Abstract
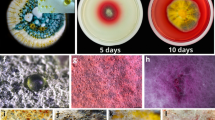
A novel yeast named HQ-C-01 was isolated from activated sludge and identified as Pichia anomala based on the morphology and 18S rDNA sequence analysis. The HQ-C-01 strain degraded 95.2% of carbofuran when the insecticide was used as the only C source and added at 50 mg/L in a mineral salts medium within 48 h. The optimal concentration, temperature, and pH of medium for degradation of carbofuran were 50 mg/L, 30°C, and pH 7.5, respectively. Strain HQ-C-01 could also effectively degrade other carbamate insecticides including carbaryl, indoxacarb, and fenobucarb, and the degradation rates were 99%, 85%, and 67%, respectively. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis showed that the strain metabolized carbofuran to produce benzofuranol as the intermediate metabolite, which was further degraded. Degradation of carbofuran added at 50 mg/kg of soil was higher in yeast-inoculated soil than in the control. These results indicated that strain HQ-C-01 may potentially be used in bioremediation of carbofuran-contaminated soil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachman J, Patterson HH (1999) Photodecomposition of the carbamate pesticide carbofuran: kinetics and the influence of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 33:874–881
Bano N, Musarrat J (2004) Characterization of a novel carbofuran degrading Pseudomonas sp. with collateral biocontrol and plant growth promoting potential. FEMS Microb lett 231:13–17
Beltran FJ, Garciaaraya JF, Acedo B (1994) Advanced oxidation of atrazine in water: II. Ozonation combined with ultraviolet radiation. Water Res 28:2165–2174
Campbell S, David MD, Woodward LA, Li QX (2004) Persistence of carbofuran in marine sand and water. Chemosphere 54:1155–1161
Chaudhry GR, Mateen A, Kaskar B, Bloda M, Riazuddin S (2002) Purification and biochemical characterization of the carbamate hydrolase from Pseudomonas sp. 50432. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 36:63–70
Chen SH, Lai KP, Li YN, Hu MY, Zhang YB, Zeng Y (2011a) Biodegradation of deltamethrin and its hydrolysis product 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde by a newly isolated Streptomyces aureus strain HP-S-01. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1471–1483
Chen SH, Hu MY, Liu JJ, Zhong GH, Yang L, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Han HT (2011b) Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Ochrobactrum lupini DG-S-01. J Hazard Mater 187:433–440
Chen SH, Yang L, Hu MY, Liu JJ (2011c) Biodegradation of fenvalerate and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Stenotrophomonas sp. strain ZS-S-01 and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:755–767
Cort T, Bielefeldt A (2000) Effects of surfactants and temperature on PCP biodegradation. J Environ Eng 126:635–643
Daneshvar N, Aber S, Khani A, Rasoulifard MH (2007) Investigation of adsorption kinetics and isotherms of imidacloprid as a pollutant from aqueous solution by adsorption onto industrial granular activated carbon. J Food Agric Environ 5:425–429
Das AC, Mukherjee D (2000) Influence of insecticides on microbial transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus in typic orchraqualf soil. J Agric Food Chem 48:3728–3732
Fahmy MA, Fukuto TR, Myers RO, March RB (1970) The selective toxicity of new N-phosphorothioyl-carbamate esters. J Agric Food Chem 18:793–796
Farahani GHN, Sahid IB, Zakaria Z, Kuntom A, Omar D (2008) Study on the downward movement of carbofuran in two malaysian soils. B Environ Contam Tox 81:294–298
Hashimoto M, Fukui M, Hayano K, Hayatsu M (2002) Nucleotide sequence and genetic structure of a novel carbaryl hydrolase gene (cehA) from Rhizobium sp. strain AC100. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1220–1227
Hashimoto M, Mizutani A, Tago K, Ohnishi-Kameyama M, Shimojo T, Hayatsu M (2006) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of carbaryl hydrolase gene (cahA) from Arthrobacter sp. RC100. J Biosci Bioeng 101:410–414
Hong J, Kim H, Kim D, Seo J, Kim K (2004) Rapid determination of chlorinated pesticides in fish by freezing-lipid filtration, solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1038:27–35
Jiang JD, Zhang RF, Li R, Gu JD, Li SP (2007) Simultaneous biodegradation of methyl parathion and carbofuran by a genetically engineered microorganism constructed by mini-Tn5 transposon. Biodegradation 18:403–412
Karakousis A, Tan L, Ellis D, Alexiou H, Wormald P (2006) An assessment of the efficiency of fungal DNA extraction methods for maximizing the detection of medically important fungi using PCR. J Microbiol Meth 65:38–48
Kumar S, Tamura NM (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Kuo WS, Chiang YH, Lai LS (2006) Degradation of carbofuran in water by solar photocatalysis in presence of photosensitizers. J Environ Sci Health B 41:937–948
