Abstract
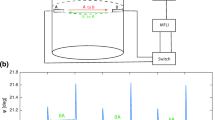
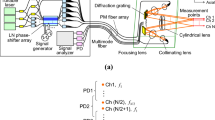
The main advantage of the described Doppler global velocimeter (DGV) systems based on frequency modulation (FM) or frequency shift keying (FSK) is that no reference detector is required. The frequency variation of the laser light during one modulation period additionally allows an on-line calibration of the complete DGV system. Thus, the new method has the potential to reduce the uncertainty of conventional DGV velocity measurements since time resolved velocity field measurements on a spinning disc have shown standard deviations down to 0.02 m/s. On investigating flow fields, velocity components notably less than 0.5 m/s were resolved.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth RW, Thorpe SJ, Manners RJ (1997) A new approach to flow-field measurement: a view of Doppler global velocimetry techniques. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 18:116–130
Fischer A, Büttner L, Czarske J, Eggert M, Grosche G, Müller H (2007) Investigation of time-resolved single-detector Doppler global velocimetry using sinusoidal laser frequency modulation. Meas Sci Technol 18:2529–2545
Ford HD, Nobes DS, Tatam RP (2001) Acousto-optic frequency switching for single-camera planar Doppler velocimetry. Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng 4448:272–282
Meyers JF, Lee JW, Schwartz RJ (2001) Characterization of measurement error sources in Doppler global velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 12:357–368
Morrison GL, Gaharan Jr CA (2001) Uncertainty estimates in DGV systems due to pixel location and velocity gradients. Meas Sci Technol 12:369–377
Müller H, Lehmacher T, Grosche G (1999) Profile sensor based on Doppler global velocimetry. 8th International conference laser anemometry advances and applications 1999, Rome, pp 475–482
Müller H, Pape N, Grosche G, Strunck V, Dopheide D (2002) Simplified DGV on-line profile sensor. 11th International symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, paper 9.3, Lisbon
Müller H, Eggert M, Pape N, Dopheide D, Czarske J, Büttner L, Razik T (2004) Time-resolved DGV based on laser frequency modulation. 12th International symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, paper 25.2, Lisbon
Röhle I, Schodl R (1994) Evaluation of the accuracy of the Doppler global technique. In: Proceedings of optical methods and data processing in heat and fluid flow. London, pp 155–161
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for the support of the project within the framework of the SPP 1147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, H., Eggert, M., Czarske, J. et al. Single-camera Doppler global velocimetry based on frequency modulation techniques. Exp Fluids 43, 223–232 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-007-0353-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-007-0353-8