Abstract
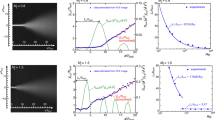
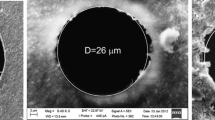
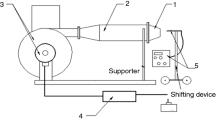
In the present study, the characteristics of supersonic rectangular microjets are investigated experimentally using molecular tagging velocimetry. The jets are discharged from a convergent–divergent rectangular nozzle whose exit height is 500 μm. The jet Mach number is set to 2.0 for all tested jets, and the Reynolds number Re is altered from 154 to 5,560 by changing the stagnation pressure. The experimental results reveal that jet velocity decays principally due to abrupt jet spreading caused by jet instability for relatively high Reynolds numbers (Re > ~450). The results also reveal that the jet rapidly decelerates to a subsonic speed near the nozzle exit for a low Reynolds number (Re = 154), although the jet does not spread abruptly; i.e., a transition in velocity decay processes occurs as the Reynolds number decreases. A supersonic core length is estimated from the streamwise distribution of the centerline velocity, and the length is then normalized by the nozzle exit height and plotted against the Reynolds number. As a result, it is found that the normalized supersonic core length attains a maximum value at a certain Reynolds number near which the transition in the velocity decay process occurs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovich GN (1963) The theory of turbulent jets. MIT Press, Cambridge
Aniskin V, Mironov S, Maslov A (2013) Investigation of the structure of supersonic nitrogen microjets. Microfluid Nanofluidics 14:605–614
Bruccoleri AR, Leiter R, Drela M, Lozano P (2012) Experimental effects of nozzle geometry on flow efficiency at low Reynolds numbers. J Propuls Power 28:96–105
Castelain T, Sunyach M, Juvé D, Béra J-C (2008) Jet-noise reduction by impinging microjets: an acoustic investigation testing microjets parameters. AIAA J 46:1081–1087
Doms M, Muller J (2005) A micromachined vapor jet pump. Sens Actuators A 119:462–467
Fan M, Suzuki Y, Kasagi N (2006) Development of a large-entrainment-ratio axisymmetric supersonic ejector for micro butane combustor. J Micromech Microeng 16:S211–S219
Gau C, Shen CH, Wang ZB (2009) Peculiar phenomenon of micro-free-jet flow. Phys Fluids 21:092001
Handa T, Masuda M, Kashitani M, Yamaguchi Y (2011) Measurement of number densities in supersonic flows using a method based on laser-induced acetone fluorescence. Exp Fluids 50:1685–1694
Lempert WR, Jiang N, Sethuram S, Samimy M (2002) Molecular tagging velocimetry measurements in supersonic microjets. AIAA J 40:1065–1070
Lempert WR, Boehem M, Jiang N, Gimelshein S, Levin D (2003) Comparison of molecular tagging velocimetry data and direct simulation of Monte Carlo simulations in supersonic micro jet flows. Exp Fluids 34:403–411
Mai C-C, Lin J (2002) Flow structures around an inclined substrate subjected to a supersonic impinging jet in laser cutting. Opt Laser Technol 34:479–486
Phalnikar KA, Kumar R, Alvi FS (2008) Experiments on free and impinging supersonic microjets. Exp Fluids 44:819–830
Roe PL (1981) Approximate Riemann solvers, parameter vectors, and difference schemes. J Comput Phys 43:357–372
Satoh D, Tanaka S, Yoshida K, Esashi M (2005) Micro-ejector to supply fuel–air mixture to a micro-combustor. Sens Actuators A 119:528–536
Scroggs SD, Settles GS (1996) An experimental study of microjets. Exp Fluids 21:401–409
Torre FL, Kenjeres S, Kleijn CR, Moerel JLPA (2010) Effects of wavy surface roughness on the performance of micronozzles. J Propuls Power 26:655–662
Walker SH, Thomas FO (1997) Experiments characterizing nonlinear shear layer dynamics in a supersonic rectangular jet undergoing screech. Phys Fluids 9:2562–2579
Willcox DC (1988) Reassessment of the scale determining equation for advanced turbulence models. AIAA J 26:1299–1310
Willcox DC (1992) Dilatation-dissipation corrections for advanced turbulence models. AIAA J 30:2639–2646
Xie C (2007) Characteristics of micronozzle gas flows. Phys Fluids 19:037102
Yamamoto S, Daiguji H (1993) Higher-order-accurate upwind schemes for solving the compressible Euler and Navier–Stokes equations. Comput Fluids 22:259–270
Yüceil KB, Ötügen MV (2002) Scaling parameters for underexpanded supersonic jets. Phys Fluids 14:4206–4215
Zhuang N, Alvi FS, Alkislar MB, Shin C (2006) Supersonic cavity flows and their control. AIAA J 44:2118–2128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Handa, T., Mii, K., Sakurai, T. et al. Study on supersonic rectangular microjets using molecular tagging velocimetry. Exp Fluids 55, 1725 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1725-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1725-5