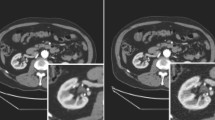
Abstract
Low-dose CT image (LDCT) restoration is a challenging task attracting the interest of researchers extensively. However, reducing the radiation dose may lead to increased noise and artifacts. Over the past years, deep learning has produced impressive results in low-dose CT image restoration by learning a nonlinear mapping function. However, the limited number of image pairs may be unavailable in medical applications. And the mapping space from high-resolution images (HR) to low-resolution images (LR) is extremely large, which can hardly find a good result. Furthermore, it is difficult to directly remove noise due to the lack of prior knowledge. Therefore, we introduce a noise prior regression network (NPRN) by providing a prior of the noise distribution and introducing a constraint to estimate the HR → LR mapping space. Furthermore, the noise prior makes the network focus on the noisy regions but also explicitly assesses the local consistency of the recovered regions. Simultaneously, the regression process does not depend on the pair images. We also compare our method with some state-of-the-art algorithms. The experimental results show that the proposed NPRN recovers structural textures effectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herzog, P., Rieger, C.T.: Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays. The Lancet 363(9427), 2192–2193 (2004)
Naidich, D.P., Marshall, C.H., Gribbin, C., Arams, R.S., McCauley, D.I.: Low-dose CT of the lungs: preliminary observations. Radiology 175(3), 729–731 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.175.3.2343122
Ramírez, R.R., Kopell, B.H., Butson, C.R., Hiner, B.C., Baillet, S.: Spectral signal space projection algorithm for frequency domain MEG and EEG denoising, whitening, and source imaging. Neuroimage 56(1), 78–92 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.02.002
Hara, A.K., Paden, R.G., Silva, A.C., Kujak, J.L., Lawder, H.J., Pavlicek, W.: Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 193(3), 764–771 (2009)
Wang, J., Li, T., Lu, H., Liang, Z.: Penalized weighted least-squares approach to sinogram noise reduction and image reconstruction for low-dose X-ray computed tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 25(10), 1272–1283 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2006.882141
Singh, S., Kalra, M.K., Hsieh, J., et al.: Abdominal CT: comparison of adaptive statistical iterative and filtered back projection reconstruction techniques. Radiology 257(2), 373–383 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10092212
Lewitt, R.M.: Multidimensional digital image representations using generalized Kaiser-Bessel window functions. JOSA A 7(10), 1834–1846 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.7.001834
Elbakri, I.A., Fessler, J.A.: Statistical image reconstruction for polyenergetic X-ray computed tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 21(2), 89–99 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/42.993128
Tian, Z., Jia, X., Yuan, K., Pan, T., Jiang, S.B.: Low-dose CT reconstruction via edge-preserving total variation regularization. Phys. Med. Biol. 56(18), 5949 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Mou, X., Wang, G., Yu, H.: Tensor-based dictionary learning for spectral CT reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 36(1), 142–154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2600249
Li, Z., Yu, L., Trzasko, J.D., et al.: Adaptive nonlocal means filtering based on local noise level for CT denoising. Med. Phys. 41(1), 011908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4851635
Hanchate, V., Joshi, K.: MRI denoising using BM3D equipped with noise invalidation denoising technique and VST for improved contrast. SN Appl. Sci. 2(2), 1–8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-1937-7
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Yang, H., Min, K.: Classification of basic artistic media based on a deep convolutional approach. Vis. Comput. 36(3), 559–578 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01641-6
Güera, D., Delp, E. J.: Deepfake video detection using recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 15th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS): IEEE, pp. 1–6 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Lu, Y., Fu, S., Zhang, X.H., Xie, N.: Denoising Monte Carlo renderings via a multi-scale featured dual-residual GAN. Vis. Comput. 37, 2513–2525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02204-4
Lai, W.-S., Huang, J.-B., Ahuja, N., Yang, M.-H.: Deep laplacian pyramid networks for fast and accurate super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 624–632 (2017)
Kim, J., Lee, J. K., Lee, K. M.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1646–1654 (2016)
Chen, Y., Shi, F., Christodoulou, A. G., Xie, Y., Zhoum, Z., Li, D.: Efficient and accurate MRI super-resolution using a generative adversarial network and 3D multi-level densely connected network. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, pp. 91–99 (2018)
Yu, H., Liu, D., Shi, H., et al.: Computed tomography super-resolution using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP): IEEE, pp. 3944–3948 (2017
Jiang, X., Jin, Y., Yao, Y.: Low-dose CT lung images denoising based on multiscale parallel convolution neural network. Vis. Comput. 37, 2419–2431 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01996-1
Yang, Q., Yan, P., Zhang, Y., et al.: Low-dose CT image denoising using a generative adversarial network with Wasserstein distance and perceptual loss. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 37(6), 1348–1357 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2827462
Su, S.-Y., Huang, C.-W., Chen, Y.-N.: Dual supervised learning for natural language understanding and generation (2019)
Fan, J., Cao, X., Yap, P.-T., Shen, D.: BIRNet: brain image registration using dual-supervised fully convolutional networks. Med. Image Anal. 54, 193–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.03.006
Xia, Y., Qin, T., Chen, W., Bian, J., Yu, N., Liu, T.-Y.: Dual supervised learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning: PMLR, pp. 3789–3798 (2017)
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A. A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
You, C., Li, G., Zhang, Y., et al.: CT super-resolution GAN constrained by the identical, residual, and cycle learning ensemble (GAN-CIRCLE). IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 39(1), 188–203 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2922960
Guo, Y., Chen, J., Wang, J., et al.: Closed-loop matters: dual regression networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5407–5416 (2020)
Batson, J., Royer, L.: Noise2self: blind denoising by self-supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning: PMLR, pp. 524–533 (2019)
Tran, L. D., Nguyen, S. M., Arai, M.: GAN-based noise model for denoising real images. In: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (2020)
Jia, X., Liu, S., Feng, X., Zhang, L.: Focnet: a fractional optimal control network for image denoising. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6054–6063 (2019)
AAPM.: Low dose CT grand challenge (2017). https://www.aapm.org/GrandChallenge/LowDoseCT/#
TCGA-KICH.: The cancer genome atlas kidney chromophobe (TCGA-KICH). https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/TCGA-KICH
Kingma, D. P., Salimans, T., Welling, M.: Variational dropout and the local reparameterization trick (2015)
Lim, B., Son, S., Kim, H., Nah, S., Lee, K. M., IEEE.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 1132–1140 (2017)
Haris, M., Shakhnarovich, G., Ukita, N.: Deep back-projection networks for super-resolution. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Wang, L., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 286–301 (2018)
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszár, F., et al.: Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 4681–4690 (2017
Wang, X., Yu, K., Wu, S., et al.: Esrgan: enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Jiang, Z., Huang, M. et al. Low-dose CT image restoration based on noise prior regression network. Vis Comput 39, 459–471 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02341-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02341-w