Abstract
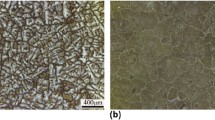
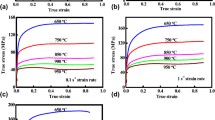
In order to reveal the flow characteristics of Cu-6 %Ag alloy on the condition of hot deformation, the isothermal compression experiments are carried out at the temperatures of 973–1123 K under strain rates of 0.01–10 s−1. The effects of deformation condition on the hot compression deformation behavior are investigated. The low instability strain (ɛ i) behavior at high strain rate (10 s−1) is discussed in this paper. According to the experiment results and analyses, the deformation twinning and inhomogeneous grains are thought to be the possible reasons for low strain cracking. Then, a modified physically based constitutive model is established. The strain for maximum softening rate \( (\varepsilon_{ *} ) \) is quoted in the constitutive equation which is proved that there is a nearly linear relationship between \( { \ln }\varepsilon_{ *} \) and \( { \ln }Z \). What’s more, the correlation coefficient (R) and the average absolute relative error (AARE) are used to evaluate the accuracy of the established constitutive model. The values of R and AARE are 0.99612 and 3.47 %, respectively, which show that the modified constitutive model can exactly reveal the flow stress of Cu-6 %Ag alloy.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Zhang, C. Hu, Q. Zhu, C.G. Ding, H.Y. Qin, Hot compression deformation and constitutive modeling of GH4698 alloy. Mater. Des. 65, 1153–1160 (2015)
X. Luo, L. Kang, Q. Li, Y. Chai, Microstructure and hot compression deformation of the as-cast Mg−5.0Sn−1.5Y−0.1Zr alloy. Appl. Phys. A 120(2), 699–705 (2015)
Y.C. Lin, X.M. Chen, A critical review of experimental results and constitutive descriptions for metals and alloys in hot working. Mater. Des. 32(4), 1733–1759 (2011)
A. He, G. Xie, X. Yang, X. Wang, H. Zhang, A physically-based constitutive model for a nitrogen alloyed ultralow carbon stainless steel. Comp. Mater. Sci. 98, 64–69 (2015)
W. Peng, W. Zeng, Q. Wang, H. Yu, Comparative study on constitutive relationship of as-cast Ti60 titanium alloy during hot deformation based on Arrhenius-type and artificial neural network models. Mater. Des. 51, 95–104 (2013)
A.T. Adorno, M.R. Guerreiro, R.A.G. Silva, Kinetics of Ag-rich precipitates formation in Cu–Al–Ag alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 374(1–2), 170–176 (2004)
Y.Z. Tian, Z.F. Zhang, Microstructures and tensile deformation behavior of Cu-16 wt%Ag binary alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 508(1–2), 209–213 (2009)
Y.Z. Tian, S.D. Wu, Z.F. Zhang, R.B. Figueiredo, N. Gao, T.G. Langdon, Strain hardening behavior of a two-phase Cu–Ag alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 65(6), 477–480 (2011)
Y. Sakai, K. Inoue, T. Asano, H. Wada, H. Maeda, Development of high-strength, high-conductivity Cu–Ag alloys for high-field pulsed magnet use. Appl. Phys. Lett. 59(23), 2965–3967 (1991)
Y. Sakal, K. Inoue, H. Maeda, New high-strength, high-conductivity Cu–Ag alloy sheets. Acta Metall. Mater. 43(4), 1517–1522 (1995)
Y. Sakal, H.J. Schneider, Ultra-high strength, high conductivity Cu–Ag alloy wires. Acta Metall. Mater. 45(3), 1017–1023 (1997)
A. Benghalem, D.G. Morris, Microstructure and strength of wire-drawn Cu–Ag filamentary composites. Acta Mater. 45(1), 397–406 (1997)
J.B. Liu, L. Zhang, D.W. Yao, L. Meng, Microstructure evolution of Cu/Ag interface in the Cu–6 wt% Ag filamentary nanocomposite. Acta Mater. 59(3), 1191–1197 (2011)
D.W. Yao, L.N. Song, A.P. Dong, L.T. Wang, L. Zhang, L. Meng, The role of Ag precipitates in Cu-12 wt% Ag. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 607–610 (2012)
