Abstract
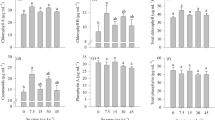
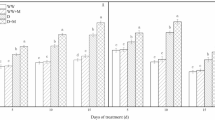
Melatonin (MT) may be related to plant growth and act on stress tolerance, and there is evidence of its role in the acquisition and assimilation of sulfur (S) remains with little information. The research hypothesis is that the application of melatonin helps in the mitigation of the stress of sulfur in soybean metabolism. In this research, we report that low S conditions affect growth by reducing chlorophyll content, photosynthesis, and soybean yield. One of the key nutrients for soybean cultivation is S; however, the management of S fertilization in tropical soils is a major challenge for agricultural producers because the currently adopted production systems can cause deficiencies in this essential element, thereby affecting crop productivity. S is the primary structural component of plants, some amino acids, and vegetable proteins, and it is involved in the formation of chlorophyll. The application of MT is a new alternative strategy for S stress reduction in plants as it is directly related to S metabolism, and recent studies have shown its potential in attenuating S stress. However, the role of MT in S translocation remains unclear. In the present study, we hypothesized that the application of MT to the soil can increase S translocation in soybean plants, thereby mitigating its deficiency. This study aimed to investigate the effects of MT on chlorophyll content, photosynthesis, transpiration, and soybean productivity in the presence of S. A 2 × 2 factorial scheme with four repetitions was used: the first factor was MT (presence and absence) and the second factor was S (presence and absence), with six repetitions. The presence of MT and S favored plant growth, chlorophyll content, photosynthetic rates, S translocation, and soybean productivity. We conclude that exogenous MT application can improve S metabolism, due to greater tolerance to S stress, which is a common condition in tropical soils, thus increasing S utilization efficiency and soybean crop productivity. However, given the complexity of soil–plant–MT–S–environment interactions, more research needs to be carried out to better investigate these effects of exogenous MT application on soil and plants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahammed GJ, Choudhary SP, Chen S, Xia X, Shi K, Zhou Y, Yu J (2013) Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrene–cadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato. J Exp Bot 64(199–213):2013. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers323
Alvarez VVH, Roscoe R, Kurihara CH, Pereira NF (2007) Soil fertility. Brazilian Society of Soil Science, Viçosa, pp 595–644
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2006) The physiological function of melatonin in plants. Plant Signal Behav 1:89–95. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.1.3.2640
Arnao MB, Hernandez-Ruiz J (2014) Melatonin: plant growth regulator and/or biostimulator during stress? Trends Plant Sci 19:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.07.006
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2021) Melatonin as a regulatory hub of plant hormone levels and action in stress situations. Plant Biol 23:7–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13202
Barberon M, Berthomieu P, Clairotte M, Shibagaki N, Davidian JC, Gosti F (2008) Unequal functional redundancy between the two Arabidopsis thaliana high-afnity sulphate transporters SULTR1;1 and SULTR1;2. New Phyto 180:608–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02604.x
Bashir H, Ahmad J, Bagheri R, Nauman M, Qureshi MI (2013) Limited sulfur resource forces Arabidopsis thaliana to shif towards non-sulfur tolerance under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 94:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.05.004
Battin EE, Brumaghim JL (2009) Antioxidant activity of sulfur and selenium: a review of reactive oxygen species scavenging, glutathione peroxidase, and metal-binding antioxidant mechanisms. Cell Biochem Biophys 55:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-009-9054-7
Buttar ZA, Wu SN, Arnao MB, Wang C, Ullah I, Wang C (2020) Melatonin suppressed the heat stress-induced damage in wheat seedlings by modulating the antioxidant machinery. Plants 9:809
Campos CN, Ávila RG, Souza KRD, Azevedo LM, Alves JD (2019) Melatonin reduces oxidative stress and promotes drought tolerance in young Coffea arabica L. plants. Agric Water Manag 211:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.025
Capaldi FR, Gratao PL, Reis AR, Lima LW, Azevedo RA (2015) Sulfur metabolism and stress defense responses in plants. Tropical Plant Biology 8:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-015-9152-1
Carciochi WD, Divito GA, Fernandez LA, Echeverria HE (2017) Sulfur afects root growth and improves nitrogen recovery and internal efficiency in wheat. J Plant Nutr 40:1231–1242. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1187740
