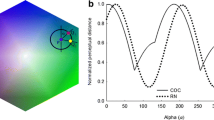
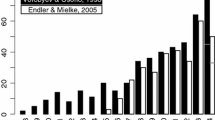
Abstract
Most of our current understanding on colour discrimination by animal observers is built on models. These typically set strict limits on the capacity of an animal to discriminate between colour stimuli imposed by physiological characteristics of the visual system and different assumptions about the underlying mechanisms of colour processing by the brain. Such physiologically driven models were not designed to accommodate sigmoidal-type discrimination functions as those observed in recent behavioural experiments. Unfortunately, many of the fundamental assumptions on which commonly used colour models are based have been tested against empirical data for very few species and many colour vision studies solely rely on physiological measurements of these species for predicting colour discrimination processes. Here, we test the assumption of a universal principle of colour discrimination only mediated by physiological parameters using behavioural data from four closely related hymenopteran species, considering two frequently used models. Results indicate that there is not a unique function describing colour discrimination by closely related bee species, and that this process is independent of specific model assumptions; in fact, different models produce comparable results for specific test species if calibrated against behavioural data.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avargués-Weber A, de Brito Sanchez MG, Giurfa M, Dyer AG (2010) Aversive reinforcement improves visual discrimination learning in free-flying honeybees. PLoS One 5(e15):370. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015370
Avargués-Weber A, Giurfa M (2014) Cognitive components of color vision in honey bees: how conditioning variables modulate color learning and discrimination. J Comp Physiol A 200:449–461
Backhaus W (1991) Color opponent coding in the visual system of the honeybee. Vis Res 31:1381–1397
Backhaus W (1998) Physiological and psychophysical simulations of color vision in humans and animals. In: Backhaus W, Reinhold K, Werner JS (eds) Color vision: perspectives from different disciplines. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 45–75
Benes ES (1969) Behavioral evidence for color discrimination by the whiptail lizard, Cnemidophorus tigris. Copeia 1969:707–722
Bobeth H (1979) Dressurversuche zum Farbensehen der Bienen: Die Sättigung von Spektralfarben. PhD thesis, Albert-Ludwigs-Universität zu Freigburg i.Br
Brandt R, Vorobyev M (1997) Metric analysis of threshold spectral sensitivity in the honeybee. Vis Res 37:425–439. doi:10.1016/S0042-6989(96)00195-2
Briscoe AD, Chittka L (2001) The evolution of color vision in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 46:471–510
Bukovac Z, Shrestha M, Garcia JE, Burd M, Dorin A, Dyer AG (2017) Why background colour matters to bees and flowers. J Comp Physiol A 203:369–380. doi:10.1007/s00359-017-1175-7
Bukovac Z, Dorin A, Dyer AG (2013) A-bees see: a simulation to assess social bee visual attention during complex search tasks. In: Lio’ P, Miglino O, Nicosia G, Nolfi G, Pavone M (eds) Advances in artificial life ECAL 2013. Proceedings of the twelfth European conference on the synthesis and simulation of living systems, Taormina, September 2013. MIT Press, Cambridge, Complex adaptive systems, pp 276–283
Burns JG, Dyer AG (2008) Diversity of speed-accuracy strategies benefits social insects. Curr Biol 18:R953–R954
Champ CM, Vorobyev M, Marshall NJ (2016) Colour thresholds in a coral reef fish. R Soc Open Sci 3(160):399. doi:10.1098/rsos.160399
Chittka L (1992) The colour hexagon: a chromaticity diagram based on photoreceptor excitations as a generalized representation of colour opponency. J Comp Physiol A 170:533–543
Crawley MJ (2012) The R book, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Daumer K (1956) Reizmetrische Untersuchung des Farbensehens der Bienen. Z Vergleich Physiol 38:413–478
Dyer AG (2006) Discrimination of flower colours in natural settings by the bumblebee species Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Entomol Gen 28:257–268
Dyer AG, Arikawa K (2014) A hundred years of color studies in insects: with thanks to Karl von Frisch and the workers he inspired. J Comp Physiol A 200:409–410
Dyer AG, Boyd-Gerny S, McLoughlin S, Rosa MG, Simonov V, Wong BB (2012) Parallel evolution of angiosperm colour signals: common evolutionary pressures linked to hymenopteran vision. Proc R Soc B 279:3606–3615. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.0827
Dyer AG, Chittka L (2004a) Biological significance of distinguishing between similar colours in spectrally variable illumination: Bumblebees (Bombus terrestris) as a case study. J Comp Physiol A 190:105–114. doi:10.1007/s00359-003-0475-2
Dyer AG, Chittka L (2004b) Fine colour discrimination requires differential conditioning in bumblebees. Naturwissenschaften 91:224–227
Dyer AG (2012) Psychophysics of honey bee color processing in complex environments. In: Galizia CG, Eisenhardt D, Giurfa M (eds) Honeybee neurobiology and behaviour. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 303–314
