Abstract
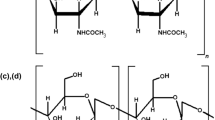
Agar, agarose, and agaropectin were extracted from the red alga Ahnfeltia plicata, and their properties and structures were characterized. Agar was extracted by a comparatively low alkaline consumption of 1.2%. It exhibited a gel strength of 1 152.50±74.25 g/cm2 and a sulfate content of 0.55%±0.08%. The yield of agar from A. plicata was 24.53%, which is higher than those of other agarophytes commonly used in China. Three kinds of the method were compared for the purification of agarose, and the physicochemical properties of agarose that was prepared under the optimal condition were identical to those of commercially available agarose. Furthermore, agaropectin was purified from A. plicata and characterized by GC, HPLC, UV-spectrum, and FI-IR to understand its composition and structure. It was the first time to comprehensively study the agar and its fractions from the red alga of A. plicata. This research provided an eco-friendly agar extraction method from A. plicata and revealed its potential application for the production of agar, agarose, and agaropectin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armisen R. 1995. World-wide use and importance of Gracilaria. Journal of Applied Phycology, 7(3): 231–243.
Bixler H J, Porse H. 2011. A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry. Journal of Applied Phycology, 23(3): 321–335.
Blethen J. 1966-10-25. Method for the separation of agaropectin from agarose: US, US3281409A.
Cook R B, Witt H J. 1981-09-22. Agarose composition, aqueous gel and method of making same: US, US4290911A.
Cordover R. 2007. Seaweed Agronomy: Cropping in Inland Saline Groundwater Evaporation Basins. Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation, Tasmania.
Costa L S, Fidelis G P, Cordeiro S L. 2010. Biological activities of sulfated polysaccharides from tropical seaweeds. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 64(1): 21–28.
Dodgson K S, Price R G. 1962. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides. Biochemical Journal, 84(1): 106–110.
Duckworth M, Yaphe W. 1971. Preparation of agarose by fractionation from the spectrum of polysaccharides in agar. Analytical Biochemistry, 44(2): 636–641.
Freile-Pelegrin Y, Murano E. 2005. Agars from three species of Gracilaria (Rhodophyta) from Yucatan Peninsula. Bioresource Technology, 96(3): 295–302.
He B Y, Ou G N, Li X M, Chen W J, Zhang X R. 2006. Primary study on the composition and structure of polysaccharides from Bangia fusco-purpurea. Food Science, 27(11): 210–214. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hegenauer J C, Nace G W. 1965. An improved method for preparing agarose. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 111(1): 334–336.
Hjertén S. 1964. The preparation of agarose spheres for chromatography of molecules and particles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Specialized Section on Biophysical Subjects, 79(2): 393–398.
Huang T T, Ye L Y, Sha Y, Tu S, Xiao Z Y, Li X M, Li Y Z, Li J B. 2010. Optimization of alkali treatment technological conditions for agar prepared from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, (10): 12–15, 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huo P, Zhang K C, XU R. 1999. Studies on using stillage producing polysaccharide by submerged fermentation of lentinus edodes. Journal of Wuxi University of Light Industry, 18(1): 47–49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hurtado-Ponce A Q, Umezaki I. 1988. Physical properties of agar gel from Gracilaria (Rhodophyta) of the Philippines. Botanica Marina, 31(2): 171–174.
Ji M H. 1997. IR Spectra of Agar. Seaweed Chemistry. Science Press, Beijing, China. p.89–92.
Kang X J, Qu J S. 2006. Analysis of Angelica dahurica polysaccharide by gas chromatography. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 26(7): 891–894. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kirkpatrick F H, Guiseley K, Provonchee R, Nochumson S. 1991-01-08. High gel strength low electroendosmosis agarose: US, US4983268A.
Kloareg B, Quatrano R S. 1988. Structure of the cell walls of marine algae and ecophysiological functions of the matrix polysaccharides. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 26: 259–315.
Lee W K, Lim Y Y, Leow A T C, Namasivayam P, Abdullah J O, Ho C L. 2017. Factors affecting yield and gelling properties of agar. Journal of Applied Phycology, 29(3): 1 527–1 540.
Lins K O A L, Bezerra D P, Alves A P N N, Alencar N M N, Lima M W, Torres V M, Farias W R L, Pessoa C, De Moraes M O, Costa-Lotufo L V. 2009. Antitumor properties of a sulfated polysaccharide from the red seaweed Champia feldmannii (Diaz-Pifferer). Journal of Applied Toxicology, 29(1): 20–26.
Matsuhiro B, Zanlungo A. 1983. Colorimetric determination of 3,6-anhydrogalactose in polysaccharides from red seaweeds. Carbohydrate Research, 118: 276–279.
