Abstract
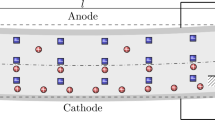
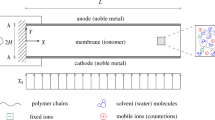
Ionic polymer-metal composite (IPMC) actuators are a class of electroactive polymer composites that exhibit some interesting electromechanical characteristics such as low voltage actuation, large displacements, and benefit from low density and elastic modulus. Elastic modulus and surface resistance are basic properties of IPMCs that play a role in almost all practical applications of these materials. The prediction of the elastic modulus and surface resistance is of extreme importance to better grasp the mechanical behavior of IPMCs and to evaluate the success of the design. This paper has proposed a theoretical framework for predicting the elastic modulus and surface resistance of copper electrodes IPMCs. A five layers analytical assemblage model is introduced for the IPMCs relied upon improved classical lamination theory. The depositional metallic atoms were used as the exterior layer, the ionic polymer was used as the middle layer, and the material between the two layers was a gradient layer. Based on Mori–Tanaka methodology and gradient mechanics, the overall elastic properties of composites are obtained and lie between those obtained from the experiment. The prediction showed a good agreement with the experimental elastic modulus values with a maximum deviation of less than 10%. The overall results have provided useful insight into the elastic modulus and surface resistance effects to the properties of the IPMC. This would open further opportunities toward the higher application of IPMC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Tamagawa, K. Okada, T. Mulembo, M. Sasaki, K. Naito, G. Nagai, T. Nitta, K.C. Yew, K. Ikeda, Simultaneous enhancement of bending and blocking force of an ionic polymer-metal composite (IPMC) by the active use of its material characteristics change. Actuators 8, 29 (2019)
L. Yang, D. Zhang, X. Zhang, A. Tian, X. Wang, Models of displacement and blocking force of ionic-polymer metal composites based on actuation mechanism. Appl. Phys. A 126, 365 (2020)
A. Khan, R.K. Inamuddin, M. Jain, A.M.Asiri Luqman, Development of sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol)/aluminium oxide/graphene based ionic polymer-metal composite (IPMC) actuator. Sensor. Actuat. A Phys. 280, 114–124 (2018)
L. Yang, D.S. Zhang, X.N. Zhang, A.F. Tian, Fabrication and actuation of Cu-ionic polymer metal composite. Polymers 12, 460 (2020)
Z. Hojat, N. Naghavi, B. Hasan, A combined fuzzy logic and artificial neural network approach for non-linear identification of IPMC actuators with hysteresis modification. Expert Syst. 35, e12283 (2018)
H.R. Cheong, N.T. Nguyen, M.K. Khaw, B.Y. Teoh, P.S. Chee, Wirelessly activated device with an integrated ionic polymer metal composite(IPMC) cantilever valve for targeted drug delivery. Lab Chip 18, 3207–3215 (2018)
L. Yang, D. Zhang, X. Zhang, A. Tian, Prediction of the actuation property of Cu ionic polymer–metal composites based on backpropagation neural networks. ACS Omega 5, 4067–4074 (2020)
E. Esmaeli, M. Ganjian, H. Rastegar, M. Kolahdouz, Z. Kolahdouz, G.Q. Zhang, Humidity sensor based on the ionic polymer metal composite. Sensor Actuator B Chem. 247, 498–504 (2017)
S. Budhe, S. de Barros, M.D. Banea, Theoretical assessment of the elastic modulus of natural fiber-based intra-ply hybrid composites. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 41, 263 (2019)
K.S. Ahmed, S. Vijayarangan, Elastic property evaluation of jute-glass fiber hybrid composite using experimental and CLT approach. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 13, 435–442 (2006)
N. Phan-Thien, D.C. Pham, Differential multiphase models for polydispersed spheroidal inclusions: thermal conductivity and effective viscosity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 38, 73–88 (2000)
S. Giordano, Nonlinear effective behavior of a dispersion of randomly oriented coated ellipsoids with arbitrary temporal dispersion. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 98, 14–35 (2016)
W.X. Xu, D. Zhang, P. Lan, Y. Jiao, Multiple-inclusion model for the transport properties of porous composites considering coupled effects of pores and interphase around spheroidal particles. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 150, 610–616 (2019)
W.X. Xu, M.K. Jia, Z.G. Zhu, M. Liu, D. Lei, X.F. Gou, N-phase micromechanical framework for the conductivity and elastic modulus of particulate composites: design to microencapsulated phase change materials (mpcms)-cementitious composites. Mater. Des. 145, 108–115 (2018)
E. García-Macías, R. Castro-Triguero, A. Sáez, F. Ubertini, 3D mixed micromechanics-FEM modelling of piezoresistive carbon nanotube smart concrete. Comput. Methods Appl. Meth. Eng. 340, 396–423 (2018)