Chandra N, Pandey N (2014) Influence of sulfur induced stress on oxidative status and antioxidative machinery in leaves of Allium cepa L. Int Sch Res Notices 29:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/568081
Dubbels R, Reiter R, Klenke E, Goebel A, Schnakenberg E, Ehlers C, Schiwara H, Schloot W (1995) Melatonin in edible plants identifed by radioimmunoassay and by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pineal Res 18:28–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1995.tb00136.x
Embrapa (2000) Technical recommendations for soybean cultivation in central Brazil 2000/01. Londrina
Embrapa (2011) Soybean production technologies - Central Region of Brazil 2012 and 2013, Londrina
Embrapa (2018) Brazilian soil classification system 5th revised and expanded edition. Brasilia
Ferreira DF (2011) Sisvar: a computer statistical analysis system. Ciênc agrotec 35:1039–1042. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542011000600001
Hasan MK, Ahammed GJ, Yin L, Shi K, Xia X, Zhou Y, Yu J, Zhou J (2015) Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front Plant Sci 6:601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00601
Hasan MK, Liu C, Wang F, Ahammed GJ, Zhou J, Xu MX, Yu JQ, Xia XJ (2016) Glutathione-mediated regulation of nitric oxide, S-nitrosothiol and redox homeostasis confers cadmium tolerance by inducing transcription factors and stress response genes in tomato. Chemosphere 161:536–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.053
Hasan MK, Liu CX, Pan YT, Ahammed GJ, Qi ZY, Zhou J (2018) Melatonin alleviates low-sulfur stress by promoting sulfur homeostasis in tomato plants. Sci Rep 8:10182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28561-0
Hattori A, Migitaka H, Iigo M, Itoh M, Yamamoto K, Ohtani KR, Hara M, Suzuki T, Reiter RJ (1995) Identifcation of melatonin in plants and its efects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochem Mol Biol Int 35:627
Ibrahim MFM, Elbar OHA, Farag R, Hikal M, El-Kelish A, El-Yazied AA, Alkahtani J, El-Gaward HGA (2020) Melatonin counteracts drought induced oxidative damage and stimulates growth, productivity and fruit quality properties of tomato plants. Plants 9:1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101276
Iqrar S, Abdin MZ (2017) Stress signaling in plants: genomics and proteomics perspective. In: Sarwat M, Ahmad A, Abdin MZ, Ibrahim MM (eds) Vol 2. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 317–340
Jez JM, Ravilious GE, Herrmann J (2016) Structural biology and regulation of the plant sulfation pathway. Chem Biol Interact 25:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.02.017
Jiang C, Cui Q, Feng K, Xu D, Li C, Zheng Q (2016) Melatonin improves antioxidant capacity and ion homeostasis and enhances salt tolerance in maize seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 38:82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2101-2
Khan NA, Asgher M, Per TS, Masood A, Fatma M, Khan MI (2016) Ethylene potentiates sulfur-mediated reversal of cadmium inhibited photosynthetic responses in mustard. Front Plant Sci 7:1628. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01628
Koprivova A, Kopriva S (2016) Sulfur metabolism and its manipulation in crops. J Genet Genom 43:623–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2016.07.001
Liang B, Ma C, Zhang Z, Wei Z, Gao T, Zhao Q, Ma F, Li C (2018) Long-term exogenous application of melatonin improves nutrient uptake fluxes in apple plants under moderate drought stress. Environ Exp Bot 155:650–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.08.016
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophyll and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes”. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Liu J, Wang W, Wang L, Sun Y (2015) Exogenous melatonin improves seedling health index and drought tolerance in tomato. Plant Growth Regul 77:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0066-6
Malavolta E (2006) Manual of plant mineral nutrition. Agronomic Ceres, Sao Paulo, p 638
Marques DJ, Bianchini HC, Maciel GM, Mendonça TFN, Silva MF (2022) Morphophysiological changes resulting from the application of silicon in corn plants under water stress. J Plant Growth Regul 41:569–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10322-5
Novais RF, Neves JCL, Barros NF (1991) Soil fertility research methods.1:89–253
Randall PJ (2014) Diagnosis of sulfur status of winged bean [Psophocarpus Tetragonolobus (L.) Dc] by plant tissue analysis. J Plant Nutr 38:212–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2014.934473
Roy M, Niu J, Irshad A, Kareem HA, Hassan MU, Xu N, Sui X, Guo Z, Amo A, Wang Q (2021) Exogenous melatonin protects alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seedlings from drought-induced damage by modulating reactive oxygen species metabolism, mineral balance and photosynthetic efficiency. Plant Stress 2:100044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2021.1000448
