Abstract.
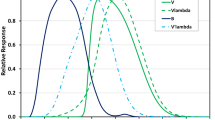
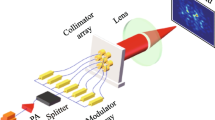
We demonstrate monitoring of H2O and CO2 emitted in a volcanic area, using a spectrometer equipped with two distributed feedback (DFB) semiconductor diode lasers. Each laser is resonant with a molecular species and is fiber-coupled to allow remote operation of the spectrometer. Recordings of H2O and CO2 lines made at the Solfatara volcano, in southern Italy, are shown, and the application of such a spectrometer as a new tool for the continuous monitoring and surveillance of volcanoes is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 June 1999 / Revised version: 20 December 1999 / Published online: 23 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gianfrani, L., De Natale, P. & De Natale, G. Remote sensing of volcanic gases with a DFB-laser-based fiber spectrometer . Appl Phys B 70, 467–470 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400000236
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400000236