T. Kenta, J.F. Li, S. Yokoyama, R. Watanabe, A. Almajid, M. Taya, Design and fabrication of functionally graded PZT-Pt piezoelectric bimorph actuator. Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater. 3, 217–224 (2002)
S.J. Kim, S.M. Kim, K.J. Kim, Y.H. Kim, An electrode model for ionic polymer-metal composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 2286–2295 (2007)
H.G. Liu, K. Xiong, M. Wang, A gradient model for Young’s modulus and Surface electrode resistance of ionic polymer-metal composite. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 32, 754–766 (2019)
Y. Cha, M. Aureli, M. Porfiri, A physics-based model of the electrical impedance of ionic polymer metal composites. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 124901 (2012)
Y. Wang, Z. Zhu, H. Chen, B. Luo, L. Chang, Y. Wang, Effects of preparation steps on the physical parameters and electromechanical properties of IPMC actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 125015 (2014)
A. Kloke, F. Stetten, R. Zengerle, S. Kerzenmacher, Strategies for the fabrication of porous platinum electrodes. Adv. Mater. 23, 4976–5008 (2011)
R. Tiwari, K.J. Kim, Effect of metal diffusion on mechanoelectric property of ionic polymer-metal composite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 244104 (2010)
W.X. Xu, Y. Jiao, Theoretical framework for percolation threshold, tortuosity and transport properties of porous materials containing 3d non-spherical pores. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 134, 31–46 (2019)
J.D. Eshelby, The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 241, 376–396 (1957)
W. Pabst, E. Gregorová, Young’s modulus of isotropic porous materials with spheroidal pores. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 3195–3207 (2014)
J.Y. Li, S. Nemat-Nasser, Micromechanical analysis of ionic clustering in Nafion perfluorinated membrane. Mech. Mater. 32, 303–314 (2000)
W. Pabst, E. Gregorová, Effective elastic properties of alumina-zirconia composite ceramics-part II: micromechanical modeling. Ceram. Silik. 48, 14–23 (2004)
W. Xu, Y. Wu, X. Gou, Effective elastic moduli of nonspherical particle-reinforced composites with inhomogeneous interphase considering graded evolutions of elastic modulus and porosity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 350, 535–553 (2019)
W. Liu, L. Bian, Influences of inclusions and corresponding interphase on elastic properties of composites. Arch. Appl. Mech. 88, 1507–1524 (2018)
H. Tan, Y. Huang, C. Liu, G. Ravichandran, H.M. Inglis, P.H. Geubelle, The uniaxial tension of particulate composite materials with nonlinear interface debonding. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 1809–1822 (2007)
W. Pabst, E. Gregorová, Effective elastic properties of alumina-zirconia composite ceramics-part I: rational continuum theory of linear elasticity. Ceram. Silik. 47, 1–7 (2003)
P. Huang, Principles of powder metallurgy(second edition) (Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1997), pp. 391–392
M. Sabet, M. Salavati-Niasari, O. Amiri, Using different chemical methods for deposition of CdS on TiO2 surface and investigation of their influences on the dye-sensitized solar cell performance. Electrochim. Acta 117, 504–520 (2014)
F. Mohandes, F. Davar, M. Salavati-Niasari, Magnesium oxide nanocrystals via thermal decomposition of magnesium oxalate. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 1623–1628 (2010)
M. Mousavi-Kamazani, Z. Zarghami, M. Salavati-Niasari, Facile and novel chemical synthesis, characterization, and formation mechanism of copper sulfide (Cu2S, Cu2S/CuS, CuS) nanostructures for increasing the efficiency of solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 2096–2108 (2016)
F. Davar, M. Salavati-Niasari, N. Mir, K. Saberyan, M. Monemzadeh, E. Ahmadi, Thermal decomposition route for synthesis of Mn3O4 nanoparticles in presence of a novel precursor. Polyhedron 29, 1747–1753 (2010)
M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Shaterian, M.R. Ganjali, P. Norouzi, Oxidation of cyclohexene with tert-butylhydroperoxide catalysted by host (nanocavity of zeolite-Y)/guest (Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes of N, N′-bis(salicylidene)phenylene-1,3-diamine) nanocomposite materials (HGNM). J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 261, 147–155 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Science and Technology Program of Shaanxi Province, China (2016KTZDGY-02-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zhang, D., Zhang, X. et al. Property of Nafion-ionic polymer-metal composites based on Mori–Tanaka methodology and gradient mechanics. Appl. Phys. A 126, 633 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03807-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03807-9