Abstract
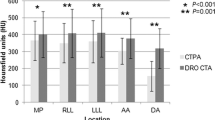
To compare the impact of iodine concentration using two different contrast aterials (CM) at standardized iodine delivery rate (IDR) and overall iodine load in 16-multidetector-row-CT-angiography (MDCTA) of the pulmonary arteries of 192 patients with known or suspected pulmonary embolism. One hundred three patients (group A) received 148 ml of a CM containing 300 mg iodine/ml (Ultravist 300™, BayerScheringPharma) at a flow rate of 4.9 ml/s. Eighty-nine patients (group B) received 120 ml of a CM with a concentration of 370 mg iodine/ml (Ultravist370™) at a flow rate of 4.0 ml/s, resulting in a standardized IDR (~1.5 gI/s) and the same overall amount of iodine (44.4 g). Both CM injections were followed by a saline chaser. Mean density values were determined in the pulmonary trunk, the ascending and the descending aorta, respectively. Applying repeated-measures ANOVA, no statistically significant differences between both MDCTA protocols were found (p = 0.5790): the mean density in the pulmonary trunk was 355 ± 116 Hounsfield Units (group A) and 358 ± 115 (group B). The corresponding values for the ascending and descending aorta were 295 ± 79 (group A) and 284 ± 65 (group B) as well as 272 ± 71 and 262 ± 70. In conclusion, the use of standardized IDR and overall iodine load provides comparable intravascular CM density in pulmonary 16-MDCTA for delivering contrast materials with different iodine concentrations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Winer-Muram HT, Rydberg J, Johnson MS, Tarver RD, Williams MD, Shah H, Namyslowski J, Conces D, Jennings SG, Ying J, Trerotola SO, Kopecky KK (2004) Suspected acute pulmonary embolism: evaluation with multi-detector row CT versus digital subtraction pulmonary arteriography. Radiology 233:806–815
Patel S, Kazerooni EA, Cascade PN (2003) Pulmonary embolism: optimization of small pulmonary artery visualization at multi-detector row CT. Radiology 227:455–460
Schoepf UJ, Costelo P (2004) CT Angiography for diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism: State of the Art. Radiology 230:329–337
Schoellnast H, Deutschmann AH, Fritz GA, Schaffler GJ, Tillich M (2005) MDCT angiography of the pulmonary arteries: influence of iodine flow concentration on vessel attenuation and visualization. Am J Roentgenol 184:1935–1939
Jones SE, Wittram C (2005) The indeterminate CT pulmonary angiogram: imaging characteristics and patient clinical outcome. Radiology 237:329–337
Arakawa H, Kohno T, Hiki T, Kaji Y (2007) CT pulmonary angiography and CT venography: factors associated with vessel enhancement. Am J Roentgenol 189:156–161
Bae KT, Tao C, Gürel S, Hong C, Zhu F, Gebke TA, Milite M, Hildebolt CF (2007) Effect of patient weight and scanning duration on contrast enhancement during pulmonary multidetector CT angiography. Radiology 242:582–589
Schoellnast H, Deutschmann HA, Berghold A, Fritz GA, Schaffler GJ, Tillich M (2006) MDCT angiography of the pulmonary arteries: influence of body weight, body mass index, and scan length at different iodine flow rates. Am J Roentgenol 187:1074–1078
Hartmann IJ, Lo RT, Bakker J, de Monye W, van Waes PF, Pattynama PM (2002) Optimal scan delay in spiral CT for the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:21–25
Lee CH, Goo JM, Lee HJ, Kim KG, Im JG, Bae KT (2007) Determination of optimal timing window for pulmonary artery MDCT angiography. Am J Roentgenol 188:313–317
Yankelevitz DF, Shaham D, Shah A, Rademacker J, Henschke CI (1998) Optimization of contrast delivery for pulmonary CT angiography. Clin Imaging 22:398–403
Han JK, Kim AY, Lee KY, Seo JB, Kim TK, Choi BI, Lhee CS, Han MC (2000) Factors influencing vascular and hepatic enhancement at CT: experimental study on injection protocol using a canine model. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24:400–406
Awai K, Takada K, Onishi H, Hori S (2002) Aortic and hepatic enhancement and tumor-to-liver contrast: analysis of the effect of different concentrations of contrast material at multi-detector row helical CT. Radiology 224:757–763
Awai K, Inoue M, Yagyu Y, Watanabe M, Sano T, Nin S, Koike R, Nishimura Y, Yamashita Y (2004) Moderate versus high concentration of contrast material for aortic and hepatic enhancement and tumor-to-liver contrast at multi-detector row CT. Radiology 233:682–688
Cademartiri F, de Monye C, Pugliese F, Mollet NR, Runza G, van der Lugt A, Midiri M, de Feyter PJ, Lagalla R, Krestin GP (2006) High iodine concentration contrast material for non-invasive multislice computed tomography coronary angiography: iopromide 370 versus iomeprol 400. Invest Radiol 41:349–353
Setty BN, Sahani DV, Ouellette-Piazzo K, Hahn PF, Shepard JA (2006) Comparison of enhancement, image quality, cost, and adverse reactions using 2 different contrast medium concentrations for routine chest CT on 16-slice MDCT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:818–822
Rist C, Nikolaou K, Kirchin MA, van Gessel R, Bae KT, von Ziegler F, Knez A, Wintersperger BJ, Reiser MF, Becker CR (2006) Contrast bolus optimization for cardiac 16-slice computed tomography: comparison of contrast medium formulations containing 300 and 400 milligrams of iodine per millilitre. Invest Radiol 41:460–467
Fleischmann D (2003) Use of high-concentration contrast media in multiple-detector-row CT: principles and rationale. Eur Radiol 13(Suppl5):M14–M20
Fleischmann D (2003) High-concentration contrast media in MDCT angiography: principles and rationale. Eur Radiol 13(Suppl3):N39–N43
Sandstede JJ, Werner A, Kaupert C, Roth A, Jenett M, Harz C, Hahn D (2006) A prospective study comparing different iodine concentrations for triphasic multidetector row CT of the upper abdomen. Eur J Radiol 60:95–99
Haage P, Schmitz-Rode T, Hübner D, Piroth W, Günther RW (2000) Reduction of contrast material dose and artifacts by a saline flush using a double power injector in helical CT of the thorax. Am J Roentgenol 174:1049–1053
Federle MP, Chang PJ, Confer S, Ozgun B (1998) Frequency and effects of extravasation of ionic and nonionic CT contrast media during rapid bolus injection. Radiology 206:637–640
Platt JF, Reige KA, Ellis JH (1999) Aortic enhancement during abdominal CT angiography: correlation with test injections, flow rates, and patient demographics. Am J Roentgenol 172:53–56
Bae KT, Heiken JP, Brink JA (1998) Aortic and hepatic contrast medium enhancement at CT. Part II. Effect of reduced cardiac output in a porcine model. Radiology 207:657–662
Wildberger JE, Mahnken AH, Sinha AM, Stargardt A, Haage P, Schaller S, Gunther RW (2002) A differentiated approach to the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis using multi-slice CT. Rofo 174:301–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keil, S., Plumhans, C., Behrendt, F.F. et al. MDCT angiography of the pulmonary arteries: intravascular contrast enhancement does not depend on iodine concentration when injecting equal amounts of iodine at standardized iodine delivery rates. Eur Radiol 18, 1690–1695 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0942-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0942-9