Abstract
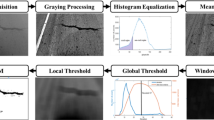
In many countries, the common practice for monitoring road surface conditions consists in collecting pavement images at traffic speed by devoted imaging devices. Among the surface distresses, cracking can serve as a condition indicator of the pavement structure. Image processing techniques have been then developed to computerize the survey of cracking as the support of human visual control. Among the existing automatic crack detection methods, the minimal path selection (MPS) technique has shown a better performance compared to other methods on simulated and field pavement images (Amhaz et al. in IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 17:2718–2729, 2016; Amhaz, in: Détection automatique de fissures dans des images de chaussée par sélection de chemins minimaux, 2015). As a counterpart, MPS suffers from a large computing time. Within this scope, the aim of this paper has been to improve the efficiency of the original MPS method and to present more efficient strategies for the selection of minimal paths. Among the five main steps of the original MPS version, the improvements address the first three steps that enable the segmentation of the crack skeleton and reduce the computing burden on the last two steps. The tests of the two improved MPS versions on some image samples illustrate the large reduction in false positive paths without reducing the overall performance of the segmentation technique. Moreover, the computing time is divided by a factor sixty roughly for the latest MPS version.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amhaz, R., Chambon, S., Idier, J., Baltazart, V.: Automatic crack detection on 2D pavement images: an algorithm based on minimal path selection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 17, 2718–2729 (2016)
Amhaz, R.: Détection automatique de fissures dans des images de chaussée par sélection de chemins minimaux. Ph.D. dissertation, IRCCyN, École Centrale de Nantes, Nantes, France (2015)
PIARC: Evaluating the performance of automated pavement cracking measurement equipment. Technical Committee CT 4.2 on the Interactions Vehicle/Road (2012)
Wang, K.C., Smadi, O.: Automated imaging technologies for pavement distress surveys. Transportation Research E-Circular, E-C156 (2011)
Karlsson, R.: Implementation of advanced monitoring techniques in road asset management results from the TRIMM project. Transport Research Arena, Paris (2014)
Alessandroni, G., Klopfenstein, L.C., Delpriori, S., Dromedari, M., Luchetti, G., Paolini, B.D., Seraghiti, A., Lattanzi, E., Freschi, V., Carini, A., Bogliolo, A.: SmartRoadSense: collaborative road surface condition monitoring. In: UBICOMM: Proceedings of the 18th international conference on mobile ubiquitous computing, systems, services and technologies, Rome, Italy (2014)
Martin, J.M.: Des smartphones dans les véhicules traceurs à la restitution automatique de l’état du réseau pour le gestionnaire routier. XXVth World Road Congress, Seoul, South Korea (2015)
Vavrik, W., Evans, L., Stefanski, J., Sargand, S: PCR evaluation considering transition from manual to semi-automated pavement distress collection and analysis. Ohio Department of Transportation, USA (2013)
McRobbie, S., Wright, A.: Review of survey methods. Published Project Report PPR-001, UK (2004)
Wright, D., Baltazart, V., Elsworth, N., Hamrouche, R., Karup, J., Antunes, M.L., McRobbie, S., Merecos, V., Saarenketo, T.: D4.3 Monitoring structural and surface conditions, Tomorrow’s Road Infrastructure Monitoring and Management (TRIMM), FP7 project 285119 (2014)
Ryu, S.K., Kim, T., Kim, Y.R.: Image-Based Pothole Detection System for ITS Service and Road Management System. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, Cairo (2015)
Li, Q., Zou, Q., Liu, X.: Pavement crack classification via spatial distribution features. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2011, 649675 (2011)
Chambon, S., Moliard, J.M.: Automatic road pavement assessment with image processing. Int. J. Geophys. Rev. Comp. 2011, 1–20 (2011)
Shi, Y., Cui, L., Qi, Z., Meng, F., Chen, Z.: Automatic road crack detection using random structured forests. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 17, 3434–3445 (2016)
Baltazart, V., Moliard, J.M., Amhaz, R., Cottineau, L.M., Wright, A., Jethwa, M.: Automatic crack detection on pavement images for monitoring road surface conditions. In: Proceedings of the 8th RILEM International Conference on Mechanisms of Cracking and Debonding in Pavements, some results from the collaborative FP7 TRIMM project, Nantes, France (2016)
Oliveira, H., Correia, P.L.: Automatic road crack detection and characterization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 14, 155–168 (2013)
Zou, Q., Cao, Y., Li, Q., Mao, Q., Wang, S.: CrackTree: automatic crack detection from pavement images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 33, 227–238 (2012)
Tang, J., Gu, Y.: Automatic crack detection and segmentation using a hybrid algorithm for road distress analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Manchester, UK (2013)
