Abstract
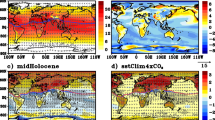
The spatial patterns and regional-scale surface air temperature (SAT) changes during the last millennium, as well as the variability of the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) were simulated with a low-resolution version of Flexible Global Ocean-Atmosphere-Land-Sea-ice (FGOALS-gl) model. The model was driven by both natural and anthropogenic forcing agents. Major features of the simulated past millennial Northern Hemisphere (NH) mean SAT variations, including the Medieval Climate Anomaly (MCA), the Little Ice Age (LIA) and the 20th Century Warming (20CW), were generally consistent with the reconstructions. The simulated MCA showed a global cooling pattern with reference to the 1961–90 mean conditions, indicating the 20CW to be unprecedented over the last millennium in the simulation. The LIA was characterized by pronounced coldness over the continental extratropical NH in both the reconstruction and the simulation. The simulated global mean SAT difference between the MCA and LIA was 0.14°C, with enhanced warming over high-latitude NH continental regions. Consistencies between the simulation and the reconstruction on regional scales were lower than those on hemispheric scales. The major features agreed well between the simulated and reconstructed SAT variations over the Chinese domain, despite some inconsistency in details among different reconstructions. The EASM circulation during the MCA was stronger than that during the LIA The corresponding rainfall anomalies exhibited excessive rainfall in the north but deficient rainfall in the south. Both the zonal and meridional thermal contrast were enhanced during the MCA. This temperature anomaly pattern favored a stronger monsoon circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann, C M., F. Joos, D. Schimel, B. L. Otto-Bliesner, and R. A. Tomas, 2007: Solar influence on climate during the past millennium: Results from transient simulations with the NCAR Climate System Model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(10), 3713–3718.
Bauer, E., M. Claussen, V. Brovkin, and A. Huenerbein, 2003: Assessing climate forcings of the Earth system for the past millennium. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30(6), 1276, doi: 101029/2002GL016639.
Bertrand, C., M-F. Loutre, M. Crucifix, and A. Berger, 2002: Climate of the last millennium: A sensitivity study. Tellus, 54, 221–244.
Bonan, G. B., K. W. Oleson, M. Vertenstein, and S. Levis, 2002: The land surface climatology of the Community Land Model coupled to the NCAR Community Climate Model. J. Climate, 15, 3123–3149.
Briegleb, B. P., C. M. Bitz, E. C. Hunke, and W. H. Lipscomb, 2004: Scientific description of the sea ice component in the Community Climate System Model: Version Three. NCAR Tech. Note NCARTN-463+STR, 70 pp.
Chang, C. P., Y. S. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000: Inter-annual and interdecadal variation of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. J. Climate, 13, 4310–4340.
Christiansen, B., T. Schmith and P. Thejll, 2009: A surrogate ensemble study of climate reconstruction methods: stochasticity and robustness. J. Climate, 22, 951–976.
Cobb, K M., C. D. Charles, H. Cheng, and R. L. Edwards, 2003: El Niño/Southern Oscillation and tropical Pacific climate during the last millennium. Nature, 424, 271–276.
Cook, E R., J. Esper, and R. D’Arrigo, 2004: Extra-tropical Northern Hemisphere land temperature variability over the past 1000 years. Quaternary Science Reviews, 23, 2063–2074.
Crowley, T., 2000: Causes of climate change over the past 1000 years. Science, 289, 270–277.
Crowley, T J., S. K. Baum, K-Y. Kim, G. C. Hegerl, and W. T. Hyde, 2003: Modeling ocean heat content changes during the last millennium. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30(18), 1932, doi: 101029/2003GL017801.
D’Arrigo, R., R. Wilson, and G. Jacoby, 2006: On the long-term context for late twentieth century warming. J. Geophys. Res., 111(D3), doi: 101029/2005JD006352.
Dawdy, D., and N. Matalas, 1964: Statistical and probability analysis of hydrologic data, part III: Analysis of variance, covariance and time series. Handbook of Applied Hydrology: A Compendium of Water-Resources Technology, V. Chow Ed., McGraw-Hill, 868–890.
Esper, J., E. R. Cook, and F. H. Schweingruber, 2002: Lowfrequency signals in long tree-ring chronologies for reconstructing past temperature variability. Science, 295(5563), 2250–2253.
Fernandez-Donado, F., and Coauthors, 2013: Large-scale temperature response to external forcing in simulations and reconstructions of the last millennium. Climate of the Past, 9, 393–421.
Ge, Q S., J. Y. Zheng, X. Q. Fang, Z. M. Man, X. Q. Zhang, P. Y. Zhang, and W. C. Wang, 2003: Winter half-year temperature reconstruction for the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River and Yangtze River, China, during the past 2000 years. The Holocene, 13(6), 933–940.
Ge, Q S., J. Y. Zheng Z. X. Hao, X. M. Shao, W. C. Wang, and J. Luterbacher 2010: Temperature variation through 2000 years in China: An uncertainty analysis of reconstruction and regional difference. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L03703, doi: 10.1029/2009GL04128.