McHugh D J. 2003. A Guide to the Seaweed Industry. FAO Fish Tech Pap 441, Rome, Italy. 105p.
Mclachlan J, Bird C J. 1986. Gracilaria (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) and productivity. Aquatic Botany, 26: 27–49.
Meena R, Prasad K, Siddhanta A K. 2011. Preparation of superior quality products from two Indian agarophytes. Journal of Applied Phycology, 23(2): 183–189.
Meena R, Siddhanta A K, Prasad K, Ramavat B K, Eswaran K, Thiruppathi S, Ganesan M, Mantri V A, Rao P V S. 2007. Preparation, characterization and benchmarking of agarose from Gracilaria dura of Indian waters. Carbohydrate Polymers, 69(1): 179–188.
Nishinari K, Fang Y P. 2017. Relation between structure and rheological/thermal properties of agar. A mini-review on the effect of alkali treatment and the role of agaropectin. Food Structure, 13: 24–34.
Nishino T, Nagumo T, Kiyohara H, Yamada H. 1991. Structural characterization of a new anticoagulant fucan sulfate from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome. Carbohydrate Research, 211(1): 77–90.
Poison A. 1967-08-08. Fractionation of mixtures of agarose and agaropectin: US, US3335127A.
Provonchee R B. 1991-02-05. Agarose purification method using glycol: US, US4990611A.
Qi H M, Li D X, Zhang J J, Liu L, Zhang Q B. 2008. Study on extraction of agaropectin from Gelidium amansii and its anticoagulant activity. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 26(2): 186–189.
Rebello J, Ohno M, Ukeda H, Kusunose H, Sawamura M. 1997. 3,6 anhydrogalactose, sulfate and methoxyl contents of commercial agarophytes from different geographical origins. Journal of Applied Phycology, 9(4): 367–370.
Rees D A. 1961. Enzymic synthesis of 3:6-anhydro-L-galactose within porphyran from L-galactose 6-sulphate units. Biochemical Journal, 81(2): 347–352.
Rupérez P, Ahrazem O, Leal J A. 2002. Potential antioxidant capacity of sulfated polysaccharides from the edible marine brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(4): 840–845.
Rupérez P. 2002. Mineral content of edible marine seaweeds. Food Chemistry, 79(1): 23–26.
Salehi P, Dashti Y, Tajabadi F M, Safidkon F, Rabei R. 2011. Structural and compositional characteristics of a sulfated galactan from the red alga Gracilariopsis persica. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(4): 1 570–1 574.
Shanmugam M, Mody K H. 2000. Heparinoid-active sulphated polysaccharides from marine algae as potential blood anticoagulant agents. Current Science, 79(12): 1 672–1 683.
Souza B W S, Cerqueira M A, Bourbon A I, Pinheiro A C, Martins J T, Teixeira J A, Coimbra M A, Vicente A A. 2012. Chemical characterization and antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide from the red seaweed Gracilaria birdiae. Food Hydrocolloids, 27(2): 287–292.
Sukhoverkhov S V, Kadnikova I A, Podkorytova A V. 2000. Production of agar and agarose from the red alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 36(2): 201–203.
Wang L, Liu L, Wang Y M, Yuan Q Y, Li Z E, Xu Z H. 2001. Comparative research on the structures and physical-chemical properties of agars from several agarophyta. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 32(6): 658–664. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang X Y, Duan D L, Fu X T. 2016. Enzymatic desulfation of the red seaweeds agar by Marinomonas arylsulfatase. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 93: 600–608.
Watase M, Nishinari K. 1986. Rheological and thermal properties of polysaccharide gels extracted from Ahnfeltia plicata. Colloid and Polymer Science, 264(10): 877–882.
Whyte J N C, Foreman R E, DeWreede R E. 1984. Phycocolloid screening of British Columbia red algae. Hydrobiologia, 116–117(1): 537–541.
Zhang L, Xu J Z, Xue C H, Gao X, Zhang D. 2009. Rheological properties and gel properties of agar. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 28(2): 11–17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao M M, Liu T X, Wu H, Peng Z Y, Gao K R. 1996. A study of the alkali-treatment effect on the extraction yield, properties and chemical composition of agar. Food and Fermentation Industries, (6): 1–7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (No. 201405040), the Key Research and Development Program in Shandong Province (No. 2016GSF121034), and the Jiangsu Provincial Key R&D Project (No. BE2015335)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Fu, X., Duan, D. et al. Preparation and characterization of agar, agarose, and agaropectin from the red alga Ahnfeltia plicata. J. Ocean. Limnol. 37, 815–824 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8129-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8129-6