Abstract
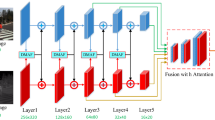
For pedestrian detection in all weather conditions, multispectral imagery is the preferred solution for multimodal data acquisition. Due to the complementarity of multispectral data, the performance of pedestrian detection has been continuously improved. However, it is precise because of the diversity of data that the complexity of the model is increased. How to obtain a simple and lightweight high-performance network is the primary problem that the industry needs to solve. To solve this problem, this paper firstly proposes a lightweight high-performance network multi-receptive field and attention mechanism for multispectral pedestrian detection (MAPD). MAPD is a new scalable network based on multi-receptive field and attention mechanism. It cleverly combines multi-receptive field module and convolutional block attention module (CBAM) attention module to obtain multi-receptive field and attention module (MA). The module can be easily embedded into other network structures. After that, we analyze the proportion of pedestrian objects in the image to determine the receptive field range of the target, and use this range to design the multi-receptive field module of the network to obtain a network model suitable for detecting different object tasks. The MAPD network proposed in this paper has a very low parameter amount. Ablation studies on KAIST and CVC-14 datasets show that our method is effective and achieves state-of-the-art detection performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, S., Park, J., Kim, N., Choi, Y., So Kweon, I.: Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1037–1045 (2015)
Liu, J., Zhang, S., Wang, S., Metaxas, D.N.: Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.02644 (2016)
Konig, D., Adam, M., Jarvers, C., Layher, G., Neumann, H., Teutsch, M.: Fully convolutional region proposal networks for multispectral person detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 49–56 (2017)
Xu, D., Ouyang, W., Ricci, E., Wang, X., Sebe, N.: Learning cross-modal deep representations for robust pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5363–5371 (2017)
Li, C., Song, D., Tong, R., Tang, M.: Multispectral pedestrian detection via simultaneous detection and segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.04818 (2018)
Park, K., Kim, S., Sohn, K.: Unified multi-spectral pedestrian detection based on probabilistic fusion networks. Pattern Recogn. 80, 143–155 (2018)
Zheng, Y., Izzat, I.H., Ziaee, S.: Gfd-ssd: gated fusion double ssd for multispectral pedestrian detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.06999 (2019)
Zhang, L., Zhu, X., Chen, X., Yang, X., Lei, Z., Liu, Z.: Weakly aligned cross-modal learning for multispectral pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5127–5137 (2019)
Li, C., Song, D., Tong, R., Tang, M.: Illumination-aware faster r-cnn for robust multispectral pedestrian detection. Pattern Recogn. 85, 161–171 (2019)
Zhou, K., Chen, L., Cao, X.: Improving multispectral pedestrian detection by addressing modality imbalance problems. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XVIII 16, pp. 787–803 (2020)
Kim, J., Kim, H., Kim, T., Kim, N., Choi, Y.: Mlpd: multi-label pedestrian detector in multispectral domain. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6(4), 7846–7853 (2021)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Girshick, R.B., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(9), 1627–1645 (2009)
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S., Fu, C.-Y., Berg, A.C.: Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part I 14, pp. 21–37 (2016)
Lin, T.-Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Liu, S., Qi, L., Qin, H., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8759–8768 (2018)
Wang, X., Zhang, S., Yu, Z., Feng, L., Zhang, W.: Scale-equalizing pyramid convolution for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13359–13368 (2020)
Zhang, H., Fromont, E., Lefèvre, S., Avignon, B.: Guided attentive feature fusion for multispectral pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 72–80 (2021)
Chen, Y.-T., Shi, J., Ye, Z., Mertz, C., Ramanan, D., Kong, S.: Multimodal object detection via probabilistic ensembling. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part IX, pp. 139–158 (2022)
Liu, D., Cui, Y., Yan, L., Mousas, C., Yang, B., Chen, Y.: Densernet: Weakly supervised visual localization using multi-scale feature aggregation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 6101–6109 (2021)
Li, Z., Liu, F., Yang, W., Peng, S., Zhou, J.: A survey of convolutional neural networks: analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2021)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Dai, J., Qi, H., Xiong, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, G., Hu, H., Wei, Y.: Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 764–773 (2017)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 16, pp. 213–229 (2020)
Yuan, Y., Huang, L., Guo, J., Zhang, C., Chen, X., Wang, J.: Ocnet: Object context network for scene parsing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00916 (2018)
Fu, J., Liu, J., Tian, H., Li, Y., Bao, Y., Fang, Z., Lu, H.: Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3146–3154 (2019)
Yang, J., Ren, P., Zhang, D., Chen, D., Wen, F., Li, H., Hua, G.: Neural aggregation network for video face recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4362–4371 (2017)
Wang, Q., Wu, T., Zheng, H., Guo, G.: Hierarchical pyramid diverse attention networks for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8326–8335 (2020)
Li, W., Sun, Y., Wang, J., Cao, J., Xu, H., Yang, X., Sun, G., Ma, Y., Long, Y.: Collaborative attention network for person re-identification. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1848, 012074 (2021)
Chen, B., Deng, W., Hu, J.: Mixed high-order attention network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 371–381 (2019)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Du, W., Wang, Y., Qiao, Y.: Recurrent spatial-temporal attention network for action recognition in videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(3), 1347–1360 (2017)
Su, W., Zhu, X., Cao, Y., Li, B., Lu, L., Wei, F., Dai, J.: Vl-bert: Pre-training of generic visual-linguistic representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.08530 (2019)
Xu, T., Zhang, P., Huang, Q., Zhang, H., Gan, Z., Huang, X., He, X.: Attngan: Fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1316–1324 (2018)
Mnih, V., Heess, N., Graves, A., et al.: Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27 (2014)
Gregor, K., Danihelka, I., Graves, A., Rezende, D., Wierstra, D.: Draw: A recurrent neural network for image generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1462–1471 (2015)
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A., Salakhudinov, R., Zemel, R., Bengio, Y.: Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2048–2057 (2015)
Jaderberg, M., Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A., et al.: Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 28 (2015)
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P., Li, P., Zuo, W., Hu, Q.: Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11534–11542 (2020)
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Wang, W., Liang, J., Liu, D.: Learning equivariant segmentation with instance-unique querying. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.00911 (2022)
Cui, Y., Yan, L., Cao, Z., Liu, D.: Tf-blender: Temporal feature blender for video object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8138–8147 (2021)
González, A., Fang, Z., Socarras, Y., Serrat, J., Vázquez, D., Xu, J., López, A.M.: Pedestrian detection at day/night time with visible and fir cameras: a comparison. Sensors 16(6), 820 (2016)
Guan, D., Cao, Y., Yang, J., Cao, Y., Yang, M.Y.: Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 50, 148–157 (2019)
Zhang, L., Liu, Z., Zhang, S., Yang, X., Qiao, H., Huang, K., Hussain, A.: Cross-modality interactive attention network for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 50, 20–29 (2019)
Choi, H., Kim, S., Park, K., Sohn, K.: Multi-spectral pedestrian detection based on accumulated object proposal with fully convolutional networks. In: 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 621–626 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zang, Y., Cao, R., Li, H. et al. MAPD: multi-receptive field and attention mechanism for multispectral pedestrian detection. Vis Comput 40, 2819–2831 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02988-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02988-7