Abstract
Objectives
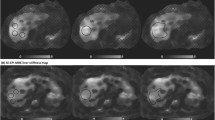
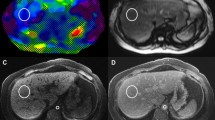
This study was conducted to quantify the heterogeneity of liver stiffness (LS) on MR elastography (MRE) by comparing ROI-based and volumetric measurements.
Methods
LS was measured by ROI-based and volumetric segmentation of the liver parenchyma. Mean LS (MLS) was calculated and used to assign stages of fibrosis. Volumetric measurements of stiffness maps were used to determine the percentage of liver volume above/below MLS and presence of LS heterogeneity. Heterogeneous stiffness was defined when the first and second most predominant stages were more than one category apart. MLS values by each method were compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
We included 128 patients with suspected liver fibrosis (mean age 54.4 ± 14.8 years). MLS was 2.7 ± 1.0 kPa for ROI measurements and 2.6 ± 0.9 kPa for the volumetric method (p = 0.001). Of 59 patients with normal stage (F0), 31 patients (52.5%) had > 20% of liver volume with abnormal LS (F1–F4). Heterogeneous LS was reported in 18 patients (14%).
Conclusions
MLS measurement may not represent the entire spectrum of hepatic fibrosis. Volumetric segmentation may potentially improve the detection of heterogeneous fibrosis and the accuracy of LS measurement.
Key Points
• Heterogeneity of hepatic fibrosis may occur in patients with chronic liver disease.
• MR elastography is used to assess hepatic fibrosis by measuring liver stiffness.
• Measuring liver stiffness by the ROI method and reporting a mean value may fail to detect heterogeneity of hepatic fibrosis. Volumetric assessment of liver stiffness by MR elastography may detect heterogeneity of parenchymal involvement.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CLD:
-
Chronic liver diseases
- LS:
-
Liver stiffness
- MLS stage:
-
Stage of fibrosis assigned to each patient based on mean liver stiffness value of ROIs
- MLS:
-
Mean liver stiffness
- MRE:
-
Magnetic resonance elastography
- ROI-Seg:
-
ROI-based segmentation for liver stiffness measurement
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- V-Seg:
-
Volumetric segmentation for liver stiffness measurement
References
Friedman SL (2003) Liver fibrosis—from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 38(Suppl 1):S38–S53
Pinzani M, Rombouts K (2004) Liver fibrosis: from the bench to clinical targets. Dig Liver Dis 36:231–242
Poynard T, Mathurin P, Lai CL et al (2003) A comparison of fibrosis progression in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol 38:257–265
Caballero T, Perez-Milena A, Masseroli M et al (2001) Liver fibrosis assessment with semiquantitative indexes and image analysis quantification in sustained-responder and non-responder interferon-treated patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 34:740–747
Duchatelle V, Marcellin P, Giostra E et al (1998) Changes in liver fibrosis at the end of alpha interferon therapy and 6 to 18 months later in patients with chronic hepatitis C: quantitative assessment by a morphometric method. J Hepatol 29:20–28
Friedman SL, Bansal MB (2006) Reversal of hepatic fibrosis—fact or fantasy? Hepatology 43:S82–S88
Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD (2009) Liver biopsy. Hepatology 49:1017–1044
Goldstein NS, Hastah F, Galan MV, Gordon SC (2005) Fibrosis heterogeneity in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatitis C virus needle core biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol 123:382–387
Dhall D, Kim SA, Mc Phaul C et al (2018) Heterogeneity of fibrosis in liver biopsies of patients with heart failure undergoing heart transplant evaluation. Am J Surg Pathol 42:1617–1624
Tacke F, Zimmermann HW (2014) Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. J Hepatol 60:1090–1096
Li J, Qureshi M, Gupta A, Anderson SW, Soto J, Li B (2019) Quantification of degree of liver fibrosis using fibrosis area fraction based on statistical chi-square analysis of heterogeneity of liver tissue texture on routine ultrasound images. Acad Radiol 26:1001–1007
Venkatesh SK, Yin M, Ehman RL (2013) Magnetic resonance elastography of liver: technique, analysis, and clinical applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 37:544–555
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ et al (2007) Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:1207–1213 e1202
Kim BH, Lee JM, Lee YJ et al (2011) MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: experience from a tertiary center in Asia. J Magn Reson Imaging 34:1110–1116
