu, L. C., Z. B. Shen, T. Wang, M. X. Zhou, Y. Sadayo, and K. Shinji, 2005: Observation study on mass concentration of dust aerosols in Dunhuang. Plateau Meteorology, 24, 765–771. (in Chinese)
Lund, M. T., and T. Berntsen, 2013: Contributions of diesel vehicle emissions to Arctic black carbon in the OsloCTM2. AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, American Geophysical Union, 9–13 December 2013, San Francisco, USA.
Mahowald, N., and Coauthors, 2011: Aerosol impacts on climate and biogeochemistry. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 36, 45–74.
Pace, G., A. di Sarra, D. Meloni, S. Piacentino, and P. Chamard, 2006: Aerosol optical properties at Lampedusa (Central Mediterranean). 1. Influence of transport and identification of different aerosol types. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 697–713.
Peppler, R. A., and Coauthors, 2000: ARM southern great plains site observations of the smoke pall associated with the 1998 central American fires. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 81, 2563–2592.
Power, H. C., S. C. Sheridan, and J. C. Senkbeil, 2006: Synoptic climatological influences on the spatial and Temporal variability of aerosols over North America. Int. J. Climatol., 26, 723–741.
Ramanathan, V., and G. Carmichael, 2008: Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nature Geoscience, 1, 221–227.
Salinas, S. V., B. N. Chew, and S. C. Liew, 2009: Retrievals of aerosol optical depth and Ångström exponent from groundbased sun-photometer data of Singapore. Applied Optics, 48, 1473–1484.
Satheesh, S. K., and K. K. Moorthy, 2005: Radiative effects of natural aerosols: A review. Atmos. Environ., 39, 2089–2110.
Segla, A., A. Aguirre, and V. Vladutescu, 2011: Determination of Aerosol Optical Depth Using a Micro Total Ozone Spectrometer II (MICROTOPS II) Sun-photometer.
Shen, Z., J. J. Cao, X. X. Li, T. Okuda, Y. Q. Wang, and X. Y. Zhang, 2006: Mass concentration and mineralogical characteristics of aerosol particles collected at Dunhuang during ACE-Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 23, 291–298, doi: 10.1007/s00376-006-0291-z.
Solar Light Company, 2001: Microtops II User’s Guide. Solar Light Company, USA.
Tanré, D., and Coauthors, 2001: Climatology of dust aerosol size distribution and optical properties derived from remotely sensed data in the solar spectrum. J. Geophys. Res., 106, 18205–18217.
Trochkine, D., and Coauthors, 2003: Comparison of the chemical composition of mineral particles collected in Dunhuang, China and those collected in the free troposphere over Japan: Possible chemical modification during long-range transport. Water, Air and Soil Pollution: Focus, 3, 161–172.
Trochkine, D., and Coauthors, 2012: Mineral aerosol particles collected in Dunhuang, China, and their comparison with chemically modified particles collected over Japan. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D23), doi: 10.1029/2002JD003268.
Uchiyama, A., A. Yamazaki, H. Togawa, and J. Asano, 2005: Characteristics of Aeolian dust observed by sky-radiometer in the Intensive Observation Period 1 (IOP1). J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 83A, 291–305.
Wang, L. L., J. Y. Xin, Y. S. Wang, Z. Q. Li, P. C. Wang, G. R. Liu, and T. X. Wen, 2007: Validation of MODIS aerosol products by CSHNET over China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52, 1708–1718.
Wang, Y. Q., X. Y. Zhang, and R. R. Draxler, 2009: TrajStat: GISbased software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environmental Modeling and Software, 24, 938–939.
Wang, L. C., W. Gong, X. A. Xia, J. Zhu, J. Li, and Z. M. Zhu, 2014: Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in Central China. Atmos. Environ., 101, 94–102.
Xia, X. A., H. B. Chen, and P. Wang, 2004: Aerosol properties in a Chinese semiarid region. Atmos. Environ., 38, 4571–4581.
Xin, J. Y., Y. S. Wang, Z. Q. Li, P. C. Wang, S. G. Wang, T. X. Wen, and Y. Sun, 2006: Introduction and calibration of the Chinese sun hazemeter network. Environmental Science, 27, 1697–1702. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xin, J. Y., and Coauthors, 2007: Aerosol optical depth (AOD) and angstrom exponent of aerosols observed by the Chinese sun hazemeter network from August 2004 to September 2005. J. Geophys. Res., 112(D5), doi: 10.1029/2006JD007075.
Xin, J. Y., L. L. Wang, Y. S. Wang, Z. Q. Li, and P. C. Wang, 2011: Trends in aerosol optical properties over the Bohai Rim in Northeast China from 2004 to 2010. Atmos. Environ., 45, 6317–6325.
Xin, J. Y., Q. Zhang, C. S. Gong, Y. S. Wang, W. P. Du, and Y. F. Zhao, 2014: Aerosol direct radiative forcing over Shandong Peninsula in East Asia from 2004 to 2011. Atmos. and Oceanic Sci. Lett., 7, 74–79.
Xin, J. Y., and Coauthors, 2015: The campaign on atmospheric aerosol research network of China: CARE-China. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 96, 1137–1155.
Yan, H., 2007: Aerosol scattering properties in northern China. Atmos. Environ., 41, 6916–6922.
Yumimoto, K., K. Eguchi, I. Uno, T. Takemura, Z. Liu, A. Shimizu, and N. Sugimoto, 2009: An elevated largescale dust veil from the Taklimakan Desert: Intercontinental transport and three-dimensional structure as captured by CALIPSO and regional and global models. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 8545–8558.
Zhu, J., X. A. Xia, H. Z. Che, J. Wang, J. Zhang, and Y. Duan, 2015: Study of aerosol optical properties at Kunming in southwest China and long-range transport of biomass burning aerosols from North Burma. Atmos. Res., 169, 237–247.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41375036 and 41222033), the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC0202001, 973 Program 2014CB441200) and the CAS Strategic Priority Research Program (Grant No. XDB05020103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Xin, J., Ma, Y. et al. Optical properties and source analysis of aerosols over a desert area in Dunhuang, Northwest china. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34, 1017–1026 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-016-6224-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-016-6224-6