Abstract
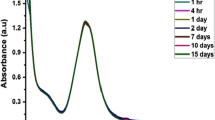
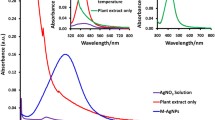
Metal ion sensors are a significant and challenging area in the analytical sciences. In this study, the use of grape juice for bio-synthesizing of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and using it for simple and rapid colorimetric detection of Cd2+ ions is described. The as-prepared AgNPs were characterized by standard analytical techniques including UV–visible and FTIR spectroscopic methods and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The plasmon resonance band of the silver nanoparticles was observed at 410 nm and it was found that its intensity is related to the grape juice concentration and pH. The TEM image showed the average size of 5–10 nm for AgNPs. The detection of Cd2+ ions was based on the changes of absorbance due to complex formation of the metal ion. The colorimetric detection of Cd2+ was led to a linear dynamic range from 0 to 150 µmol/L (r2 = 0.9993) and a low detection limit of 4.95 µmol/L for cadmium in aqueous solution. These results are close to or better than the previous reports. This bio-synthesized AgNPs can be used as simple alternative design for colorimetric sensing of Cd2+ in water samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Vanek, L. Boruvka, O. Drabek, M. Mihaljevic, M. Komarek, Mobility of lead, zinc and cadmium in alluvial soils heavily polluted by smelting industry. Plant Soil Environ. 51, 316–321 (2005)
M.P. Waalkes, Cadmium carcinogenesis in review. J. Inorg. Biochem. 79, 241–244 (2000)
S.J. Stohs, D. Bagchi, Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radical Biol. Med. 18, 321–336 (1995)
J.P. Groten, P.J. Bladeren, Cadmium bioavailability and health risk in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 5, 50–55 (1994)
World Halth Organization, Cadmium in drinking-water: background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality (2003)
M. Ghanei-Motlagh, M.A. Taher, Novel imprinted polymeric nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel technique for electrochemical detection of toxic cadmium(II) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 327, 135–141 (2017)
A. Malekpour, S. Hajialigol, M.A. Taher, Study on solid-phase extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry for the selective determination of cadmium in water and plant samples with modified clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 172, 229–233 (2009)
D. Beauchemin, S.S. Berman, Determination of trace metals in reference water standards by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with on-line preconcentration. Anal. Chem. 61, 1857–1862 (1989)
W. Guo, S. Hu, Y. Xiao, H. Zhang, X. Xie, Direct determination of trace cadmium in environmental samples by dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 81, 1463–1468 (2010)
A. Matsumoto, S. Osaki, T. Kobata, B. Hashimoto, H. Uchihara, T. Nakahara, Determination of cadmium by an improved double chamber electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Microchem. J. 95, 85–89 (2010)
C.R. Lan, Z.B. Alfassi, Direct determination of manganese in sea-water by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry with sodium hydroxide as chemical modifier for interference removal. Analyst 119, 1033–1035 (1994)
S. Yunus, S. Charles, F. Dubois, E.V. Donckt, Simultaneous determination of cadmium (II) and zinc (II) by molecular fluorescence spectroscopy and multiple linear regression using an anthrylpentaazamacrocycle chemosensor. J. Fluoresc. 18, 499–506 (2008)
M.G.A. Korn, G.L. dos Santos, S.M. Rosa, L.S.G. Teixeira, P.V. de Oliveira, Determination of cadmium and lead in cetacean Dolphinidae tissue from the coast of Bahia state in Brazil by GFAAS. Microchem. J. 96, 12–16 (2010)
M.R. Awual, M. Khraisheh, N.H. Alharthi, M. Luqman, A. Islam, M.R. Karim, M.M. Rahman, M.A. Khaleque, Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium(II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chem. Eng. J. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.116
A.J. Nozik, Nanoscience and nanostructures for photovoltaics and solar fuels. Nano Lett. 10, 2735–2741 (2010)
N.L. Rosi, C.A. Mirkin, Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem. Rev. 105, 1547–1562 (2005)
M.D. Malinsky, K.L. Kelly, G.C. Schatz, R.P.V. Duyne, Chain length dependence and sensing capabilities of the localized surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles chemically modified with alkanethiol self-assembled monolayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 1471–1482 (2001)
X. Xu, W.L. Daniel, W. Wei, C.A. Mirkin, Colorimetric Cu2+ detection using DNA modified gold nanoparticle aggregates as probes and click chemistry. Small 6, 623–626 (2010)
X. Zhang, R. Kong, Y. Lu, Metal ion sensors based on DNAzymes and related DNA molecules. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 4, 105–128 (2011)
C. Han, L. Zhanga, H. Li, Highly selective and sensitive colorimetric probes for Yb3+ ions based on supramolecular aggregates assembled from β-cyclodextrin–4,4′-dipyridine inclusion complex modified silver nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 24, 3545–3547 (2009)
S.K. Ghosh, T. Pal, Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: from theory to applications. Chem. Rev. 107, 4797–4862 (2007)
V.V. Kumar, S.P. Anthony, Silver nanoparticles based selective colorimetric sensor for Cd2+, Hg2+and Pb2+ions: tuning sensitivity and selectivity using co-stabilizingagents. Sens. Actuators B 191, 31–36 (2014)
K. Aslan, J.R. Lakowicz, C.D. Geddes, Nanogold-plasmon-resonance-based glucose sensing. Anal. Biochem. 330, 145–155 (2004)
