Abstract.
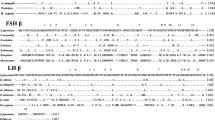
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays an important role in the reproductive cycles of all mammals. There is a large amount of both nucleotide and amino acid sequence data available for LH from eutherian mammals, but little is known about the primary structure of LH in marsupials. We have used consensus PCR primers to generate specific probes for screening pituitary cDNA libraries and report the cloning of the cDNAs encoding the α-subunit of LH (also shared by a number of other glycoprotein hormones) and the LH-specific β-subunit, from the common brushtail possum, Trichosurus vulpecula, and the red kangaroo, Macropus rufus. Southern blotting experiments indicated that both genes are probably present as single copies. Comparison of the deduced marsupial protein sequences with homologous sequences from other vertebrates revealed a high degree of conservation, especially for the α-subunit. These sequences represent the first complete primary structures for a marsupial glycoprotein hormone to have been elucidated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 January 1998 / Accepted: 10 April 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harrison, G., Deane, E. & Cooper, D. cDNA cloning of luteinizing hormone subunits from brushtail possum and red kangaroo. 9, 638–642 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900836
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900836