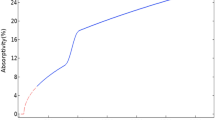
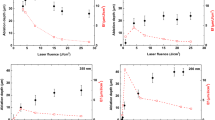
Abstract
In this paper, we present a hybrid laser-plasma ablation method for material processing applications. For this purpose, a coaxial configuration consisting of a low-temperature atmospheric pressure argon plasma beam and a Nd:YAG-laser at a wavelength of 355 nm was used. Both pure laser ablation and hybrid laser-plasma ablation experiments were performed on aluminum at different laser energies and numbers of laser pulses. In the case of hybrid ablation, both the depth and volume ablation rates were increased significantly in comparison to pure laser ablation. This effect is described by a linear interrelationship of both the ablation rate and the particularly applied laser energy and is thus due to energetic synergies. Such behavior can be explained by the de-excitation of argon plasma species and an accompanying energy deposition at the generated debris and the sample surface. The energetic effect was found to abate with increasing ablation depth. However, considerable improvements in terms of ablation rate are achieved in the near-surface depth range of approx. 500 microns.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Armon, M. Hill, I.J. Spalding, Y. Zvirin, J. Appl. Phys. 65, 5003–5006 (1989)
M. Lapczyna, K.P. Chen, P.R. Herman, H.W. Tan, R.S. Marjoribanks, Appl. Phys. A 69 [Suppl.], S883–S886 (1999)
C. Gerhard, F. Druon, P. Blandin, M. Hanna, F. Balembois, P. Georges, F. Falcoz, Appl. Opt. 47(7), 967–974 (2008)
A.C. Forsman, P.S. Banks, M.D. Perry, E.M. Campbell, A.L. Dadell, M.S. Armas, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 1.1–1.6 (2005)
J. Lu, R.Q. Xu, X. Chen, Z.H. Shen, X.W. Ni, S.Y. Zhang, C.M. Gao, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3890–3894 (2004)
W. Perrie, M. Gill, G. Robinson, P. Fox, W. O’Neill, Appl. Surf. Sci. 230, 50–59 (2004)
P.M. Schaible, W.C. Metzger, J.P. Anderson, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 15, 334–337 (1978)
D.A. Danner, M. Dalvie, D.W. Hess, J. Electrochem. Soc. 134, 669–673 (1987)
J.W. Coburn, H.F. Winters, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 16, 391–403 (1979)
S. Brückner, S. Rösner, C. Gerhard, S. Wieneke, W. Viöl, Mater. Test 53, 639–642 (2011)
T.C. Manley, Electrochem. Soc. Trans. 84, 83–96 (1943)
A. Helmke, D. Hoffmeister, N. Mertens, S. Emmert, J. Schuette, W. Viöl, New J. Phys. 11, 115025 (2009)
T.A. Mai, Ind. Laser Sol. 23, 16–18 (2008)
A. Weck, T.H.R. Crawford, D.S. Wilkinson, H.K. Haugen, J.S. Preston, Appl. Phys. A 90, 537–543 (2008)
G.K.L. Ng, L. Li, Opt. Laser Technol. 33, 393–402 (2001)
C. Körner, R. Mayerhofer, M. Hartmann, H.W. Bergmann, Appl. Phys. A 63, 123–131 (1996)
A. Bogaerts, R. Gijbels, Spectrochim. Acta B 52, 553–565 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Regional Development Funds (EFRE) and the Workgroup Innovative Projects of Lower Saxony (AGiP) in the frame of the Lower Saxony Innovation Network for Plasma Technology (NIP). The authors thank Rika Unkelbach and Lucas Beste for their help during the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerhard, C., Roux, S., Brückner, S. et al. Atmospheric pressure argon plasma-assisted enhancement of laser ablation of aluminum. Appl. Phys. A 108, 107–112 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6942-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6942-2