A.J. Reynolds, A.H. Haines, D.A. Russell, Gold glyconanoparticles for mimics and measurement of metal ion-mediated carbohydrate–carbohydrate interactions. Langmuir 22, 1156–1163 (2006)
D.C. Hone, A.H. Haines, D.A. Russell, Rapid, quantitative colorimetric detection of a lectin using mannose-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 19, 7141–7144 (2003)
C.S. Tsai, T.B. Yu, C.T. Chen, Gold nanoparticle-based competitive colorimetric assay for detection of protein–protein interactions. Chem. Commun. 34, 4273–4275 (2005)
A. Laromaine, L.L. Koh, M. Murugesan, R.V. Ulijn, M.M. Stevens, Protease triggered dispersion of nanoparticle assemblies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 4156–4157 (2007)
I.V. Anambiga, V. Suganthan, N.A.N. Raj, G. Buvaneswari, T.S.S. Kumar, Colorimetric detection of lead ions using glutathione stabilized silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 4, 710–715 (2013)
T.A. Saleh, M.M. Al-Shalalfeh, A.A. Al-Saadi, Graphene dendrimer-stabilized silver nanoparticles for detection of methimazole using surfaceenhanced raman scattering with computational assignment. Sci. Rep. 6, 32185 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32185
Z. Shervani, Y. Ikushima, M.S. Hajime, K. Yukiya, H. Toshirou, Y. Takako, N. Hironobu, K. Aramaki, Morphology and size-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles in aqueous surfactant polymer solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 286, 403–410 (2008)
E.O. Dare, C.O. Oseghale, A.H. Labulo, E.T. Adesuji, E.E. Elemike, J.C. Onwuka, J.T. Bamgbose, Green synthesis and growth kinetics of nanosilver under bio-diversified plant extracts influence. J. Nanostructure Chem. 5, 85–94 (2015)
S.A. Ogundare, W.E. Zyl, Nanocrystalline cellulose as reducing- and stabilizing agent in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Application as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate. Surf. Interfaces (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2018.06.004
M. Firdaus, S. Andriana, W.A. Elvinawati, E. Swistoro, A. Ruyani, A. Sundaryono, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Carica papaya fruit extract under sunlight irradiation and their colorimetric detection of mercury ions. J. Phys. 817, 012029 (2017)
S. Maiti, G. Barman, J.K. Laha, Biosynthesized gold nanoparticles as catalyst. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 5, 1226–1230 (2014)
C. Venkata, S. Prakash, I. Prakash, Bioactive chemical constituents from pomegranate (Punica granatum) juice seed and peel-a review. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 1, 1–18 (2011)
X. Huang, H. Wu, X. Liao, B. Sh, One-step, size-controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles at room temperature using plant tannin. Green Chem. 12, 395–399 (2010)
S. Maiti, G. Barman, J.K. Laha, Detection of heavy metals (Cu+2, Hg+2) by biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 529–538 (2016)
A. Chhatre, P. Solasa, S. Sakle, R. Thaokar, A. Mehra, Color and surface plasmon effects in nanoparticle systems: case of silver nanoparticles prepared by microemulsion route. Colloids Surf. A 404, 83–92 (2012)
F. Cosme, T. Pinto, A. Vilela, Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in grape juices: a chemical and sensory view. Beverages 4, 22 (2018)
H. Schulza, M. Baranska, Identification and quantification of valuable plant substances by IR and Raman spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 43, 13–25 (2007)
C. Yohannan, P. Hema, T. Varghese, D. Philip, FT-IR, FT-Raman and SERS spectra of vitamin C. Spectrochim. Acta 65, 802–804 (2006)
S.D. Silva, R.P. Feliciano, L.V. Boasa, M.R. Bronze, Application of FTIR-ATR to moscatel dessert wines for prediction of total phenolic and flavonoid contents and antioxidant capacity. Food Chem. 150, 489–493 (2014)
J. Krajczewski, K.K. Taj, A. Kudelski, Plasmonic nanoparticles in chemical analysis. RSC Adv. 7, 17559 (2017)
V.K.N. Mehta, J.K.V. Rohit, S.K. Kailasa, Functionalization of silver nanoparticles with 5-sulfoanthranilic acid dithiocarbamate for selective colorimetric detection of Mn2+ and Cd2+ ions. New J. Chem. 40, 4566–4574 (2016)
Y. Sun, T. Zuo, F. Guo, J. Sun, Z. Liu, G. Diao, Perylene dye-functionalized silver nanoparticles serving as pH-dependent metal sensor systems. RSC Adv. 7, 24215–24220 (2017)
Y. Guo, Y. Zhang, H. Shao, Z. Wang, X. Wang, X. Jiang, Label-free colorimetric detection of cadmium ions in rice samples using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 86, 8530–8534 (2014)
V.V. Kumar, S.P. Anthony, Silver nanoparticles based selective colorimetric sensor for Cd2+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ ions: tuning sensitivity and selectivity using co-stabilizing agents. Sens. Actuators B 191, 31–36 (2014)
M.R. Fallahi, G. Khayatian, Cadmium determination based on silver nanoparticles modified with 1,13-bis(8-quinolyl)-1,4,7,10,13-pentaoxatridecane. J. Iran Chem. Soc. 14, 1469–1476 (2017)
M. Zhang, Y. Liu, B. Ye, Colorimetric assay for parallel detection of Cd2+, Ni2+ and Co2+ using peptide-modified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 137, 601–607 (2012)
W. Jin, P. Huang, F. Wu, L. Ma, Ultrasensitive colorimetric assay of cadmium ion based on silver nanoparticles functionalized with 5-sulfosalicylic acid for wide practical applications. Analyst 140, 3507–3513 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the University of Guilan for support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabariyan, S., Zanjanchi, M.A. Colorimetric detection of cadmium ions using modified silver nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 125, 872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3167-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3167-7