Abstract
Objectives
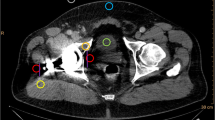
Artefacts from total hip replacement affect image quality and the visualisation of pelvic lesions on computed tomography (CT). We propose a frequency split (FS) approach in addition to the normalised metal artefact reduction (NMAR) algorithm that aims to suppress artefacts and improves image quality in patients with orthopaedic hardware.
Methods
Data from ten consecutive patients with metal artefacts from uni- (n = 5) and bilateral (n = 4) total hip replacement or osteosynthesis (n = 1) were reconstructed with filtered back projection (FBP), linear interpolation MAR (LIMAR), NMAR, FSLIMAR and FSNMAR and analysed for image quality and severity of artefacts.
Results
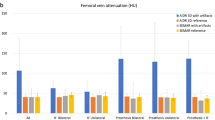
NMAR and FSNMAR significantly improved the assessment of the pelvic organs, lymph nodes and vessels compared with FBP, LIMAR or FSLIMAR (P < 0.05). Assessment of the metal hardware, joint and capsule was improved with the addition of FS (FSLIMAR, FSNMAR). No algorithm-related artefacts were detected in regions that did not contain metal.
Conclusions
NMAR, FSLIMAR and FSNMAR have the potential to improve image quality in patients with artefacts from metal hardware and to improve the diagnostic accuracy of CT of the organs of the pelvis. Although introducing some algorithm-related artefacts, FSNMAR most accurately displayed adjacent bone and tissue next to metal implants.
Key Points
• Orthopaedic metallic hardware often creates serious artefacts in computed tomography, hindering diagnosis.
• The normalised metal artefact reduction (NMAR) algorithm was developed to suppress such artefacts.
• NMAR improves CT assessment of pelvic organs in patients with orthopaedic hardware.
• Addition of the frequency split technique (FSNMAR) helps assess tissue near metal hardware.
• NMAR and FSNMAR are robust and computationally effective sinogram interpolation algorithms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greess H, Wolf H, Baum U et al (2000) Dose reduction in computed tomography by attenuation-based on-line modulation of tube current: evaluation of six anatomical regions. Eur Radiol 10:391–394
Kachelriess M, Watzke O, Kalender WA (2001) Generalized multi-dimensional adaptive filtering for conventional and spiral single-slice, multi-slice, and cone-beam CT. Med Phys 28:475–490
Kalender WA, Buchenau S, Deak P et al (2008) Technical approaches to the optimisation of CT. Phys Med 24:71–79
Glover GH, Pelc NJ (1981) An algorithm for the reduction of metal clip artifacts in CT reconstructions. Med Phys 8:799–807
Kalender WA, Hebel R, Ebersberger J (1987) Reduction of CT artifacts caused by metallic implants. Radiology 164:576–577
Mahnken AH, Raupach R, Wildberger JE et al (2003) A new algorithm for metal artifact reduction in computed tomography: in vitro and in vivo evaluation after total hip replacement. Invest Radiol 38:769–775
Veldkamp WJ, Joemai RM, van der Molen AJ, Geleijns J (2010) Development and validation of segmentation and interpolation techniques in sinograms for metal artifact suppression in CT. Med Phys 37:620–628
Yu L, Li H, Mueller J et al (2009) Metal artifact reduction from reformatted projections for hip prostheses in multislice helical computed tomography: techniques and initial clinical results. Invest Radiol 44:691–696
Meyer E, Raupach R, Lell M, Schmidt B, Kachelriess M (2010) Normalized metal artifact reduction (NMAR) in computed tomography. Med Phys 37:5482–5493
Lell MM, Meyer E, Kuefner MA et al (2012) Normalized metal artifact reduction in head and neck computed tomography. Invest Radiol 47:415–421
Meyer E, Raupach R, Lell M, Schmidt B, Kachelriess M (2012) Frequency split metal artifact reduction (FSMAR) in computed tomography. Med Phys 39:1904–1916