Gerber, S., F. Joos, P. Brügger, T. Stocker, M. Mann, S. Sitch, and M. Scholze, 2003: Constraining temperature variations over the last millenium by comparing simulated and observed atmospheric CO2. Climate Dyn., 20, 281–299.
Giorgi, F., and R. Francisco, 2000: Uncertainties in regional climate change prediction: A regional analysis of ensemble simulations with the HADCM2 coupled AOGCM. Climate Dyn., 16, 169–182.
González-Rouco, F., H. Von Storch, and E. Zorita, 2003: Deep soil temperature as proxy for surface air-temperature in a coupled model simulation of the last thousand years. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 2116. doi: 101029/2003GL018264.
Goosse, H., H. Renssen, A. Timmermann, and R. S. Bradley, 2005: Internal and forced climate variability during the last millennium: a model-data comparison using ensemble simulations. Quaternary Science Reviews, 24, 1345–1360.
Graham, N. E., and Coauthors, 2007: Tropical Pacific-mid-latitude teleconnections in medieval times. Climatic Change, 83, 241–285.
Guo, Z., and T. J. Zhou, 2013: Why does FGOALS-gl reproduce a weak Medieval Warm Period but a reasonable Little Ice Age and 20th century warming?. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 1758–1770, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2227-8.
Hegerl, G. C., T J. Crowley, M Allen, W T. Hyde, H N. Pollack, J Smerdon, and E Zorita, 2007: Detection of human influence on a new, validated 1500-year temperature reconstruction. J. Climate, 20, 650–666.
Hughes, M. K., and H. F. Diaz, 1994: Was there a “MedievalWarm Period”, and if so, where and when?. Climatic Change, 26(2–3), 109–142.
Jansen, E., and Coauthors, 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, 748–845
Jones, P., and R. S. Bradley, 1992: Climatic variations over the last 500 years. Climate since A. D. 1500. R. Bradley, and P. Jones Eds., Routledge, 649–665.
Jones, P., and M. Mann, 2004: Climate over past millennia. Rev. Geophys., 42(2), RG2002, doi: 101029/2003RG000143.
Jungclaus, J. H., and Coauthors, 2010: Climate and carbon-cycle variability over the last millennium. Climate of the Past, 6, 723–737.
Kaufman, D. S., and Coauthors, 2009: Recent warming reverses long-term Arctic cooling. Science, 325, 1236–1339.
Lean, J., J. Beer, and R. Bradley, 1995: Reconstruction of solar irradiance since 1610: Implications for climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett., 22(23), 3195–3198, doi: 10.1029/95GL03093.
Ljungqvist, F. C., 2010: A new reconstruction of temperature variability in the extra-tropical Northern Hemisphere during the last two millennia. Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography, 92, 339–351.
Liu, H L. X. H. Zhang, W. Li, Y. Q. Yu, and R. C. Yu, 2004: An eddy-permitting oceanic general circulation model and its preliminary evaluation. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 21, 675–690.
Liu, J., B. Wang, Q. H. Ding, X. Y. Kuang, W. Soon, and E. Zorita, 2009: Centennial variations of the global monsoon precipitation in the last millennium: Results from ECHO-G model. J. Climate, 22, 2356–2371.
Liu, J., B. Wang, H. L. Wang, X. Y. Kuang, and R. Y. Ti, 2011: Forced response of the East Asian summer rainfall over the past millennium: Results from a coupled model simulation. Climate Dyn., 36, 323–336, doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0693-6.
Man, W. M., and T. J. Zhou, 2011: Forced response of atmospheric oscillations during the last millennium simulated by a climate system model. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56, 3042–3052.
Man, W M., T Zhou, J Zhang, and B. Wu, 2011: The 20th century climate simulated by LASG/IAP climate system model FGOALS gl. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 69(4), 644–654. (in Chinese)
Man, W. M., T. J. Zhou and J. H. Jungclaus, 2012: Simulation of the East Asian summer monsoon during the Last Millennium with the MPI Earth System Model. J. Climate, 22(25), 7852–7866.
Mann, M. E., R. S. Bradley, and M. K. Hughes, 1999: Northern hemisphere temperatures during the past millennium: Inferences, uncertainties, and limitations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 26, 759–762.
Mann, M. E., M. A. Cane, S. E. Zebiak, and A. Clement, 2005: Volcanic and solar forcing of the tropical Pacific over the past 1000 years. J. Climate, 18 447–456.
Mann, M. E., and Coauthors, 2009: Global signatures and dynamical origins of the little ice age and Medieval Climate Anomaly. Science, 326, 1256–1260.
Moberg, A., D. M. Sonechkin, K. Holmgren, N. M. Datsenko and W. Karlén, 2005: Highly variable Northern Hemisphere temperatures reconstructed from low- and high-resolution proxy data. Nature, 433(7026), 613–617.
Osborn, T. J., S. C. B. Raper, and K. R. Briffa, 2006: Simulated climate change during the last 1, 000 years: Comparing the ECHO-G general circulation model with the MAGICC simple climate model. Climate Dyn., 27, 185–197.
Overpeck, J., and Coauthors, 1997: Arctic environmental change of the last four centuries. Science, 278(5341), 1251–1256.