Dyer AG, Garcia JE (2014) Color difference and memory recall in free-flying honeybees: forget the hard problem. Insects 5:629–638. doi:10.3390/insects5030629
Dyer AG, Neumeyer C (2005) Simultaneous and successive colour discrimination in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). J Comp Physiol A 191:547–57. doi:10.1007/s00359-005-0622-z
Dyer AG, Paulk AC, Reser DH (2011) Colour processing in complex environments: insights from the visual system of bees. Proc R Soc B 278:952–959. doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.2412
Dyer AG, Spaethe J, Prack S (2008) Comparative psychophysics of bumblebee and honeybee colour discrimination and object detection. J Comp Physiol A 194:617–627. doi:10.1007/s00359-008-0335-1
Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman & Hall, New York
Fleishman LJ, Perez CW, Yeo AI, Cummings KJ, Dick S, Almonte E (2016) Perceptual distance between colored stimuli in the lizard Anolis sagrei: comparing visual system models to empirical results. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 70:541–555. doi:10.1007/s00265-016-2072-8
von Frisch K (1914) Der Farbensinn und Formensinn der Biene. Zool Jahrb Abt allg Zool Physiol Tiere 37:1–187
Garcia JE, Hung YS, Rosa MG, Endler JA, Dyer AG (2017) Improved color constancy in honeybees enabled by parallel visual projections from dorsal ocelli. PNAS. doi:10.1073/pnas.1703454114
Giurfa M (2004) Conditioning procedure and color discrimination in the honeybee Apis Mellifera. Naturwissenschaften 91:228–231
Giurfa M (2007) Behavioral and neural analysis of associative learning in the honeybee: a taste from the magic well. J Comp Physiol A 193:801–824. doi:10.1007/s00359-007-0235-9
Grimm V, Revilla E, Berger U, Jeltsch F, Mooij WM, Railsback SF, Thulke HH, Weiner J, Wiegand T, DeAngelis DL (2005) Pattern-oriented modeling of agent-based complex systems: lessons from ecology. Science 310:987–991. doi:10.1126/science.1116681
Hall P, Hart JD (1990) Bootstrap test for difference between means in nonparametric regression. JASA 85:1039–1049
von Helmholtz H (1970) Physiological optics. In: MacAdam D (ed) Sources of color science. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 84–100
von Helversen O (1972a) Zur spektralen der Honigbiene. J Comp Physiol 80:439–472
von Helversen O (1972b) The relationship between difference in stimuli and choice frequency in training experiments with the honeybee. In: Wehner R (ed) Information processing in the visual systems of arthropods. Springer, Berlin, pp 323–334
Hempel de Ibarra N, Vorobyev M, Menzel R (2014) Mechanisms, functions and ecology of colour vision in the honeybee. J Comp Physiol A 200:411–433. doi:10.1007/s00359-014-0915-1
Howard J, Blakeslee B, Laughlin S (1987) The intracellular pupil mechanism and photoreceptor signal: noise ratios in the fly Lucilia cuprina. Proc R Soc B 231:415–435
Kelber A (2016) Colour in the eye of the beholder: receptor sensitivities and neural circuits underlying colour opponency and colour perception. Curr Opin Neurobiol 41:106–112. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2016.09.007
Kemp D, Herberstein M, Fleishman L, Endler J, Bennett A, Dyer A, Hart N, Marshall J, Whiting M (2015) An integrative framework for the appraisal of coloration in nature. Am Nat 185:705–724
Komatsu H, Ideura Y (1993) Relationships between color, shape, and pattern selectivities of neurons in the inferior temporal cortex of the monkey. J Neurophysiol 70:677–694
van der Kooi CJ, Elzenga JTM, Staal M, Stavenga DG (2016) How to colour a flower: on the optical principles of flower coloration. Proc R Soc B 283:1–9
Koshitaka H, Kinoshita M, Vorobyev M, Arikawa K (2008) Tetrachromacy in a butterfly that has eight varieties of spectral receptors. Proc R Soc B 275:947–954
Kulikowski J, Walsh V (1991) On the limits of colour detection and discrimination. In: Kulikowski J, Walsh V, Murray I (eds) Limits of vision. MacMillan Press, London, pp 202–220
Lehrer M (1999) Dorsoventral asymmetry of colour discrimination in bees. J Comp Physiol A 184:195–206. doi:10.1007/s003590050318
Lind O, Kelber A (2009) Avian colour vision: effects of variation in receptor sensitivity and noise data on model predictions as compared to behavioural results. Vis Res 49:1939–1947. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2009.05.003
Longden KD (2016) Central brain circuitry for color vision modulated behaviors. Curr Biol 26:R981–R988
Lythgoe JN (1979) The ecology of vision. Oxford University Press, New York
MacAdam DL (1942) Visual sensitivities to color differences in daylight. J Opt Soc Am 32:247–273. doi:10.1364/JOSA.32.000247
MacAdam DL (1943) Specification of small chromaticity differences. J Opt Soc Am 33:18–26. doi:10.1364/JOSA.33.000018
MacAdam DL (1985) Color measurement theme and variations, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Martínez-Harms J, Vorobyev M, Schorn J, Shmida A, Keasar T, Homberg U, Schmeling F, Menzel R (2012) Evidence of red sensitive photoreceptors in Pygopleurus israelitus (Glaphyridae: Coleoptera) and its implications for beetle pollination in the southeast Mediterranean. J Comp Physiol A 198:451–463