Asbach P, Klatt D, Schlosser B et al (2010) Viscoelasticity-based staging of hepatic fibrosis with multifrequency MR elastography. Radiology 257:80–86
Standish RA, Cholongitas E, Dhillon A, Burroughs AK, Dhillon AP (2006) An appraisal of the histopathological assessment of liver fibrosis. Gut 55:569–578
Morisaka H, Motosugi U, Ichikawa S et al (2018) Magnetic resonance elastography is as accurate as liver biopsy for liver fibrosis staging. J Magn Reson Imaging 47:1268–1275
Mariappan YK, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL (2010) Magnetic resonance elastography: a review. Clin Anat 23:497–511
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E et al (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135:32–40
Hoodeshenas S, Yin M, Venkatesh SK (2018) Magnetic resonance elastography of liver: current update. Top Magn Reson Imaging 27:319–333
Venkatesh SK, Xu S, Tai D, Yu H, Wee A (2014) Correlation of MR elastography with morphometric quantification of liver fibrosis (Fibro-C-Index) in chronic hepatitis B. Magn Reson Med 72:1123–1129
Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M (2000) Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124:1599–1607
Pinzani M, Rombouts K, Colagrande S (2005) Fibrosis in chronic liver diseases: diagnosis and management. J Hepatol 42(Suppl):S22–S36
Wanless IR, Shiota K (2004) The pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and other fatty liver diseases: a four-step model including the role of lipid release and hepatic venular obstruction in the progression to cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis 24:99–106
Sakaida I, Nagatomi A, Hironaka K, Uchida K, Okita K (1999) Quantitative analysis of liver fibrosis and stellate cell changes in patients with chronic hepatitis C after interferon therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 94:489–496
Abe H, Midorikawa Y, Matsumoto N et al (2019) Prediction of esophageal varices by liver and spleen MR elastography. Eur Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06230-8
Yin Z, Murphy MC, Li J et al (2019) Prediction of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score (NAS) with multiparametric hepatic magnetic resonance imaging and elastography. Eur Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06076-0
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Enomoto N, Onishi H (2019) Magnetic resonance elastography can predict development of hepatocellular carcinoma with longitudinally acquired two-point data. Eur Radiol 29:1013–1021
Vizzotto L, Vertemati M, Gambacorta M, Sabatella G, Spina V, Minola E (2002) Analysis of histological and immunohistochemical patterns of the liver in posthepatitic and alcoholic cirrhosis by computerized morphometry. Mod Pathol 15:798–806
Cassiman D, Roskams T (2002) Beauty is in the eye of the beholder: emerging concepts and pitfalls in hepatic stellate cell research. J Hepatol 37:527–535
Pinzani M (2015) Pathophysiology of liver fibrosis. Dig Dis 33:492–497
Chang W, Lee JM, Yoon JH et al (2016) Liver fibrosis staging with MR elastography: comparison of diagnostic performance between patients with chronic hepatitis B and those with other etiologic causes. Radiology 280:88–97
Lee VS, Miller FH, Omary RA et al (2011) Magnetic resonance elastography and biomarkers to assess fibrosis from recurrent hepatitis C in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation 92:581–586
Dzyubak B, Venkatesh SK, Glaser K et al (2013) Stable automated segmentation of liver MR elastography images for clinical stiffness measurement. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng, 8672
Dzyubak B, Venkatesh SK, Manduca A, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL (2016) Automated liver elasticity calculation for MR elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging 43:1055–1063
Bonekamp D, Bonekamp S, Halappa VG et al (2014) Interobserver agreement of semi-automated and manual measurements of functional MRI metrics of treatment response in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 83:487–496
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Ihab R Kamel, M.D., Ph.D.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• Retrospective
• Cross-sectional study diagnostic
• Performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezvani Habibabadi, R., Khoshpouri, P., Ghadimi, M. et al. Comparison between ROI-based and volumetric measurements in quantifying heterogeneity of liver stiffness using MR elastography. Eur Radiol 30, 1609–1615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06478-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06478-0