Lalah J, Wandiga S, Dauterman W (1996) Mineralization, volatilization, and degradation of carbofuran in soil samples from Kenya. B Environ Contam Tox 56:37–41
Lin QS, Chen SH, Hu MY, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Yang L, Li H (2011) Biodegradation of cypermethrin by a newly isolated actinomycetes HU-S-01 from wastewater sludge. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8:45–56
Loh KC, Wang SJ (1998) Enhancement of biodegradation of phenol and a non growth substrate 4-chlorophenol by medium augmentation with conventional carbon sources. Biodegradation 8:329–338
Ma YS, Sung CF, Lin JG (2010) Degradation of carbofuran in aqueous solution by ultrasound and fenton processes: effect of system parameters and kinetic study. J Hazard Mater 178:320–325
Nannipieri P, Bollag J (1991) Use of enzymes to detoxify pesticide-contaminated soils and waters. J Environ Qual 20:5–10
Peng X, Zhang JS, Li YY, Li W, Xu GM, Yan YC (2008) Biodegradation of insecticide carbofuran by Paracoccus sp. YM3. J Environ Sci Health B 43:588–594
Plangklang P, Reungsang A (2008) Effects of rhizosphere remediation and bioaugmentation on carbofuran removal from soil. World J Microb Biot 24:983–989
Plangklang P, Reungsang A (2009) Bioaugmentation of carbofuran residues in soil using Burkholderia cepacia PCL3 adsorbed on agricultural residues. Int Biodeter Biodegr 63:515–522
Plangklang P, Reungsang A (2010) Bioaugmentation of carbofuran by Burkholderia cepacia PCL3 in a bioslurry phase sequencing batch reactor. Process Biochem 2:230–238
Podolska M, Mulkiewicz E, Napierska D (2008) The impact of carbofuran on acetylcholinesterase activity in Anisakis simplex larvae from Baltic herring. Pestic Biochem Phys 91:104–109
Ramanand K, Sharmila M, Sethunathan N (1988) Mineralization of carbofuran by a soil bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2129–2133
Robles-Gonzalez I, Rios-Leal E, Ferrera-Cerrato R, Esparza-Garcia F, Rinderkenecht-Seijas N, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2006) Bioremediation of a mineral soil with high contents of clay and organic matter contaminated with herbicide 2,4-dichlor-ophenoxyacetic acid using slurry bioreactors: effect of electron acceptor and supplementation with an organic carbon source. Process Biochem 41:51–60
Salama AK (1998) Metabolism of carbofuran by Aspergillus and Fusarium graminearum. J Environ Sci Health 33:253
Satar S, Satar S, Sebe A, Yesilagac H (2005) Carbofuran poisoning among farm workers. Toxicol Lett S1:135–136
Seo J, Jeon J, Kim SD, Kang S, Han J, Hur HG (2007) Fungal biodegradation of carbofuran and carbofuran phenol by the fungus Mucor ramannianus: identification of metabolites. Water Sci Technol 55:163–167
Slaoui M, Ouhssine M, Berny E, Elyachioui M (2007) Biodegradation of the carbofuran by a fungus isolated from treated soil. Af J Biotechnol 6:419–423
Suneethi S, Joseph K (1998) Persistence of phorate and carbofuran in relation to their effect on the mineralization of C, N, and P in alluvial soil. B Environ Contam Tox 51:127–132
Tomasek PH, Karns JS (1989) Cloning of a carbofuran hydrolase gene from Achromobacter sp. strain WM111 and its expression in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 171:4038–4044
Tripathi G, Kachhwaha N, Dabi I (2010) Comparative studies on carbofuran-induced changes in some cytoplasmic and mitochondrial enzymes and proteins of epigeic, anecic and endogeic earthworms. Pestic Biochem Phys 96:30–35
Venkateswarlu K, Sethunathan N (1984) Degradation of carbofuran by Azospirillum lipoferum and Streptomyces spp. isolated from flooded alluvial soil. Soil Bio Biochem 33:556–560
Wang GQ, Hou ZY, Sun YA, Zhang RJ, Xie K, Liu RL (2006) Investigation of pyrolysis behavior of carbofuran by pyrolysis-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 129:22–30
Watts RJ, Dilly SE (1996) Evaluation of iron catalysts for the Fenton-like remediation of diesel-contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 51:209–224
Yan QX, Hong Q, Han P, Dong XJ, Shen YJ, Li SP (2007) Isolation and characterization of a carbofuran-degrading strain Novosphingobium sp. FND-3. FEMS Microb Lett 271:207–213
Zhang XH, Zhang GS, Zhang ZH, Xu JH, Li SP (2006) Isolation and characterization of a dichlorvos-degrading strain DDV-1 of Ochrobactrum sp. Pedosphere 16:64–71
Acknowledgments
The researchers gratefully acknowledge the grants of National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30871660) and the Project of Scientific Technological Planning of Guangdong Province, China (no. 2009B020310005). The authors would like to thank Dr. Muhammad Rizwan-ul-haq for his helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Chen, S., Hu, M. et al. Biodegradation of carbofuran by Pichia anomala strain HQ-C-01 and its application for bioremediation of contaminated soils. Biol Fertil Soils 47, 917–923 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0602-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0602-0