Morawetz L, Spaethe J (2012) Visual attention in a complex search task differs between honeybees and bumblebees. J Exp Biol 215:2515–2523
Neumeyer C (1992) Tetrachromatic color vision in goldfish: evidence from color mixture experiments. J Comp Physiol A 171:639–649. doi:10.1007/BF00194111
Newhall SM, Burnham RW, Clark JR (1957) Comparison of successive with simultaneous color matching. J Opt Soc Am 47:43–54. doi:10.1364/JOSA.47.000043
Olsson P, Lind O, Kelber A (2015) Bird colour vision: behavioural thresholds reveal receptor noise. J Exp Biol 218:184–193
Paine CET, Marthews TR, Vogt DR, Purves D, Rees M, Hector A, Turnbull LA (2012) How to fit nonlinear plant growth models and calculate growth rates: an update for ecologists. Methods Ecol Evol 3:245–256. doi:10.1111/j.2041-210X.2011.00155.x
Peitsch D, Fietz A, Hertel H, Souza J, Ventura D, Menzel R (1992) The spectral input systems of hymenopteran insects and their receptor-based colour vision. J Comp Physiol A 170:23–40. doi:10.1007/bf00190398
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team (2016) nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-125
Pommerening A, Muszta A (2016) Relative plant growth revisited: towards a mathematical standardisation of separate approaches. Ecol Model 320:383–392
R Core Team (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Renoult JP, Kelber A, Schaefer HM (2017) Colour spaces in ecology and evolutionary biology. Biol Rev 92:292–315. doi:10.1111/brv.12230
Reser DH, Wijesekara Witharanage R, Rosa MGP, Dyer AG (2012) Honeybees (Apis mellifera) learn color discriminations via differential conditioning independent of long wavelength (green) photoreceptor modulation. PLoS One 7(e48):577. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048577
Shepard R (1987) Toward a universal law of generalization for psychological science. Science 237:1317–1323. doi:10.1126/science.3629243
Shrödinger E (1926) Thresholds of color differences. In: MacAdam DL (ed) Sources of color science. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 183–193
Skorupski P, Chittka L (2010) Differences in photoreceptor processing speed for chromatic and achromatic vision in the bumblebee, Bombus terrestris. J Neurosci 30:3896–3903
Sommerlandt FMJ, Spaethe J, Rössler W, Dyer AG (2016) Does fine color discrimination learning in free-flying honeybees change mushroom-body calyx neuroarchitecture? PLoS One 11:1–17. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0164386
Spaethe J, Streinzer M, Eckert J, May S, Dyer AG (2014) Behavioural evidence of colour vision in free flying stingless bees. J Comp Physiol A 200:485–486
Stavenga D, Smits R, Hoenders B (1993) Simple exponential functions describing the absorbance bands of visual pigments. Vis Res 33:1011–1017
Tabanick BG, Fidell L (2007) Using multivariate statistics, 5th edn. Pearson Allyn and Bacon, Boston
Telles FJ, Kelber A, Rodríguez-Gironés MA (2016) Wavelength discrimination in the hummingbird hawkmoth Macroglossum stellatarum. J Exp Biol 219:553–560
Thoen HH, How MJ, Chiou TH, Marshall J (2014) A different form of color vision in mantis shrimp. Science 343:411–413. doi:10.1126/science.1245824
Vorobyev M, Brandt R (1997) How do insect pollinators discriminate colors? Israel J Plant Sci 45:103–113
Vorobyev M, Brandt R, Peitsch D, Laughlin SB, Menzel R (2001) Colour thresholds and receptor noise: behaviour and physiology compared. Vis Res 41:639–653. doi:10.1016/s0042-6989(00)00288-1
Vorobyev M, Osorio D (1998) Receptor noise as a determinant of colour thresholds. Proc R Soc B 265:351–358
Wright AA (1972) Psychometric and psychophysical hue discrimination functions for the pigeon. Vis Res 12:1447–1464. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(72)90171-X
Wyszecki G, Stiles W (1982) Color science concepts and methods, quantitative data and formulae, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Yang EC, Lin HC, Hung YS (2004) Patterns of chromatic information processing in the lobula of the honeybee, Apis Mellifera L. J Insect Physiol 50:913–925
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Saveliev AA (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York
Zwietering MH, Jongenburger I, Rombouts FM, van't Riet K (1990) Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1875–1881
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Professor Leo Fleishman for discussions and comments on a previous version of the manuscript, and Dr. Lalina Muir for careful editing. We also thank the two anonymous reviewers and editors for valuable feedback on our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
AGD was supported by the Australian Research Council (DP0878968, DP130100015), original primary data was collected with the support of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation (Germany).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, J.E., Spaethe, J. & Dyer, A.G. The path to colour discrimination is S-shaped: behaviour determines the interpretation of colour models. J Comp Physiol A 203, 983–997 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-017-1208-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-017-1208-2