Gavilán, M., Balcones, D., Marcos, O., Llorca, D.F., Sotelo, M.A., Parra, I., Ocaña, M., Aliseda, P., Yarza, P., Amírola, A.: Adaptive road crack detection system by pavement classification. Sensors 11, 9628–9657 (2011)
Medina, R., Gómez-Garcia-Bermejo, G., Zalama, E.: Automated visual inspection of road surface cracks. In: 27th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (ISARC), Valladolid, Spain (2010)
Saar, T., Talvik, O.: Automatic asphalt pavement crack detection and classification using neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 12th Biennial Baltic Electronics Conference (BEC), Tallinn, Estonia (2010)
Eisenbach, M., Stricker, R., Seichter, D., Amende, K., Debes, K., Sesselmann, M., Ebersbach, D., Stoeckert, U., Gross, H.M.: How to get pavement distress detection ready for deep learning? A systematic approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Anchorage, AK, USA (2017)
Kaddah, W., Ouerhani, Y., Alfalou, A., Desthieux, M., Brosseau, C., Gutierrez, C.: Road marking features extraction using the VIAPIX\(^{\textregistered }\) system. Opt. Commun. 371, 117–127 (2016)
Desthieux, M., Gutierrez, C., Ouerhani, Y., Kaddah, W., Alfalou, A.: ACTRIS brings its expertise in a new approach to improve knowledge and quality of topological and regulatory data dedicated to road, for OPTICITIES project needs. In: 22nd ITS World Congress, Bordeaux, France (2015)
Veit, T., Tarel, J.P., Nicolle, P., Charbonnier, P.: Evaluation of road marking feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the 11th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Beijing, China (2008)
Buttlar, W.: Mechanisms of cracking and debonding in asphalt and composite pavements. RILEM 241-MCD. http://www.rilem.org/ (2011–2016)
Special session in IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) on “Image Processing for the Detection of Road-Surface Degradations”, Paris, France (2014)
Special session in EUSIPCO Conference on “Automatic Detection of Defects in Images of Road Pavement Surface”, Kos Island, Greece (2017)
Tsai, Y.C., Kaul, V., Mersereau, R.M.: Critical assessment of pavement distress segmentation methods. J. Transp. Eng. 136, 11–19 (2010)
Yamaguchi, T., Nakamura, S., Hashimoto, S.: An efficient crack detection method using percolation-based image processing. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Singapore, Singapore (2008)
Nguyen, T.S.: Extraction de structures fines sur des images texturées : application à la détection automatique de fissures sur des images de surface de chaussées. Ph.D. dissertation, Orléans University, Orléans, France (2010)
Nguyen, T.S., Begot, S., Duculty, F., Avila, M.: Free-form anisotropy: a new method for crack detection on pavement surface images. In: Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Brussels, Belgium (2011)
Baltazart, V., Nicolle, P., Yang, L.: Ongoing tests and improvements of the MPS algorithm for the automatic crack detection within grey level pavement images. In: Proceedings of the 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Kos, Greece, August 28–September 2 2017
Zhang, L., Yang, F., Zhang, Y. D., Zhu, Y.J.: Road crack detection using deep convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA (2016)
Special session in EUSIPCO Conference “"On the Suitability of Signal Processing Strategies for the Assessment of Road Pavement Surface Condition”, Rome, Italy (2018)
Dijkstra, E.W.: A note on two problems in connection with graphs. Numer. Math. 1, 269–271 (1959)
Chambon, S.: Image database available. http://www.irit.fr/~Sylvie.Chambon/Crack_Detection_Database.html
Felner, A.: Position paper: Dijkstra’s algorithm versus uniform cost search or a case against Dijkstra’s algorithm. In: 4th International Symposium on Combinatorial Search (SoCS) (2011)
Yang, L.: Contributions to improve and speed the existing MPS-based algorithm for both the semi-automated and the automated crack segmentation on 2D pavement images. Internship report, LUNAM University, France (2015)
Sampat, M.P., Wang, Z., Gupta, S., Bovik, A.C., Markey, M.K.: Complex wavelet structural similarity: a new image similarity index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18, 2385–2401 (2009)
Otsu, N.: A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Systems Man Cybern. 9, 62–66 (1979)
Schmidlin, V., Favier, G., Stromboni, J.P., Tomasini, B.: Réseaux de neurones et fusion de données. 14\(^{\grave{{\rm e}}{\rm me}}\)colloque GRETSI-Juan-les-Pins, Valbonne, France (1993)
Cerema, Aigle-RN. http://www.normandie-centre.cerema.fr/IMG/pdf/15-AigleRNpress_cle243947.pdf. Accessed Nov 2017
VIAPIX solution: http://www.viapix.eu/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaddah, W., Elbouz, M., Ouerhani, Y. et al. Optimized minimal path selection (OMPS) method for automatic and unsupervised crack segmentation within two-dimensional pavement images. Vis Comput 35, 1293–1309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1515-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1515-9