M.H. Wang, L. Huang, M.L. Chen, Y.L. Wang, Processing map and hot working mechanisms of Cu–Ag alloy in hot compression process. J. Cent. South. Univ. 22(3), 821–828 (2015)
M.S. Chen, Y.C. Lin, X.S. Ma, The kinetics of dynamic recrystallization of 42CrMo steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556, 260–266 (2012)
Z. Zeng, L. Chen, F. Zhu, X. Liu, Dynamic recrystallization behavior of a heat-resistant martensitic stainless steel 403 Nb during hot deformation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27(10), 913–919 (2011)
H. Mirzadeh, A. Najafizadeh, Prediction of the critical conditions for initiation of dynamic recrystallization. Mater. Des. 31(3), 1174–1179 (2010)
J.J. Jonas, X. Quelennec, L. Jiang, É. Martin, The Avrami kinetics of dynamic recrystallization. Acta Mater. 57(9), 2748–2756 (2009)
E.S. Puchi-Cabrera, J.D. Guérin, M. Dubar, M.H. Staia, J. Lesage, D. Chicot, Constitutive description for the design of hot-working operations of a 20MnCr5 steel grade. Mater. Des. 62, 255–264 (2014)
X. Li, L. Duan, J. Li, X. Wu, Experimental study and numerical simulation of dynamic recrystallization behavior of a micro-alloyed plastic mold steel. Mater. Des. 66, 309–320 (2015)
A. Laasraoui, J.J. Jonas, Recrystallization of austenite after deformation at high temperatures and strain rates—analysis and modeling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 22, 1545–1588 (1991)
Y.C. Lin, X.M. Chen, D.X. Wen, M.S. Chen, A physically-based constitutive model for a typical nickel-based superalloy. Comp. Mater. Sci. 83, 282–289 (2014)
A. Najafizadeh, Predicting the critical stress for initiation of dynamic recrystallization. ISIJ Int. 46(11), 1679–1684 (2006)
L. Wang, F. Liu, Q. Zuo, C.F. Chen, Prediction of flow stress for N08028 alloy under hot working conditions. Mater. Des. 47, 737–745 (2013)
S. Mandal, V. Rakesh, P.V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, K.V. Kasiviswanathan, Constitutive equations to predict high temperature flow stress in a Ti-modified austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 500(1–2), 114–121 (2009)
Z.L. Zhao, H. Li, M.W. Fu, H.Z. Guo, Z.K. Yao, Effect of the initial microstructure on the deformation behavior of Ti60 titanium alloy at high temperature processing. J. Alloys. Comp. 617, 525–533 (2014)
D. Dong, F. Chen, Z. Cui, A physically-based constitutive model for SA508-III steel: modeling and experimental verification. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 634, 103–115 (2015)
M.H. Wang, W.H. Wang, J.J. Dong, L.H. Zhang, Y.P. Li, A. Chiba, Quantitative analysis of work hardening and dynamic softening behaviors of Cu-6 wt pct Ag binary alloy based on true stress vs strain curves. Acta. Metall. Sin-Engl. 25(6), 420–434 (2012)
Y.C.Y. Sung-II Kim, Dynamic recrystallization behavior of AISI 304 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 311(1–2), 108–113 (2001)
G.Z. Quan, L. Zhao, T. Chen, Y. Wang, Y.P. Mao, W.Q. Lv, J. Zhou, Identification for the optimal working parameters of as-extruded 42CrMo high-strength steel from a large range of strain, strain rate and temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 538, 364–373 (2012)
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, J. Zhong, Prediction of 42CrMo steel flow stress at high temperature and strain rate. Mech. Res. Commun. 35, 142–150 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. CDJZR14130006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, L., Wang, M., Liu, X. et al. Hot compression deformation behavior and a modified physically-based constitutive model of Cu-6 %Ag alloy. Appl. Phys. A 122, 387 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9956-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9956-3