Abdoli M, Ay MR, Ahmadian A, Dierckx RA, Zaidi H (2010) Reduction of dental filling metallic artifacts in CT-based attenuation correction of PET data using weighted virtual sinograms optimized by a genetic algorithm. Med Phys 37:6166–6177
Kennedy JA, Israel O, Frenkel A, Bar-Shalom R, Azhari H (2007) The reduction of artifacts due to metal hip implants in CT-attenuation corrected PET images from hybrid PET/CT scanners. Med Biol Eng Comput 45:553–562
Lee MJ, Kim S, Lee SA et al (2007) Overcoming artifacts from metallic orthopedic implants at high-field-strength MR imaging and multi-detector CT. Radiographics 27:791–803
Bamberg F, Dierks A, Nikolaou K, Reiser MF, Becker CR, Johnson TR (2011) Metal artifact reduction by dual energy computed tomography using monoenergetic extrapolation. Eur Radiol 21:1424–1429
Zhou C, Zhao YE, Luo S et al (2011) Monoenergetic imaging of dual-energy CT reduces artifacts from implanted metal orthopedic devices in patients with factures. Acad Radiol 18:1252–1257
Lee YH, Park KK, Song HT, Kim S, Suh JS (2012) Metal artefact reduction in gemstone spectral imaging dual-energy CT with and without metal artefact reduction software. Eur Radiol 22:1331–1340
Prell D, Kyriakou Y, Kachelriess M, Kalender WA (2010) Reducing metal artifacts in computed tomography caused by hip endoprostheses using a physics-based approach. Invest Radiol 45:747–754
De Man B, Nuyts J, Dupont P, Marchal G, Suetens P (2001) An iterative maximum-likelihood polychromatic algorithm for CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:999–1008
Lemmens C, Faul D, Nuyts J (2009) Suppression of metal artifacts in CT using a reconstruction procedure that combines MAP and projection completion. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:250–260
Wang G, Frei T, Vannier MW (2000) Fast iterative algorithm for metal artifact reduction in X-ray CT. Acad Radiol 7:607–614
Wang G, Snyder DL, O’Sullivan JA, Vannier MW (1996) Iterative deblurring for CT metal artifact reduction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 15:657–664
Wang G, Vannier MW, Cheng PC (1999) Iterative X-ray cone-beam tomography for metal artifact reduction and local region reconstruction. Microsc Microanal 5:58–65
Zhang X, Wang J, Xing L (2011) Metal artifact reduction in X-ray computed tomography (CT) by constrained optimization. Med Phys 38:701–711
Aootaphao S, Pintavirooj C, Sotthivirat S (2008) Penalized-likelihood reconstruction for metal artifact reduction in cone-beam CT. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2008:2733–2736
Buzug T, Oehler M (2007) Statistical image reconstruction for inconsistent CT projection data. Methods Inf Med 46:261–269
Naranjo V, Llorens R, Alcaniz M, Lopez-Mir F (2011) Metal artifact reduction in dental CT images using polar mathematical morphology. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 102:64–74
Rinkel J, Dillon WP, Funk T, Gould R, Prevrhal S (2008) Computed tomographic metal artifact reduction for the detection and quantitation of small features near large metallic implants: a comparison of published methods. J Comput Assist Tomogr 32:621–629
Watzke O, Kalender WA (2004) A pragmatic approach to metal artifact reduction in CT: merging of metal artifact reduced images. Eur Radiol 14:849–856
Liu PT, Pavlicek WP, Peter MB, Spangehl MJ, Roberts CC, Paden RG (2009) Metal artifact reduction image reconstruction algorithm for CT of implanted metal orthopedic devices: a work in progress. Skeletal Radiol 38:797–802
Acknowledgments
The first two authors contributed equally in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lell, M.M., Meyer, E., Schmid, M. et al. Frequency split metal artefact reduction in pelvic computed tomography. Eur Radiol 23, 2137–2145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2809-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2809-y