Abstract
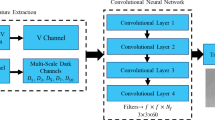
In this paper, we address the single-image haze removal problem in nighttime scenes. The night haze removal is a severely ill-posed problem due to the presence of various visible night light sources with varying colors and non-uniform illumination. These light sources are of different shapes and introduce a noticeable amount of glow in the night scenes. To overcome these effects, we introduce a deep learning-based DeGlow–DeHaze iterative model which accounts for varying colors and glows. The proposed model is a linear combination of three terms: the direct transmission attenuation, airlight and glow. First, a multi-path dilated convolution DeGlow network is introduced to interactively learn the local features with different reception fields and reduce the glow effect. The glow term is estimated by a binary mask that informs the location of the illumination source. As a result, the nighttime image is only left with only direct transmission and airlight terms. Finally, a separate post-processing DeHaze network is included to remove the haze effect from the reduced glow image. For our model training, we collected the night hazy images from internal and external resources, synthesized transmission maps from the NYU depth datasets, and consequently restored the haze-free images. The quantitative and qualitative evaluations show the effectiveness of our model on several real and synthetic images and compare our results with existing night haze models. The experimental results demonstrate that our multi-path CNN model outperforms other state-of-the-art methods in terms of PSNR (19.25 dB), SSIM (0.9958) evaluation parameters and computation time.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Middleton, W.E.K.: Vision Through the Atmosphere. University of Toronto Press, Toronto (1952)
McCartney, E.J.: Optics of the Atmosphere: Scattering by Molecules and Particles. Wiley, New York (1976)
Koschmieder, H.: Theorie der horizontalen Sichtweite: Kontrast und Sichtweite. Keim & Nemnich, Munich (1925)
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Single image haze removal using dark channel Prio. In: IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 1956–1963, Miami, USA (Aug. 2009)
Tan, R.T.: Visibility in bad weather from a single image. In: IEEE, CVPR, AK, USA (2008)
Ancuti, C.O., Ancuti, C.: Single image dehazing by multi-scale fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (TIP) 22, 3271–3282 (2013)
Fattal, R.: Dehazing using color-lines. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 1 (2014)
Tang, K., Yang, J., Wang, J.: Investigating haze relevant features in a learning framework for image dehazing. In: IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2995–3002. Columbus, Ohio (2014)
Caraffa, L., Tarel, J.P.: Markov random field model for single image defogging. In: IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Gold Coast, Australia (2013)
Meng, G., Wang, Y., Duan, J., Xiang, S., Pan, C.: Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization. In: IEEE, ICCV, pp. 617-624, Washington, DC, USA (Dec. 2013)
Eigen, D., Krishnan, D., Fergus, R.: Restoring an image taken through a window covered with dirt or rain. In: IEEE, ICCV, pp. 633–640. Australia, Sydney (2013)
Zhu, Q., Mai, J., Shao, L.: A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2, 3522–3533 (2015)
Nishino, K., Kratz, L., Lombardi, S.: Bayesian defogging. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 98(3), 263–278 (2012)
Kim, J.H., Jang, W.D., Sim, J.Y., Kim, C.S.: Optimized contrast enhancement for real-time image and video dehazing. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 24, 410–425 (2013)
Cai, B., Xu, X., Jia, K., Qing, C., Tao, D.: DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 5187–5198 (2016)
Ren, W., Liu, S., Zhang, H., Pan, J., Cao, X., Yang, M.-H.: Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks. In: IEEE European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 154–169, Amsterdam (Oct. 2016)
Pei, S.-C., Lee, T.-Y.: Nighttime haze removal using color transfer pre-processing and dark channel prior. In: IEEE, ICIP, Orlando, USA (Oct. 2012)
Zhang, J., Cao, Y., Fang, S., Kang, Y., Chen, C. W., Yang, M.-H.: Fast haze removal for nighttime image using maximum reflectance prior. In: IEEE, CVPR, pp. 7418–7426 (July 2016)
Narasimhan, S., Nayar, S.K.: Shedding light on the weather. In: IEEE CVPR, 665–672. Wisconsin, USA (2003)
Li, Y., Tan, R.T., Brown, M.S.: Nighttime haze removal with glow and multiple light colors. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 226–234, Santiago Chile (Dec. 2015)
Ancuti, C.O., Ancuti, C., De Vleeschouwer, C., Bovick, A.C.: Day and night-time dehazing by local airlight estimationg. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 6264–6275 (2020)
Yu, F., Koltun, V.: Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. In: International Conference on Learning Representations, (ICLR), Puerto Rico (Apr. 2016)
Li, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, D.: CSRNet: dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1091–1100, Salt Lake City, USA (2018)
Zoran, D., Weiss, Y.: From learning models of natural image patches to whole image restoration. In: IEEE, ICCV, Barcelona, Spain (2011)
Yang, W., Tan, R.T., Feng, J., Liu, J., Guo, Z., Yan, S., Yang, M.-H.: Deep joint rain detection and removal from a single image. In: IEEE, CVPR, Hawaii, USA (2017)
Silberman, N., Hoiem, D., Kohli, P., Fergus, R.: Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In: IEEE European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 746–760, Italy (Oct. 2012)
Scharstein, D., Szeliski, R., Zabih, R.: A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 47, 7–42 (2002)
Scharstein, D., Szeliski, R.: High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured ligh. In: IEEE, CVPR, 195–202, Madison, USA (2003)
Hirschm uller, H., Scharst, D.: Evaluation of cost functions for stereo matching. In: IEEE, CVPR, 31, 1582–1599, Minneapolis, USA (June 2007)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13, 600–612 (2004)
Shih, Y., Krishnan, D., Durand, F., Freeman, W.: Reflection removal using ghosting cues. In: IEEE, CVPR, pp. 3193–3201, Boston, USA (June 2015)
Kuanar, S., Rao, K.R., Mahapatra, D., Bilas, M.: Night time haze and glow removal using deep dilated convolutional network. Preprint arXiv:1902.00855 (2019)
Abadi, M., et al.: Tensorflow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous, distributed systems (2016). arXiv:1603.04467.pdf. Software available from www.tensorflow.org
Zhang, H., Sindagi, V., Patel, V.: Multi-scale single image dehazing using perceptual pyramid deep network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 902–911, Salt Lake City, USA (2018)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., Zhang, L.: Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(7), 3142–3155 (2017)
Mutimbu, L., Robles-Kelly, A.: Multiple illuminant color estimation via statistical inference on factor graphs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25, 5383–5396 (2016)
Lombardi, S., Nishino, K.: Reflectance and illumination recovery in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38, 129–141 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuanar, S., Mahapatra, D., Bilas, M. et al. Multi-path dilated convolution network for haze and glow removal in nighttime images. Vis Comput 38, 1121–1134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02071-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02071-z