Rubio V, Bustos R, Irigoyen ML, Cardona-López X, Rojas-Triana M, Paz-Ares J (2009) Plant hormones and nutrient signaling. Plant Mol Biol 69:361–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9380-y
Siddiqui MH, Alamri S, Alsubaie QD, Ali HM, Ibrahim AA, Alsadon A (2019) Potential roles of melatonin and sulfur in alleviation of lanthanum toxicity in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:656–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.043
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dicky DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 3rd edn. McGraw Hill, New York, p 666
Szulc W, Rutkowska B, Sosulski T, Szara E, Stepien W (2014) Assessment of sulphur demand of crops under permanent fertilization experiment. Plant Soil Environ 60:135–140. https://doi.org/10.17221/913/2013-PSE
Tan DX, Zheng X, Kong J, Manchester LC, Hardeland R, Kim SJ, Xu X, Reiter RJ (2014) Fundamental issues related to the origin of melatonin and melatonin isomers during evolution: relation to their biological functions. Int J Mol Sci 15:15858–15890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150915858
Tisdale SL, Nelson WL, Beaton JD (1995) Soil fertility and fertilizers. Macmilillan, New York, p 684
Wang C, Deng Y, Liu Z, Liao W (2021) Hydrogen sulfide in plants: crosstalk with other signal molecules in response to abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 22:12068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222112068
Wei W, Li QT, Chu YN, Reiter RJ, Yu XM, Zhu DH, Zhang WK, Ma B, Lin Q, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2015) Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. J Exp Bot 66:695–707. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru392
Wu S, Wang Y, Zhang J, Gong X, Zhang Z, Sun J, Chen X, Wang Y (2021) Exogenous melatonin improves physiological characteristics and promotes growth of strawberry seedlings under cadmium stress. Hortic Plant J 7:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2020.06.002
Xu L, Zhang F, Tang M, Wang Y, Dong J, Ying J, Chen Y, Hu B, Li C, Liu L (2020) Melatonin confers cadmium tolerance by modulating critical heavy metal chelators and transporters in radish plants. J Pineal Res 69:e12659
Ye J, Wang S, Deng X, Yin L, Xiong B, Wang X (2016) Melatonin increased maize (Zea mays L.) seedling drought tolerance by alleviating drought-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage. Acta Physiol Plant 38:48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-2045-y
Zeng L, Cai J, Li J, Lu G, Li C, Fu G, Zhang X, Ma H, Liu Q, Zou X, Cheng Y (2018) Exogenous application of a low concentration of melatonin enhances salt tolerance in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) seedlings. J Integr Agric 17:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61757-X
Zhang N, Sun Q, Zhang H, Cao Y, Weeda S, Ren S, Guo YD (2015) Roles of melatonin in abiotic stress resistance in plants. J Exp Bot 66:647–656. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru336
Zhang J, Shi Y, Zhang X, Du HM, Xu B, Huang BR (2017) Melatonin suppression of heat-induced leaf senescence involves changes in abscisic acid and cytokinin biosynthesis and signaling pathways in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Environ Exp Bot 138:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.02.012
Zhao YQ, Zhang ZW, Chen YE, Ding CB, Yuan S, Reiter RJ, Yuan M (2021) Melatonin: a potential agent in delaying leaf senescence. Crit Rev Plant Sci 40:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2020.1865637
Zou JN, Jin XJ, Zhang YX, Ren CY, Zhang MC, Wang MX (2019) Effects of melatonin on photosynthesis and soybean seed growth during grain filling under drought stress. Photosynthetica 57:512–520. https://doi.org/10.32615/ps.2019.066
Zou J, Yu H, Yu Q, Jin X, Cao L, Wang M, Wang M, Ren C, Zhang Y (2021) Physiological and UPLC-MS/MS widely targeted metabolites mechanisms of alleviation of drought stress-induced soybean growth inhibition by melatonin. Ind Crops Prod 163:113323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113323
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq/Brazil) and the Pro-Rectory of Research and Postgraduate Studies (PROPP).
Funding
Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DJM was the advisor of this research. JACS and PHM conducted the experiment in the greenhouse and performed physiological, biochemical, and productive. HCB, MCS, and EA contributed to analyses, methodology, and statistics.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stephan Pollmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Marques, D.J., Siqueira, J.A.C., Mendes Queiroz, P.H. et al. Exogenous Application of Melatonin Affects Sulfur Metabolism in Soybean Crop. J Plant Growth Regul 43, 538–549 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11110-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11110-z