Peng, Y. B., Y. Xu, and L. Y. Jin, 2009: Climate changes over eastern China during the last millennium in simulations and reconstructions. Quaternary International, 208, 11–18.
Rutherford, S., M. E. Mann, T. J. Osborn, R. S. Bradley, K. R. Briffa M. K. Hughes, and P. D. Jones, 2005: Proxy-based Northern Hemisphere surface temperature reconstructions: Sensitivity to method, predictor network, target season, and target domain. J. Climate, 18(13), 2308–2329.
Servonnat, J., P. Yiou, M. Khodri, D. Swingedouw, and S. Denvil, 2010: Influence of solar variability, CO2 and orbital forcing between 1000 and 1850 AD in the IPSLCM4 model. Climate of the Past, 6, 445–460.
Shen, C M., W. C. Wang, Z. X. Hao, and W. Gong, 2008: Characteristics of anomalous precipitation events over eastern China during the past five centuries. Climate Dyn., 31, 463–476.
Shen, S., and K. M. Lau, 1995: Biennial oscillation associated with the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific sea surface temperature anomalies. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 73, 105–124.
Schmidt, G., and Coauthors, 2011: Climate forcing reconstructions for use in PMIP simulations of the last millennium (v1.0). Geoscientific Model Development 4, 33–45.
Smerdon, J E., A. Kaplan, D. N. Chang, and M. N. Evans, 2010: A pseudoproxy evaluation of the CCA and RegEM methods for reconstructing climate fields of the last millennium. J. Climate, 23, 4856–4880.
Tan, M., T. S. Liu, J. Z. Hou, X. G. Qin, H. C. Zhang, and T. Y. Li, 2003: Cyclic rapid warming on centennial-scale revealed by a 2650-year stalagmite record of warm season temperature. Geophys. Res. Lett., 3(12), 1617, doi: 101029/2003GL017352.
Trouet, V., J. Esper, N. E. Graham, A. Baker, J. D. Scourse, and D. C Frank, 2009: Persistent positive North Atlantic Oscillation mode dominated the Medieval Climate Anomaly. Science, 324(5923), 78–80.
Wang, S W., X. Y. Wen, Y. Luo, W. J. Dong, Z. C. Zhao, and B. Yang, 2007: Reconstruction of temperature series of China for the last 1000 years. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52, 3272–3280. (in Chinese)
Wen, X Y. T. J. Zhou, S. W. Wang, B. Wang, H. Wan, and J. Li, 2007: Performance of a reconfigured atmospheric general circulation model at low resolution. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 712–728, doi: 10.1007/s00376-007-0712-7.
Yan, H., L. G. Sun, Y. H. Wang, W. Huang, S. C. Qiu, and C. Y. Yang, 2011: A record of the Southern Oscillation Index for the past 2, 000 years from precipitation proxies. Nature Geoscience, 4, 611–614, doi: 101038/NGEO1231.
Yang, B., A. Braeuning, K. R. Johnson, and Y. F. Shi, 2002: General characteristics of temperature variation in China during the last two millennia. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(9), 1324, doi: 101029/2001GL014485.
Yoshimori, M., T. F. Stocher, C. C. Raible and M. Renold, 2005: Externally forced and internal variability in ensemble climate simulations of the Maunder Minimum. J. Climate, 18, 4253–4268.
Zebiak, S. E., and M. A. Cane, 1987: A model El Niño/Southern Oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115 2262–2278.
Zhang, J., L. Li, T. J. Zhou, and X. G. Xin, 2013: Variation of surface temperature during the last millennium in a simulation with the FGOALS gl climate system model. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 699–712, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2178-0.
Zhang, P Z., and Coauthors, 2008: A test of climate, sun, and culture relationships from an 1810-Year Chinese cave record. Science, 322, 940–942.
Zhou, T. J., and R. C. Yu, 2006: Twentiethcentury surface air temperature over China and the globe simulated by coupled climate models. J. Climate, 19(22), 5843–5858.
Zhou, T. J., B. Wu, X. Y. Wen, L. J. Li, and B. Wang, 2008: A fast version of LASG/IAP climate system model and its 1000-year control integration. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25(4), 655–672, doi: 10.1007/s00376-008-0655-7.
Zhou, T. J., B. Li, W. M. Man, L. X. Zhang, and J. Zhang, 2011: A comparison of the medieval warm period, little ice age and 20th Century warming simulated by the FGOALS climate system model. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56, 3028–3041.
Zhou, T J., F. F. Song, and X. L. Chen, 2013: Historical evolutions of global and regional surface air temperature simulated by FGOALS-s2 and FGOALS-g2: How reliable are the model results?. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 638–657, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2205-1.
Zorita, E., J. F. González-Rouco, H. von Storch, J. P. Montávez, and F. Valero, 2005: Natural and anthropogenic modes of surface temperature variations in the last thousand years. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L08707, doi: 101029/2004GL021563.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Man, W., Zhou, T. Regional-scale surface air temperature and East Asian summer monsoon changes during the last millennium simulated by the FGOALS-gl climate system model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 31, 765–778 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3123-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3123-y